Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
LINEAR AND ANGULAR SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Single Correct|107 VideosLINEAR AND ANGULAR SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Multiple Correct|35 VideosLINEAR AND ANGULAR SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Exercise 4.2|23 VideosKINETIC THEORY OF GASES AND FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Interger|11 VideosMISCELLANEOUS KINEMATICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Interger type|3 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-LINEAR AND ANGULAR SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION-Subjective
- A rectangular tank having base 15 cm xx 20 cm is filled with water (de...
Text Solution
|
- A body A mass m(1) = 1 kg and body B of mass m(2) = 4.1 kg. The body A...
Text Solution
|
- In the arrangement shown in figure the sleeve M of mass m=0.20kg is f...
Text Solution
|
- A vertical pole of length l , density rho , area of cross section A fl...
Text Solution
|
- In the shown arrangement, both the spring are in their natural lengths...
Text Solution
|
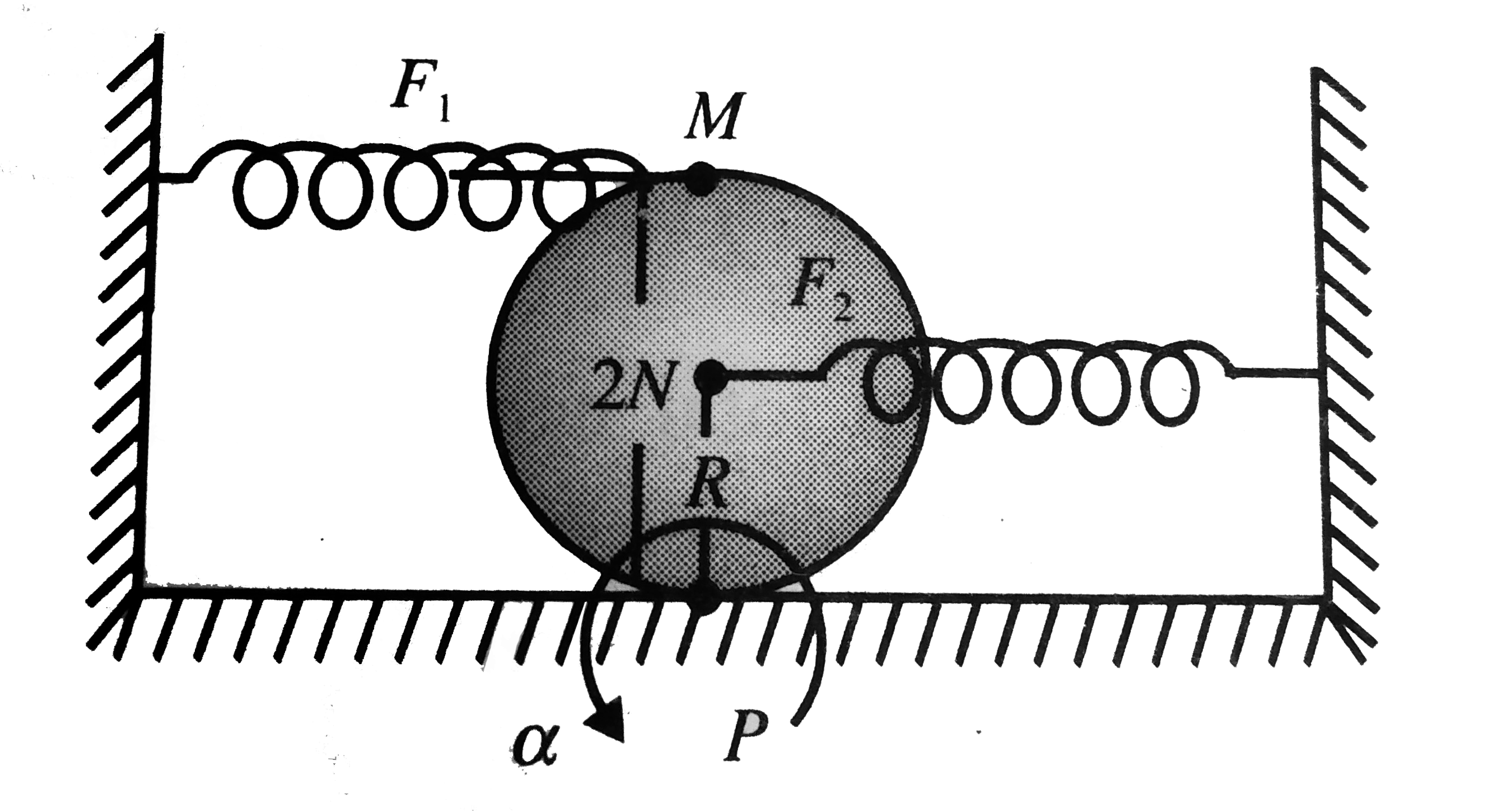
- A uniform dise of mass m and radius R is connected with two light spri...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a liquid which fills a uniform U - tube uniform U- tube, as s...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m is located in a unidimensional potential field wh...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass 2 kg is moving of a straight line under the actin f...
Text Solution
|
- A body of mass m hangs from a smooth fixed pulley P(1) by the inextens...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m connected with a smooth prismatic wedge of mass m is...
Text Solution
|
- A stepped pulley having mass m redius of gyration k is connected with ...
Text Solution
|
- A stepped dies of mass M and radius R is pivoted at its center C smoot...
Text Solution
|
- A disc of mass m hanged by a string is attached at P and a spring of s...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform cylinder of length (L) and mass (M) having cross sectional a...
Text Solution
|
- Disregading gravity, find the period of oscillation of the partical co...
Text Solution
|
- A smooth of mass m(1) is lying on a rigid horizontal string A bob of m...
Text Solution
|
- A smooth piston of mass m area of cross - section A is in equilibrium ...
Text Solution
|
- If velocity of a partical moving along a straight line changes sinuso...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown, mass 2m connected with a spring of force constant...
Text Solution
|