Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTRIC CURRENT AND CIRCUIT
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Single Correct|72 VideosELECTRIC CURRENT AND CIRCUIT
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Multiple Correct|16 VideosELECTRIC CURRENT AND CIRCUIT
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Exercise 5.2|50 VideosELECTRIC CURRENT & CIRCUITS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Kirchhoff s law and simple circuits|15 VideosELECTRIC FLUX AND GAUSS LAW
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise MCQ s|38 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-ELECTRIC CURRENT AND CIRCUIT-Subjective
- The circuit shown in fig 5.223 is in steady state. find the charges ...
Text Solution
|
- Consider an infinita ladder of network shown In fig 5.223A voltage is ...
Text Solution
|
- For a cicuit shown in fing 5.235 swhitch S1 is closed at t= 0, then at...
Text Solution
|
- Find the potential difference between the plates of the capactior C in...
Text Solution
|
- Analyze the given circuit in the steady state condition. Charge on the...
Text Solution
|
- (a) What is the potential of point a with respect to point b in figure...
Text Solution
|
- In the cicuit shown in fig. C is a parallel plate air capacitor having...
Text Solution
|
- The circuit shown in fig. Is in steady state. i. Find the energy...
Text Solution
|
- The given R-C circuit has two swithes S1 and S2 Swithc S2 is clsoed a...
Text Solution
|
- For the circuit arrangement shown in fig. a. Find the potentail d...
Text Solution
|
- The plates of a capacitor of capacitance C are given the charges Q1 an...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a parallel pate capacitor of capactance C with partially cond...
Text Solution
|
- The switch S is closed aty t = 0. the capacitor C is uncharged but C0 ...
Text Solution
|
- Only switch S1 closed in fig. a. what is the steady-state reading of...
Text Solution
|
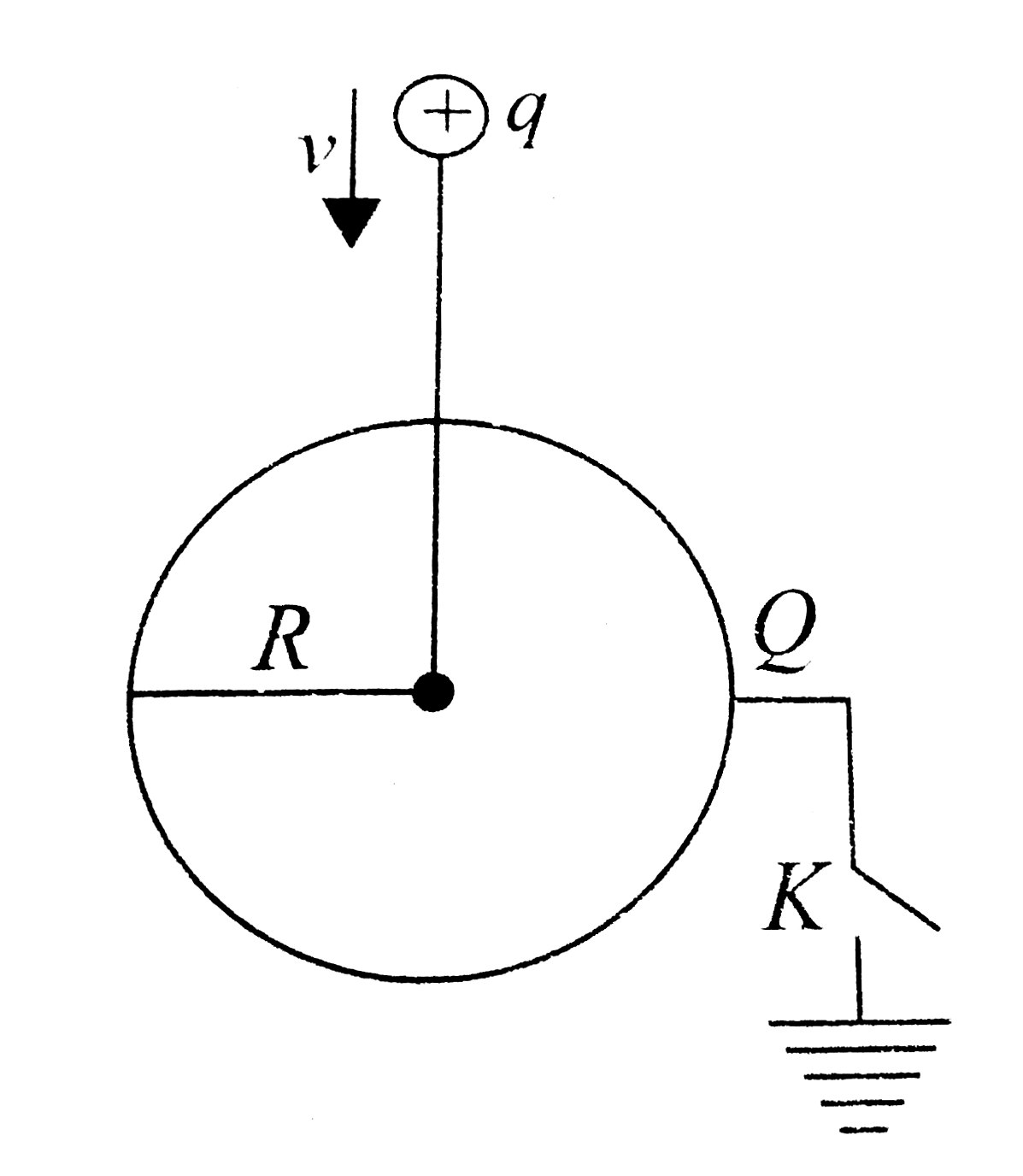
- A point charge +q is moved with a constant velocity v toward a solid c...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate equivalent resistance between A and B of the circuit shown i...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit shown in fig. calculate the following: a. Potential d...
Text Solution
|
- In the given cirucit, determine current through branch having indicate...
Text Solution
|
- Determine current through batteries epsilon(1) and epsilon(2)
Text Solution
|
- The cirucit shown in fig. extends to the right into infinity. Each bat...
Text Solution
|