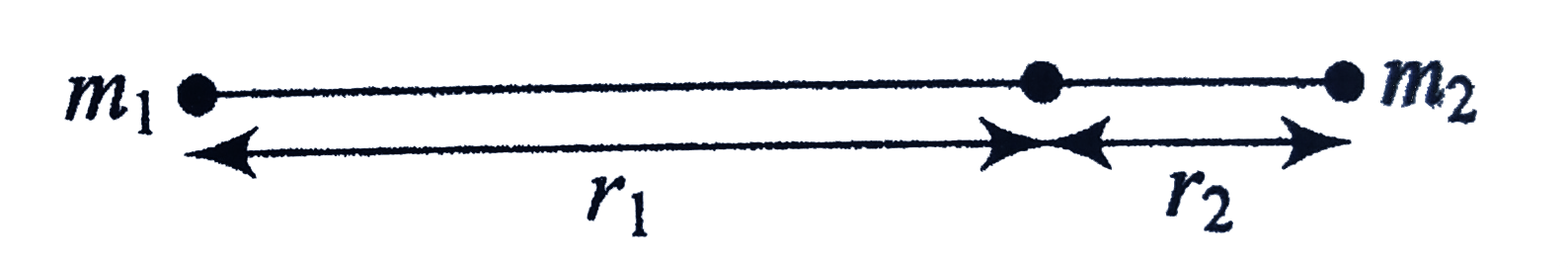
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ATOMIC PHYSICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise dpp-4.1|15 VideosATOMIC PHYSICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise dpp 4.2|15 VideosATOMIC PHYSICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Assertion-reasoning type|1 VideosALTERNATING CURRENT
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise QUESTION BANK|65 VideosATOMS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise QUESTION BANK|40 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-ATOMIC PHYSICS-Linked comprehension type
- In a mixture of H- He^(+) gas (He+ is singly ionized He atom), H atom ...
Text Solution
|
- In a mixture of H- He^(+) gas (He+ is singly ionized He atom), H atom ...
Text Solution
|
- In a mixture of H- He^(+) gas (He+ is singly ionized He atom), H atom ...
Text Solution
|
- The key feature of Bohr's spectrum of hydrogen atom is the quantizatio...
Text Solution
|
- The key feature of Bohr's spectrum of hydrogen atom is the quantizatio...
Text Solution
|
- The key feature of Bohr's spectrum of hydrogen atom is the quantizatio...
Text Solution
|