As both the resistances are same, `40 V` will be divided equally among both the resistances. Hence, the potential difference across `A` and `B` is `20 V`.
(ii) Equivalent resistance of `200 Omega ` and `2 k Omega` is
`R_(1) = (200 xx 200)/(200 + 200) = (2000)/(11) Omega`
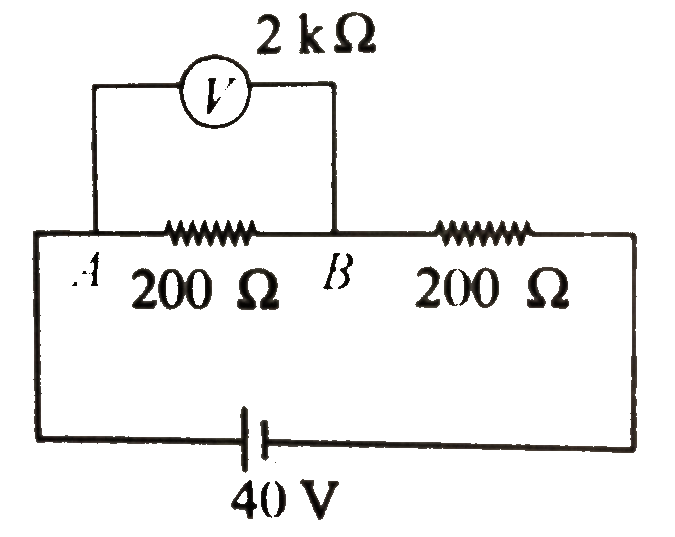
Reading of voltmeter = potential difference across `AB`
`= V_(1) = (2000//(11 xx 40))/(2000//(11 + 200)) = 19.05 V`
Percentage error `= (20 - 19.05)/(20) xx 100 = 4.75%`
(iii) In this case
`R_(1) (200 xx 20,000)/(200 + 20,000) = (20,000)/(101) Omega`
Reading of voltmeter
`=` potential difference across `AB`
`= V_(2) = (20,000//(101 xx 40))/(20,000//(101 + 200)) = 19.90 V`
Percentage error `= (20 - 19.9)/(20) xx 100 = 0.5%`
In case (iii), percentage error is less than that in case (ii). It means the more the resistance of the voltmeter, the more accurate the reading.