Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT-PROBABILITY-SOLVED EXAMPLES
- Find the sample space associated with the experiment of rolling a p...
Text Solution
|
- In a relay race there are five teams A. B, C. D and E. (a) What is ...
Text Solution
|
- Find the probability that when a hand of 7 cards is drawn from a well...
Text Solution
|
- On her vacations Veena visits four cities (A , B , C a n d D)in a rand...
Text Solution
|
- A committee of two persons is selected from two men and two women. Wh...
Text Solution
|
- Two students Anil and Ashima appeared in an examination. The probabil...
Text Solution
|
- A bag contains 9 discs of which 4 are red. 3 are blue and 2 are yello...
Text Solution
|
- One card is drawn from a well shuffled deck of 52 cards. If each outc...
Text Solution
|
- If A, B, C are three events associated with a random experiment prove...
Text Solution
|
- A coin is tossed three times, consider the following events. A : No h...
Text Solution
|
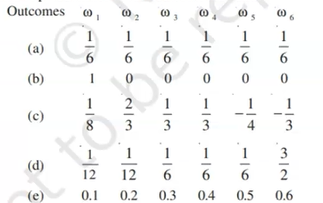
- Let a sample space be S = {omega1,omega2, .... ,omega6}. Which of the ...
Text Solution
|
- A coin is tossed. If it shows head, we draw a ball from a bag consist...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the experiment in which a coin is tossed repeatedly until a ...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the experiment of rolling a die. Let A be the event 'getting...
Text Solution
|
- Two dice are thrown and the sum of the numbers which come up on the d...
Text Solution
|
- Two coins (a one rupee coin and a two rupee coin) are tossed once. Fi...
Text Solution
|
- Find the sample space associated with the experiment of rolling a pai...
Text Solution
|
- In each of the following experiments specify appropriate sample space...
Text Solution
|