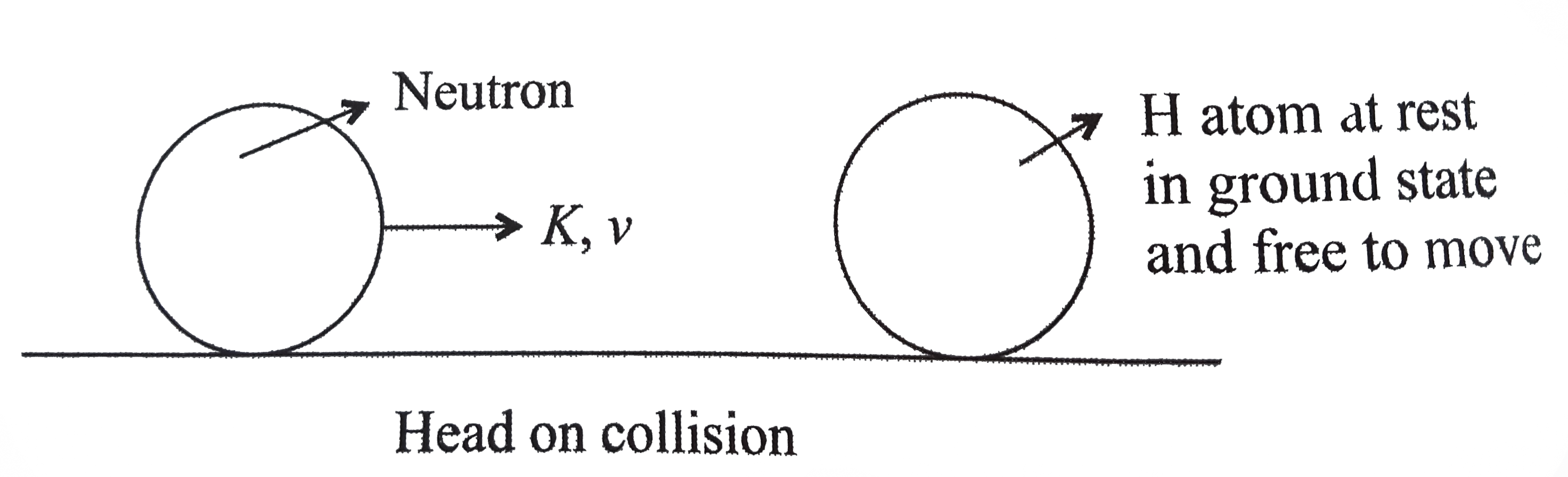Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-ATOMIC PHYSICS-ddp.4.3
- In the figure , what type of collision can be possible , if K = 14 eV,...
Text Solution
|
- The continuous x - ray spectrum obtained from a Coolidge tube is of th...
Text Solution
|
- The figure represents the observed intensity of X - rays emitted by an...
Text Solution
|
- If the potential difference between the anode and cathode of the X - r...
Text Solution
|
- One increasing the operating voltage in a x-ray tube by 1.5 times, the...
Text Solution
|
- In X-ray tube , when the accelerating voltage V is halved, the differe...
Text Solution
|
- In the diagram a graph between the intensity of X-rays emitted by a mo...
Text Solution
|
- Let lambda(alpha'), lambda(beta),and lambda'(alpha) denote the wavele...
Text Solution
|
- The graph that correctly represents the relation of frequency v of a ...
Text Solution
|
- The intensity distribution of X - rays from two Coolidge tubes operate...
Text Solution
|
- The X- ray wavelength of L(alpha) line of platinum (Z = 78) is 1.30 Å....
Text Solution
|
- The K(alpha) X - rays arising from a cobalt (z = 27) target have a w...
Text Solution
|
- For characteristic X - ray of some material
Text Solution
|
- The wavelength of k(alpha) X- rays produced by an X - rays tube is 0....
Text Solution
|
- The wavelength of K(alpha) line for an element of atomic number 43 is ...
Text Solution
|
- The potential difference applied to an X-ray tube is increased. As a r...
Text Solution
|