A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
SOUND WAVES AND DOPPLER EFFECT
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Integer|16 VideosSOUND WAVES AND DOPPLER EFFECT
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Assertion-Reasoning|24 VideosRIGID BODY DYNAMICS 2
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Interger|2 VideosSUPERPOSITION AND STANDING WAVES
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Comprehension Type|5 Videos
CENGAGE PHYSICS-SOUND WAVES AND DOPPLER EFFECT-Comprehension
- When a sound wave enters the ear, it sets the eardrum into oscillation...
Text Solution
|
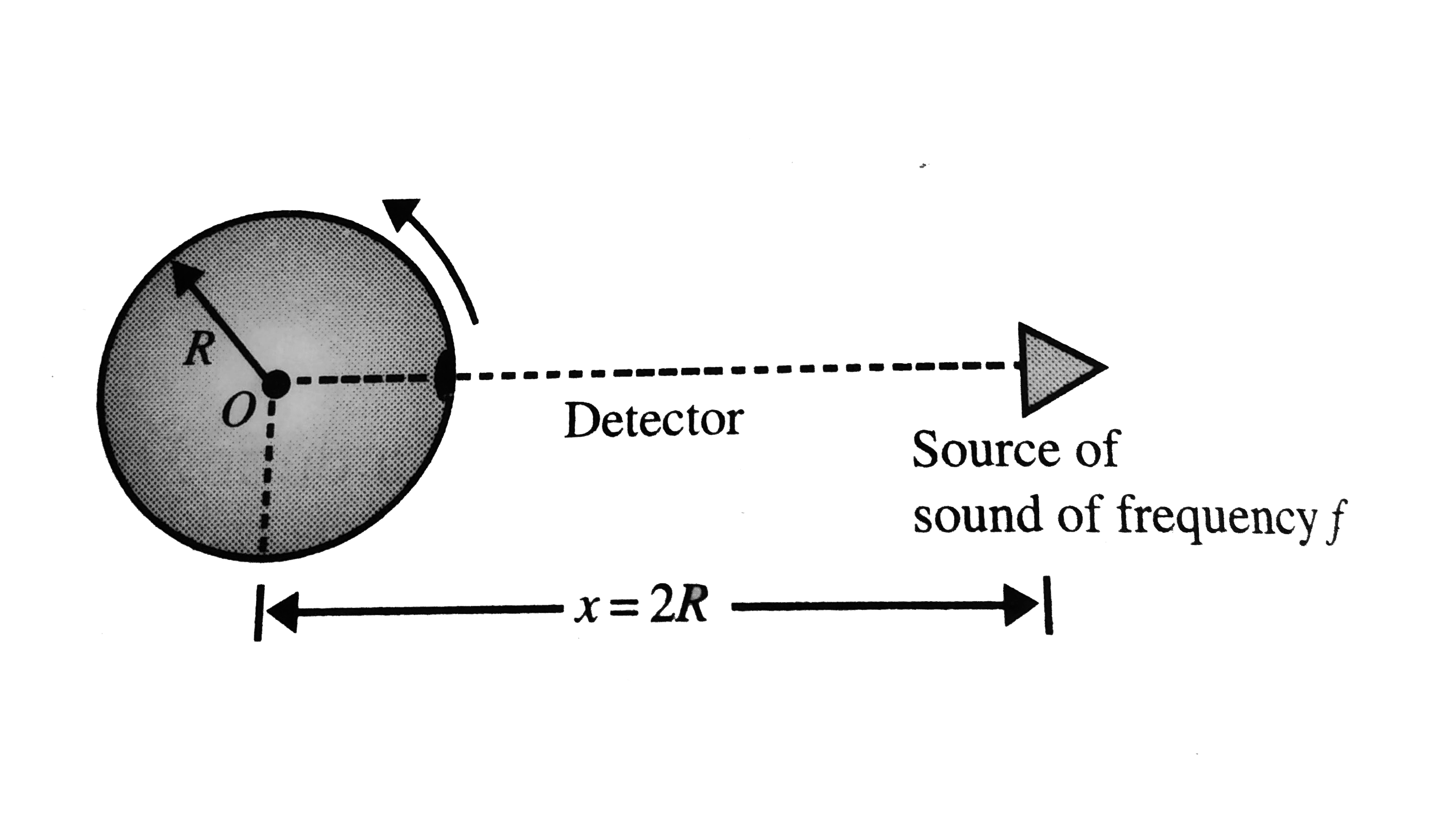
- A source of sound and detector are arranged as shown in Fig. The detec...
Text Solution
|
- A source of sound and detector are arranged as shown in Fig. The detec...
Text Solution
|
- A source of sound and detector are arranged as shown in Fig. The detec...
Text Solution
|
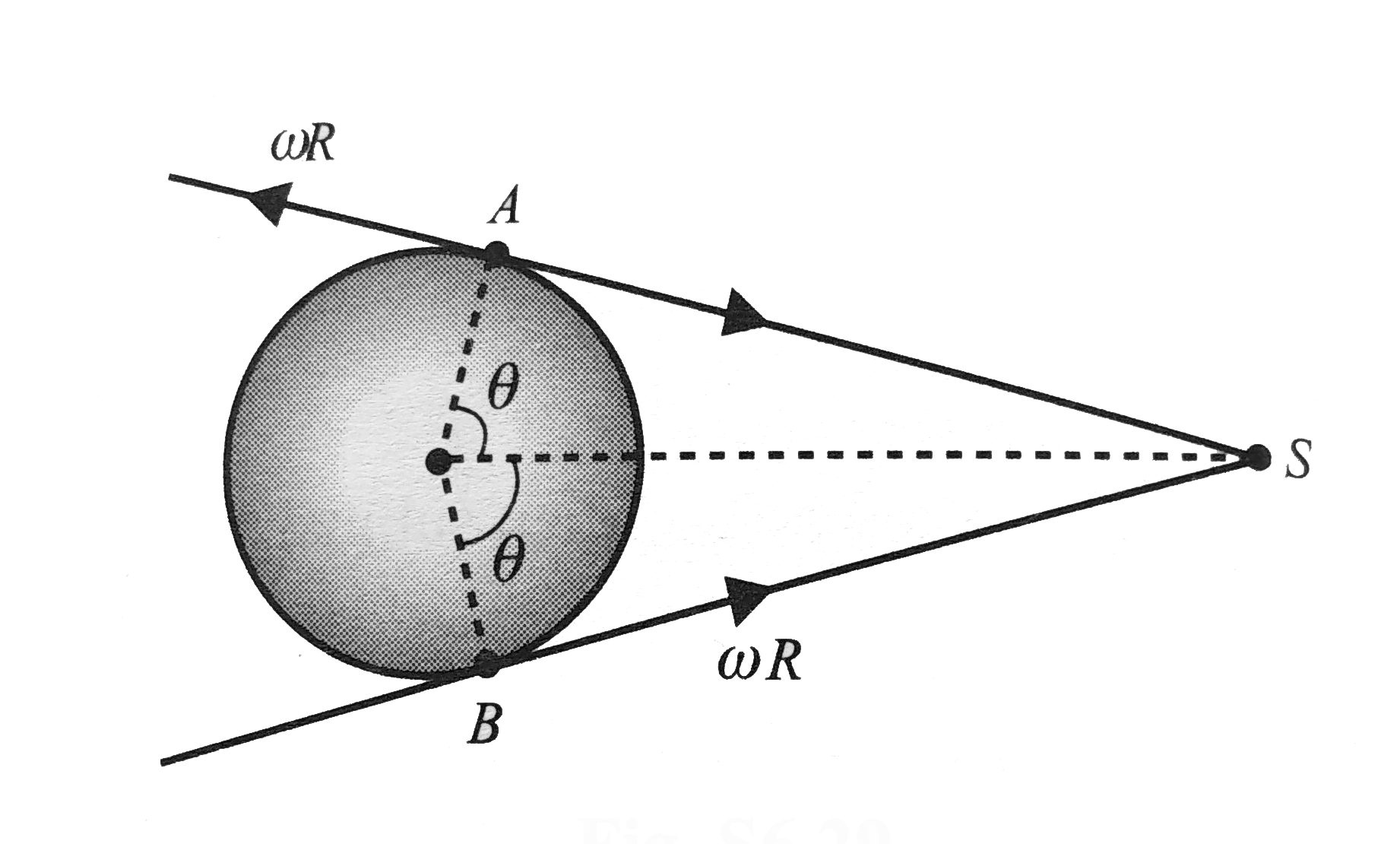
- As shown if Fig. a vibrating tuning fork of frequency 512 Hz is moving...
Text Solution
|
- As shown if Fig. a vibrating tuning fork of frequency 512 Hz is moving...
Text Solution
|
- As shown if Fig. a vibrating tuning fork of frequency 512 Hz is moving...
Text Solution
|
- As shown if Fig. a vibrating tuning fork of frequency 512 Hz is moving...
Text Solution
|
- A source of sound with natural frequency f0=1800Hz moves uniformly alo...
Text Solution
|
- A source of sound with natural frequency f0=1800Hz moves uniformly alo...
Text Solution
|
- A source of sound and a detector are placed at the same place on groun...
Text Solution
|
- A source of sound and a detector are placed at the same place on groun...
Text Solution
|
- A source of sound and a detector are placed at the same place on groun...
Text Solution
|
- A railroad train is travelling at 30(m)/(s) in still air. The frequenc...
Text Solution
|
- A railroad train is travelling at 30(m)/(s) in still air. The frequenc...
Text Solution
|
- A source of sonic oscillation with frequency n0=600Hz moves away and a...
Text Solution
|
- A source of sonic oscillation with frequency n0=600Hz moves away and a...
Text Solution
|
- A source of sonic oscillation with frequency n0=600Hz moves away and a...
Text Solution
|
- A source S of acoustic wave of the frequency v0=1700Hz and a receiver ...
Text Solution
|
- A source S of acoustic wave of the frequency v0=1700Hz and a receiver ...
Text Solution
|