A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-ARCHIVES 1 VOLUME 6-Single Correct
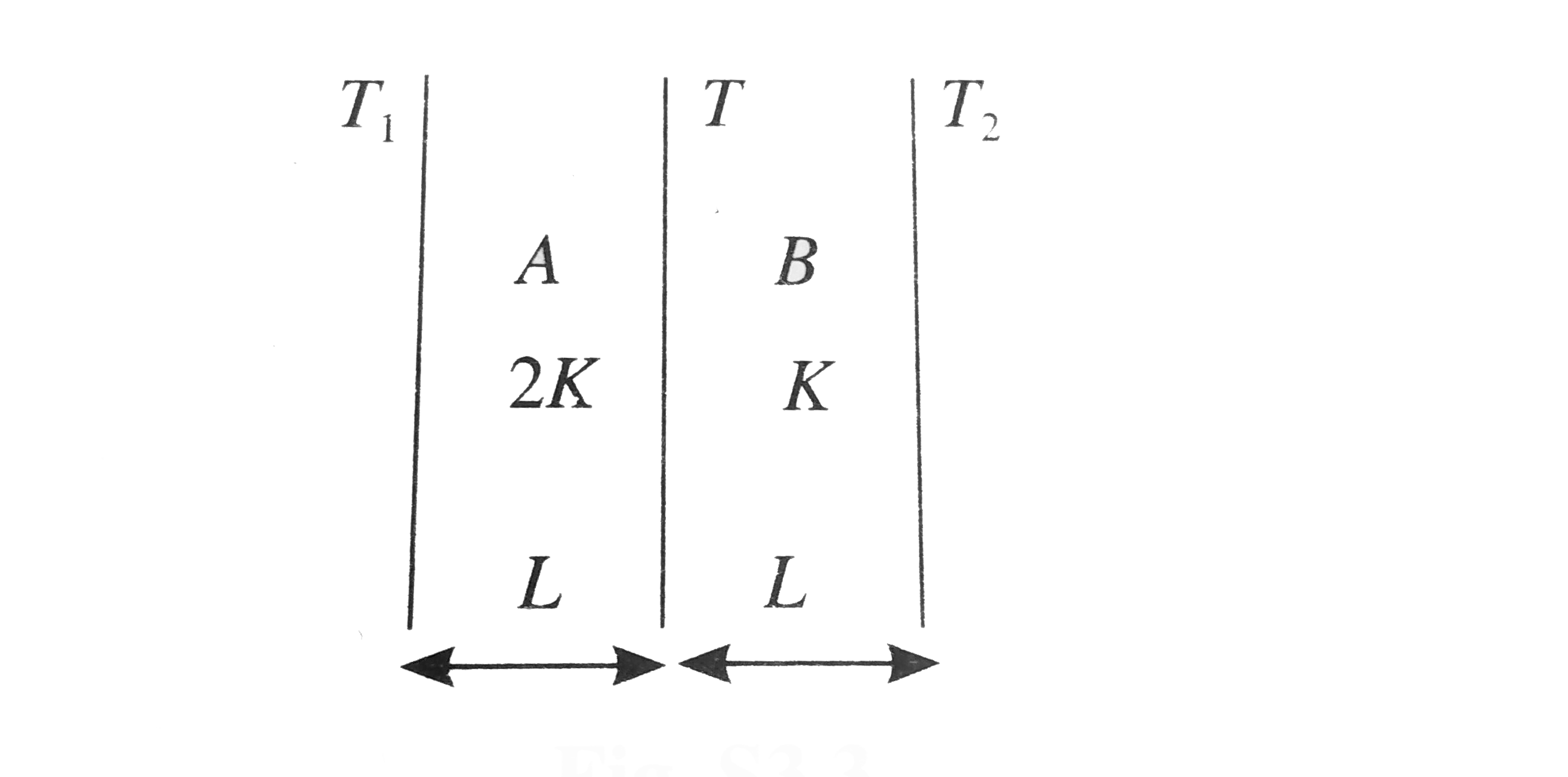
- A wall has two layers A and B, each made of different material. Both t...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal monoatomic gas is taken round the cycle ABCDA as shown in the...
Text Solution
|
- At room temperature, the rms speed of the molecules of a certain diato...
Text Solution
|
- 70 calories of heat required to raise the temperature of 2 moles of an...
Text Solution
|
- Steam at 100^@C is passed into 1.1 kg of water contained in a calorime...
Text Solution
|
- If one mole of a monatomic gas (gamma=5/3) is mixed with one mole of a...
Text Solution
|
- A cylinder of radius R made of a material of thermal conductivity K1 i...
Text Solution
|
- When an ideal diatomic gas is heated at constant pressure, the fractio...
Text Solution
|
- Three closed vessels A, B and C are at the same temperature T and cont...
Text Solution
|
- Three rods of identical cross-sectional area and made from the same me...
Text Solution
|
- Two metallic spheres S1 and S2 are made of the same material and have ...
Text Solution
|
- The temperature of an ideal gas is increased from 120K to 480K. If at ...
Text Solution
|
- The average translational energy and the rms speed of molecules in a s...
Text Solution
|
- The intensity of radiation emitted by the sun has its maximum value at...
Text Solution
|
- The average translational kinetic energy of O2 (relative molar mass 32...
Text Solution
|
- A vessel contains 1 mole of O2 gas (relative molar mass 32) at a tempe...
Text Solution
|
- A spherical black body with a radius of 12cm radiates 450W power at 50...
Text Solution
|
- A vessel contains a mixture of one mole of oxygen and two moles of nit...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical containers A and B with frictionless pistons contain the...
Text Solution
|
- Two cylinders A and B fitted with pistons contain equal amounts of an ...
Text Solution
|