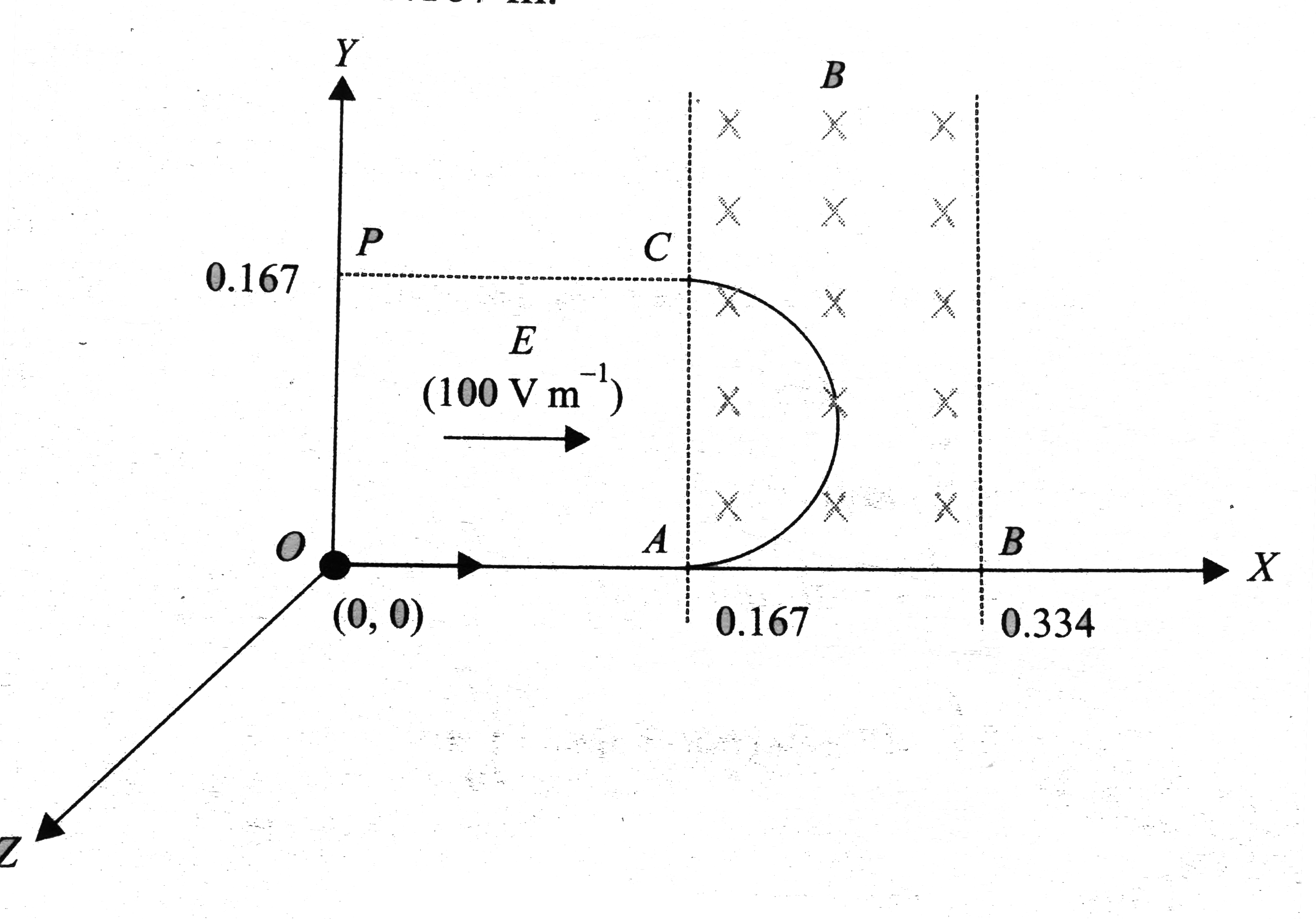Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
MAGNETIC FIELD AND MAGNETIC FORCES
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Exercise 1.1|22 VideosMAGNETIC FIELD AND MAGNETIC FORCES
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Exercise 1.2|13 VideosMAGNETIC FIELD AND MAGNETIC FORCES
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Multiple Correct Answer type|2 VideosKINETIC THEORY
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Question Bank|31 VideosMagnetism and Matter
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Question Bank|50 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-MAGNETIC FIELD AND MAGNETIC FORCES-Solved Example
- An electron in the ground state of hydrogen atom is revolving in antic...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m and charge q is moving in a region where uniform,...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform constant magnetic field B is directed at an angle of 45^(@) ...
Text Solution
|
- The region between x=o and x = L is filled with uniform, steady magn...
Text Solution
|
- A rectangular loop PQRS made from a uniform wire has length a, width b...
Text Solution
|
- A ring of radius R having unifromly distributed charge Q is mounted on...
Text Solution
|
- In a moving coil galvanometer, torque on the coil can be experessed as...
Text Solution
|
- A slightly divergent beam of charged particles accelerated by a Potent...
Text Solution
|
- A small charged ball having mass m and charge q is suspended from a ri...
Text Solution
|
- Non-relativistic protons move reactilinearly in the region of space wh...
Text Solution
|
- A current i, indicated by the crosses in figure, is established in a s...
Text Solution
|
- A straight conductor of weight 1 N and length 0.5 m, is located in a p...
Text Solution
|
- There is a constant homogeneous electric field of 100 Vm^-1 within the...
Text Solution
|
- A positively charged particle of mass m and charge q is projected on a...
Text Solution
|
- A loop of flexible conducting wire of length 0.5 m lies in a magnetic ...
Text Solution
|
- A circular coil of 100 turns has an effective radius of 0.05 m and car...
Text Solution
|
- A positively charged particle having charge q1 = 1 C and mass m1 =40 g...
Text Solution
|
- An electron accelerated by a potential difference V= 3 volt first ente...
Text Solution
|
- A particle having mass m and charge q is released from the origin in a...
Text Solution
|
- A non-relativistic charge q of mass m originates at a point A lying on...
Text Solution
|