Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
SOUND WAVES AND DOPPLER EFFECT
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Exercise 6.1|56 VideosSOUND WAVES AND DOPPLER EFFECT
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Exercise 6.2|72 VideosSOUND WAVES AND DOPPLER EFFECT
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Integer|16 VideosRIGID BODY DYNAMICS 2
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Interger|2 VideosSUPERPOSITION AND STANDING WAVES
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Comprehension Type|5 Videos
CENGAGE PHYSICS-SOUND WAVES AND DOPPLER EFFECT-Examples
- The frequency of sound produced by a bell is 500 Hz the velocity of th...
Text Solution
|
- An observer standing on a railway crossing receives frequencies 2.2 kH...
Text Solution
|
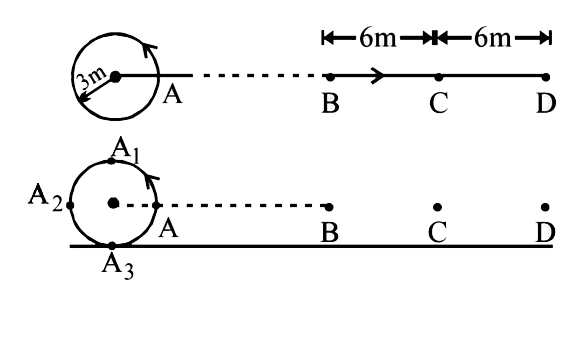
- A source of sound is moving along a circular orbit of radius 3 meter w...
Text Solution
|
- Two tuning forks with natural frequencies of 340 Hz each move relative...
Text Solution
|
- A band playing music at a frequency f is moving towards a wall at a sp...
Text Solution
|
- A boat is travelling in a river with a speed of 10 m/s along the strea...
Text Solution
|
- A sonometer wire under tension of 63 N vibrating in its fundamental mo...
Text Solution
|
- A train approaching a hill at a speed of 40 km//hr sounds a whistle of...
Text Solution
|
- A train A crosses a station with a speed of 40 m/s and whitles a short...
Text Solution
|
- The sound level at a distance of 3.00 m from a source is 120 dB. At wh...
Text Solution
|
- A student holds a tuning fork ocillating at 2456 Hz. He walks towards ...
Text Solution
|
- Two train whistles have identical frequencies of 180 Hz. When one trai...
Text Solution
|
- When a train is approaching the observer, the frequency of the whistle...
Text Solution
|
- A source S emitting sound of 300 Hz is fixed of block A which is attac...
Text Solution
|
- The frequency of sound produced by a bell is 500 Hz the velocity of th...
Text Solution
|
- An observer standing on a railway crossing receives frequencies 2.2 kH...
Text Solution
|
- A source of sound is moving along a circular orbit of radius 3 meter w...
Text Solution
|
- Two tuning forks with natural frequencies of 340 Hz each move relative...
Text Solution
|
- A band playing music at a frequency f is moving towards a wall at a sp...
Text Solution
|
- A boat is travelling in a river with a speed of 10 m/s along the strea...
Text Solution
|