Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-SUPERPOSITION AND STANDING WAVES-Comprehension Type
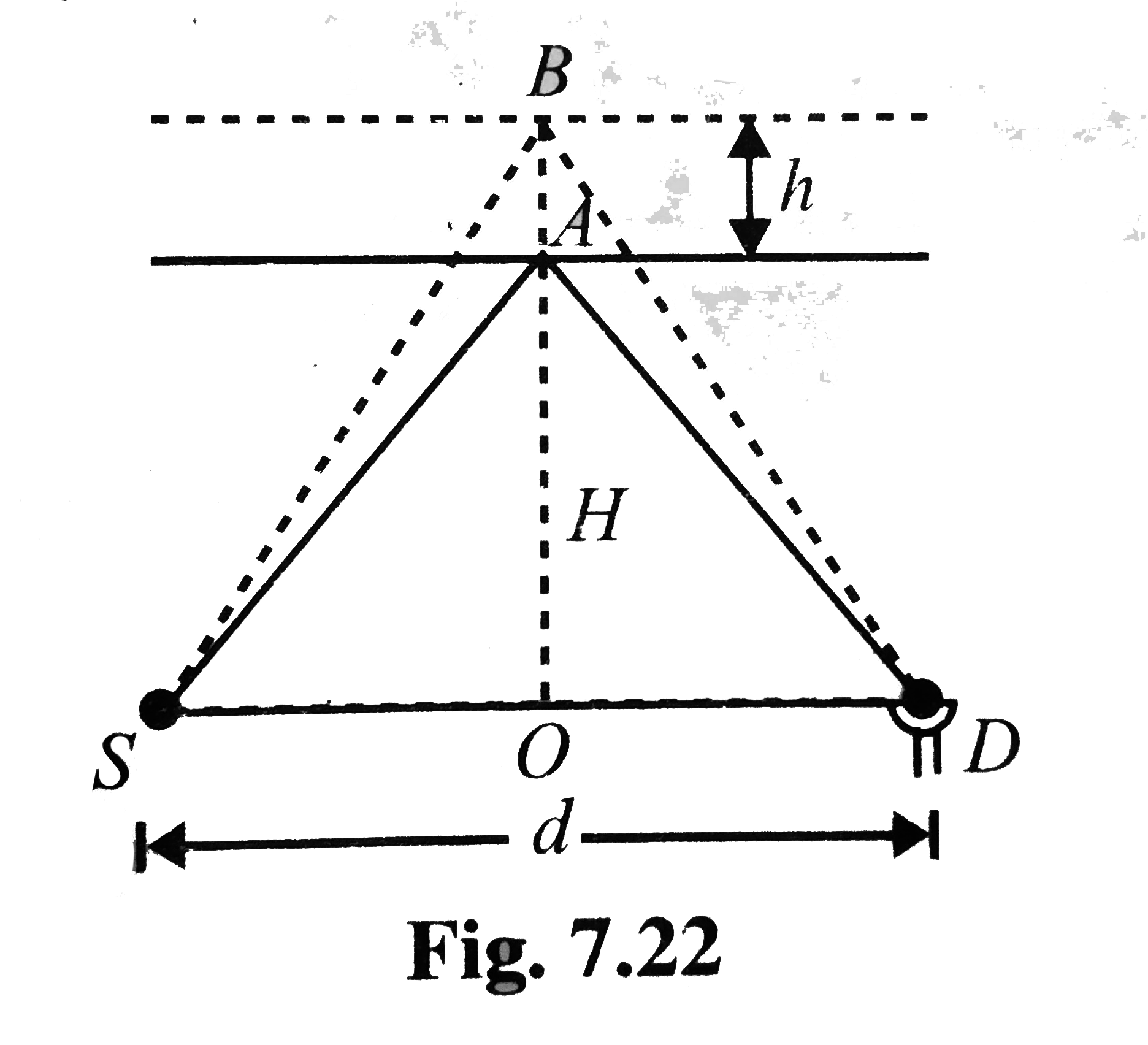
- A source and a detector D of high frequency waves are a distance d ap...
Text Solution
|
- A string of length L, fixed at its both ends is vibrating in its 1^(st...
Text Solution
|
- A string of length L, fixed at its both ends is vibrating in its 1^(st...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown a sinusoidal wave is generated at the end A the wa...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown a sinusoidal wave is generated at the end A the wa...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown a sinusoidal wave is generated at the end A the wa...
Text Solution
|