Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
COULOMB LAW AND ELECTRIC FIELD
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Single Correct|47 VideosCOULOMB LAW AND ELECTRIC FIELD
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Multiple Correct|8 VideosCOULOMB LAW AND ELECTRIC FIELD
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Exercises|58 VideosCOMMUNICATION SYSTEM
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise QUESTION BANK|19 VideosCurrent Electricity
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise QUESTION BANK|40 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-COULOMB LAW AND ELECTRIC FIELD-Subjective
- Two similarly and equally charged identical metal spheres A and B repe...
Text Solution
|
- Three point charges of +2muC, -3muC , and -3muC are kept at the vertic...
Text Solution
|
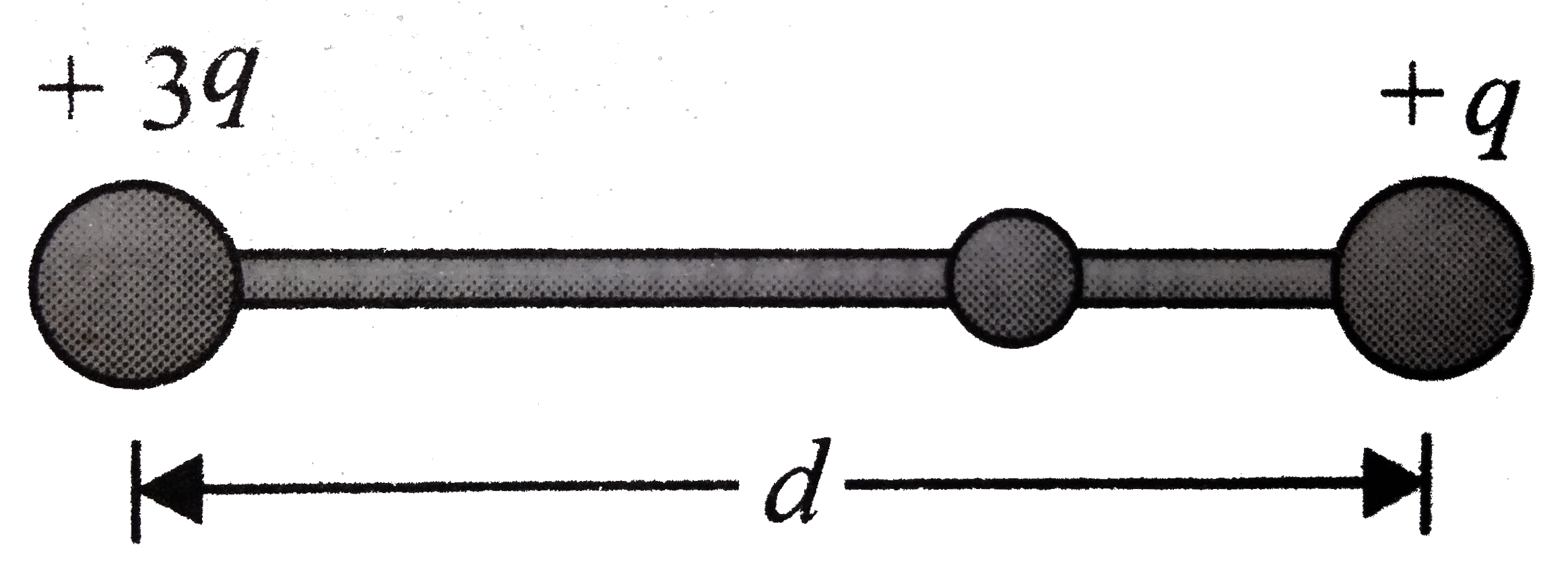
- Two small beads having positive charges 3q and q are fixed at the oppo...
Text Solution
|
- A copper atom consists of copper nucles surrounded by 29 electrons. Th...
Text Solution
|
- A flat square sheet of charge (side 50 cm) carries a uniform surface c...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass 9xx10^(-31) kg having a negative charge of 1.6xx10^...
Text Solution
|
- Point chages q and -q are located at the verticles of a squre with dia...
Text Solution
|
- Two mutually perpendicular long straight conductors carrying uniformly...
Text Solution
|
- A ring of radius 0.1m is made out of thin metallic wire of area of cro...
Text Solution
|
- A charged cork ball of mass m is suspended on a light sting in the pre...
Text Solution
|
- A ring of radius R has charge -Q distributed uniformly over it. Calcul...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical small equally charged conducting balls are suspended fro...
Text Solution
|
- Two point charge Q(a) and Q(b) are positional at point A and B. The fi...
Text Solution
|
- Two semicircle wires ABC, and ADC, each of radius R are lying on xy an...
Text Solution
|
- An infinte wire having linear charge density lambda is arranged as sho...
Text Solution
|
- Two similar balls, each of mass m and charge q, are hung from a common...
Text Solution
|
- Three equal negative charges, -q(1) each form the vertices of and equi...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of radius R carries a positive charges whose volume density at ...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform nonconducting rod of mass ma and length l, with charge densi...
Text Solution
|
- Electrically charged drops of nercury fall from an altitude h into a s...
Text Solution
|