Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-ELECTRIC POTENTIAL-DPP 3.5
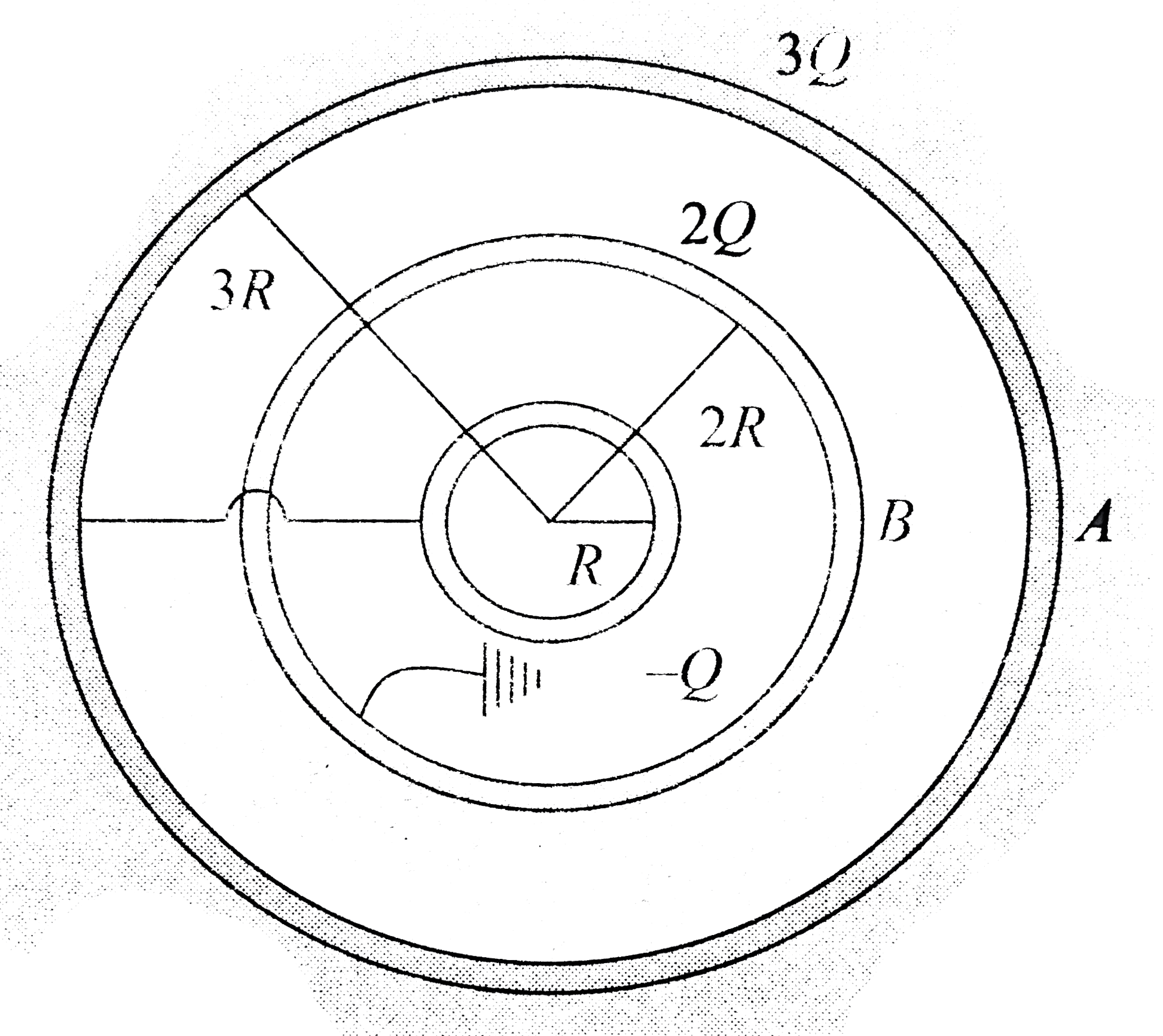
- (Figure 3.78) shows three thin concentric spherical shells A, B and C ...
Text Solution
|
- A point charge Q is situated (outside) at a distance r from the centre...
Text Solution
|
- Find the electric field potentail and strength at the centre of a hem...
Text Solution
|
- There are three concentric conducting spherical shells. All of them ar...
Text Solution
|
- Both the ring and the conducting sphere are given the same charge Q. D...
Text Solution
|
- A solid sphere of radius 'R' has a cavity of radius (R)/(2). The solid...
Text Solution
|
- A thin spherical conducting shell of radius R has a charge q. Another ...
Text Solution
|
- An arc of radius r carries charge. The linear density of charge is lam...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical thin ring, each of radius R meters, are coaxially placed...
Text Solution
|
- If the electric potential of the inner metal sphere is 10 volt & that ...
Text Solution
|
- Potential difference beween centre and surface of the sphere of radius...
Text Solution
|
- A mercury drop has potential 'V' on its surface. 1000 such drops combi...
Text Solution
|
- A solid conducting sphere of radius 'a' is surrounded by a thin unchan...
Text Solution
|
- A solid conducting sphere of radius 'a' is surrounded by a thin unchan...
Text Solution
|
- A solid conducting sphere of radius 'a' is surrounded by a thin unchan...
Text Solution
|
 .
.