A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTRIC FLUX AND GAUSS LAW
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Subjective type|7 VideosELECTRIC FLUX AND GAUSS LAW
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise MCQ s|38 VideosELECTRIC FLUX AND GAUSS LAW
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Multiple Correct|8 VideosELECTRIC CURRENT AND CIRCUIT
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Interger|8 VideosELECTRIC POTENTIAL
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise DPP 3.5|14 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-ELECTRIC FLUX AND GAUSS LAW-Comprehension
- A small conducting spherical shell with inner radius a and outer radiu...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the previous problem , let the outer shell have the charge -...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the previous problem , let the outer shell have the charge -...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the previous problem , let the outer shell have the charge -...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the previous problem , let the outer shell have the charge -...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the previous problem , let the outer shell have the charge -...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the previous problem , let the outer shell have the charge -...
Text Solution
|
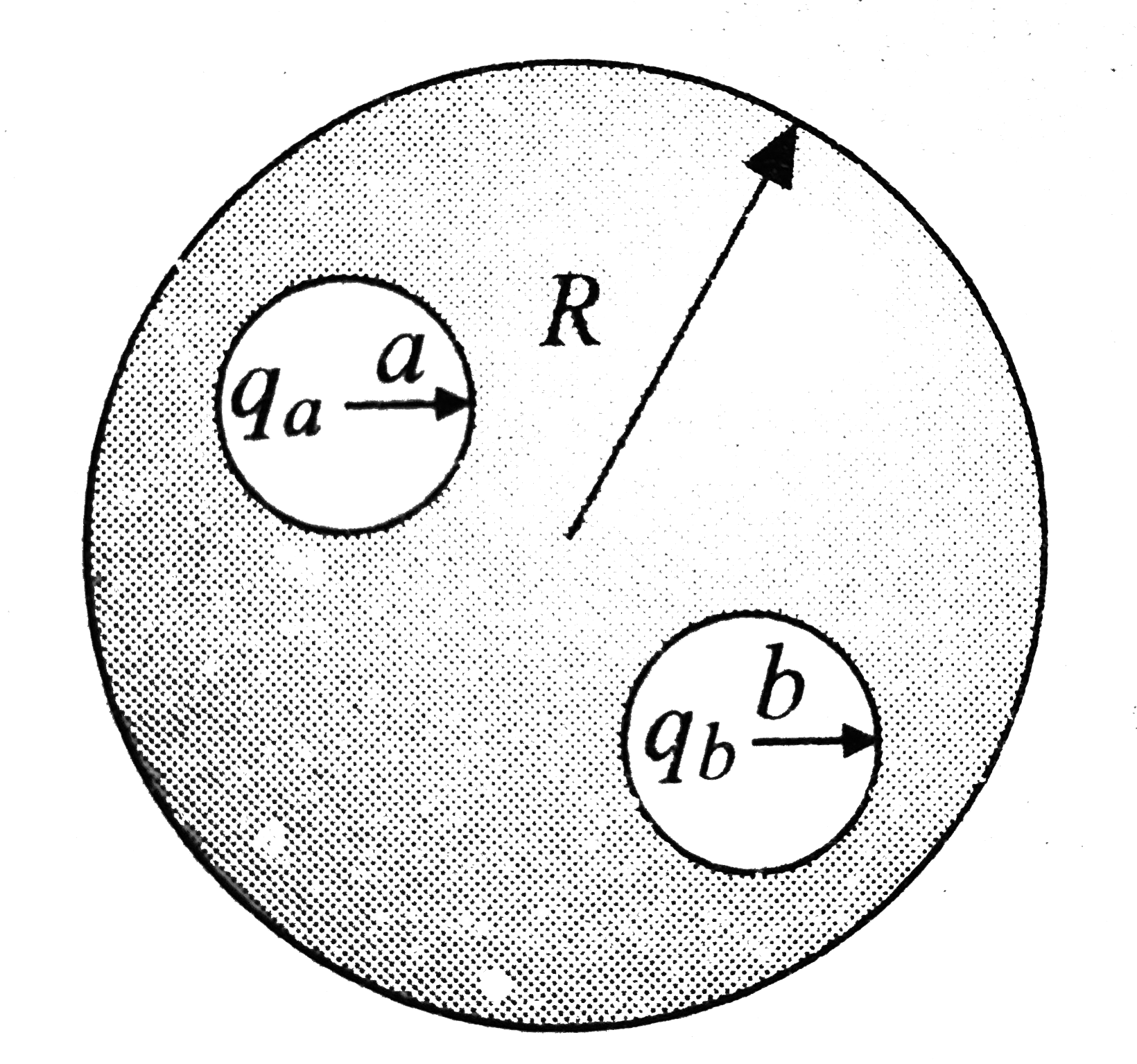
- Two spherical cavities of radii a and b are hollowed out from the inte...
Text Solution
|
- Two spherical cavities of radii a and b are hollowed out from the inte...
Text Solution
|
- Positive and negative charges of equal magnitude lie along the symmetr...
Text Solution
|
- Positive and negative charges of equal magnitude lie along the symmetr...
Text Solution
|
- There are two nonconducting spheres having uniform volume charge densi...
Text Solution
|
- There are two nonconducting spheres having uniform volume charge densi...
Text Solution
|
- Gauss's law and Coulomb's law , although expressed in different forms ...
Text Solution
|
- Gauss's law and Coulomb's law , although expressed in different forms ...
Text Solution
|
- Gauss's law and Coulomb's law , although expressed in different forms ...
Text Solution
|
- Gauss's law and Coulomb's law , although expressed in different forms ...
Text Solution
|
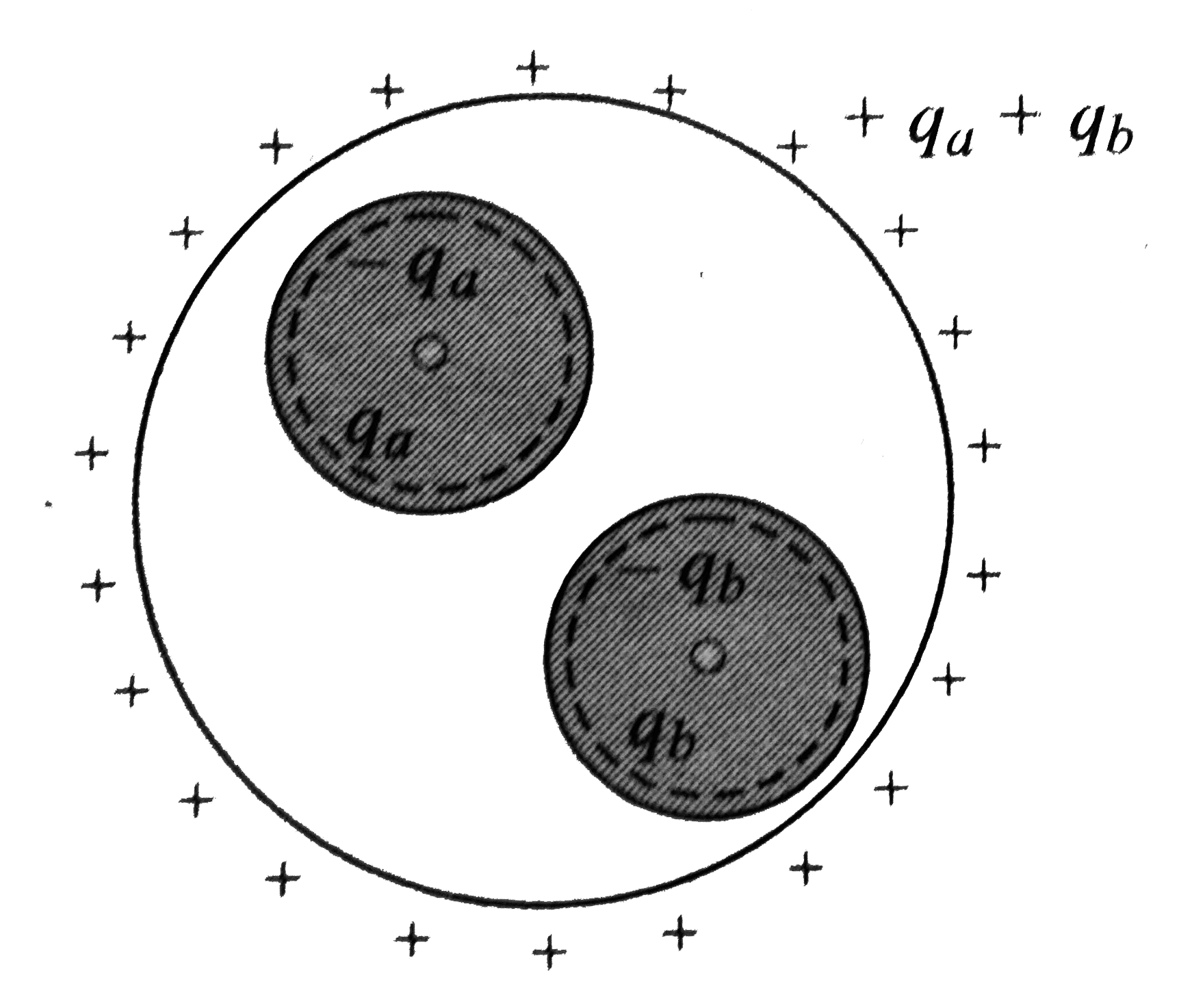
- A spherical conductor A contains two spherical cavities as shown in Fi...
Text Solution
|
- A spherical conductor A contains two spherical cavities as shown in Fi...
Text Solution
|
- A spherical conductor A contains two spherical cavities as shown in Fi...
Text Solution
|