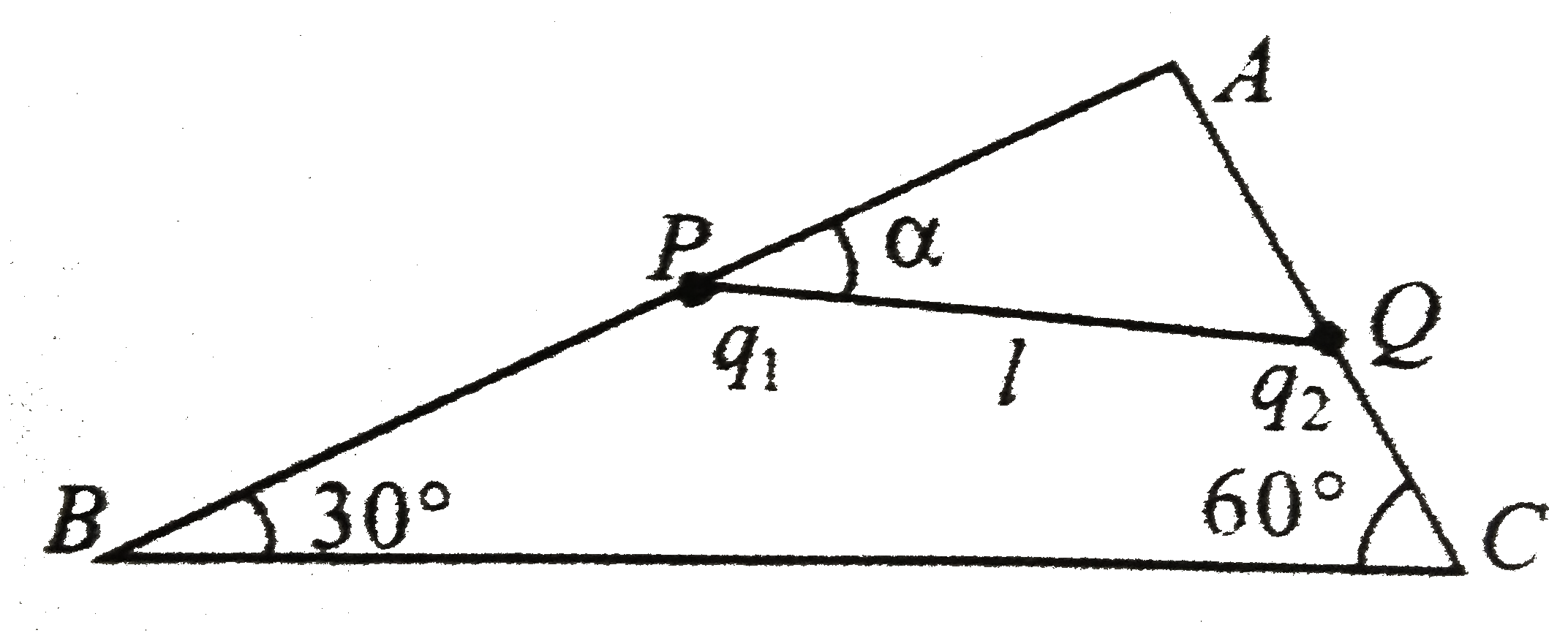
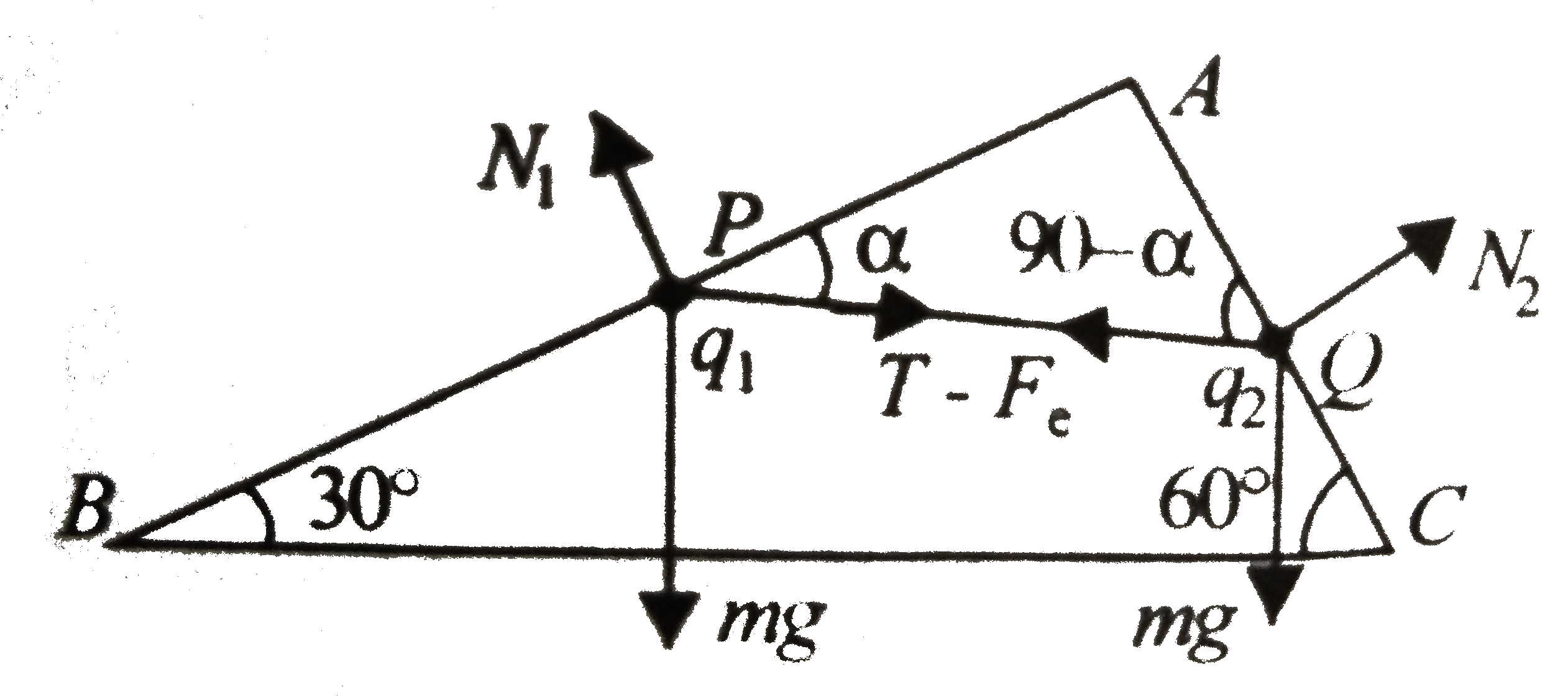
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
COULOMB LAW AND ELECTRIC FIELD
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Exercises|58 VideosCOULOMB LAW AND ELECTRIC FIELD
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Subjective|32 VideosCOULOMB LAW AND ELECTRIC FIELD
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Single Answer Correct Type|22 VideosCOMMUNICATION SYSTEM
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise QUESTION BANK|19 VideosCurrent Electricity
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise QUESTION BANK|40 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-COULOMB LAW AND ELECTRIC FIELD-Solved examples
- Two balls of charges q(1) and q(2) initially have a velocity of the sa...
Text Solution
|
- A rigeid insulated wire frame in the form of a right-angled traingle A...
Text Solution
|
- In a horizontal unifrom electirc field, a small charged disk is gently...
Text Solution
|
- A charge particle A is fixed at the base of a uniform slope of inclina...
Text Solution
|
- In a free space, a thin rod carrying uniformly distributed negative ch...
Text Solution
|
- Two charges+q(1) and -q(2) are placed at A and B respectively. A line ...
Text Solution
|
- A small point mass m has a charge q, which is constrained to move insi...
Text Solution
|
- A nonconducting ring of mass m and radius R, with charge per unit leng...
Text Solution
|
- Two small identical balls lying on a horizontal plane are connected by...
Text Solution
|
- A non-conducting ring of mass m and radius R has a charge Q uniformly ...
Text Solution
|