A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
SOURCES OF MAGNETIC FIELD
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Archives (integer)|1 VideosSOURCES OF MAGNETIC FIELD
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Subjective type|11 VideosSOURCES OF MAGNETIC FIELD
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Archives (multiple Correct )|1 VideosSEMICONDUCTOR ELECTRONIC : MATERIALS, DEVICES AND SIMPLE CIRCUITS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise QUESTION BANK|12 VideosTHERMAL PROPERTIES OF MATTER
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Question Bank|40 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-SOURCES OF MAGNETIC FIELD-Archives (linked Comprehension)
- The figure shows a circular loop of radius a with two long parallel wi...
Text Solution
|
- The figure shows a circular loop of radius a with two long parallel wi...
Text Solution
|
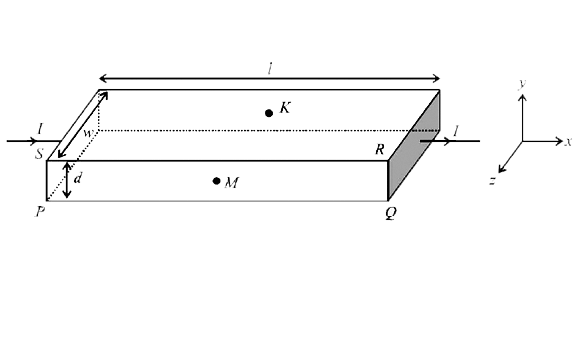
- In a thin rectangular metallic strip a constant current I flows along ...
Text Solution
|
- In a thin rectangular metallic strip a constant current I flows along ...
Text Solution
|