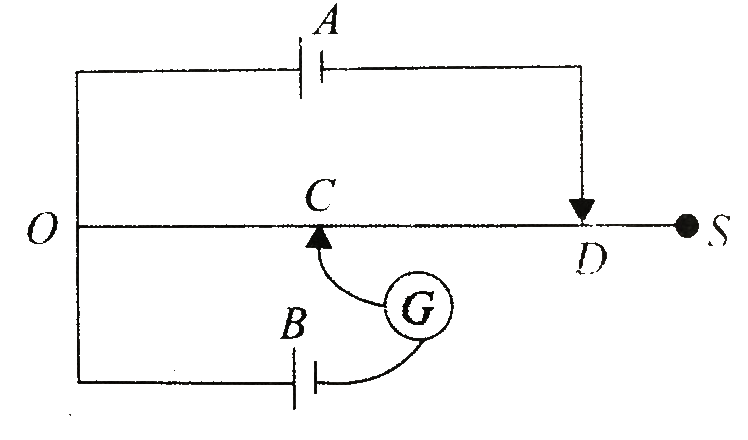
Cells `A` and `B` and a galvanometer `G` are connected to a side wire `OS` by two sliding contacts `C` and `D` as shows in Fig. `6.17`. The slide wire is `100 cm` long and has a resistance of `12 Omega`. With `OD = 75 cm`, the galvanometer gives no deflections when `OC` is `50 cm`. If `D` is moved to touch the end of wire `S`, the value of `OC` for which the galvanometer shows no deflection is `62.5 cm`. The emf of cell `B` is `1.0 V`. Calculate
(i) the potential difference across `O` and `D` when `D` is at `75 cm` mark from `O`
(ii) the potential difference across `OS` when `D` touches `S`
(iii) internal resistance of cell `A`
(iv) the emf of cell `A`