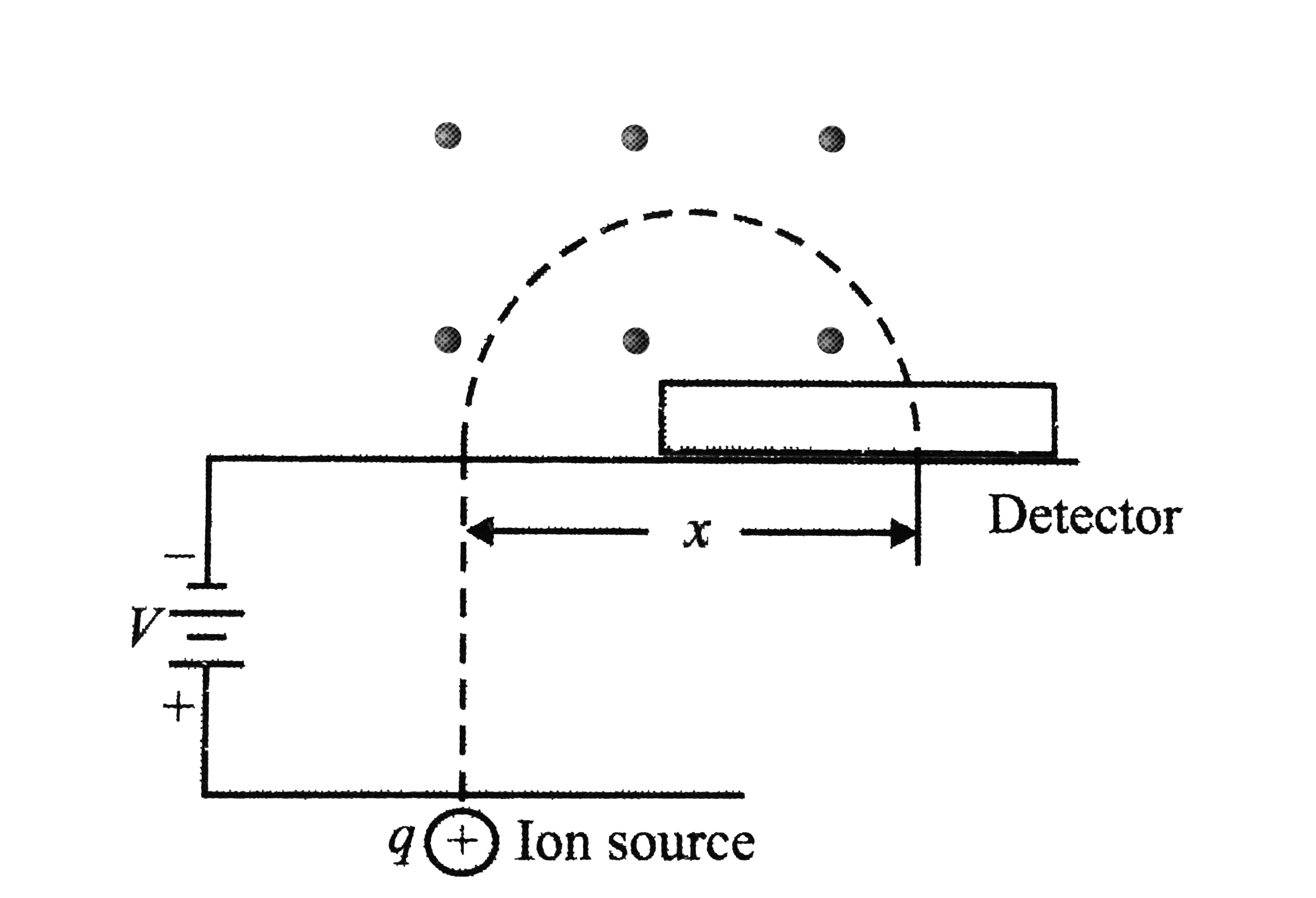
A mass spectrometer separates ions according to their ratio of charge to mass. Such devices are widely used in silence and engineering to analyze unknown mixtures and to separate isotopes of chemical elements. Figure 1.24 shows ions of charge q and mass m first being accelerated from rest through a potential difference V and then entering a region of uniform magnetic field B pointing out of the page. Only the magnetic force acts on the ions in this region, so they undergo circular motion and, after half an orbit, land on a detector. Find an expression for the horizontal distancexxfrom the entrance slit to the point where an ion lands on the detector.