Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
P-BLOCK GROUP 13 - BORON FAMILY
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Ex 6.1 (Subjective)|17 VideosP-BLOCK GROUP 13 - BORON FAMILY
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Ex 6.1 (Objective)|14 VideosP-BLOCK GROUP 13 - BORON FAMILY
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Exercise Archives (Subjecive)|9 VideosORGANIC REACTION MECHANISM
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Analytical and Descriptive|6 VideosP-BLOCK GROUP 14 - CARBON FAMILY
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Exercises Archives (Subjective)|9 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY-P-BLOCK GROUP 13 - BORON FAMILY-Solved Examples
- When an inorganic compound (X) having (3c, 2e) as well as (2c, 2e) bon...
Text Solution
|
- Boric acid on heating at 100^@ C, gives (X). (X) on heating at 160^@ C...
Text Solution
|
- Amorphous boron is extracted from borax by the following steps : "Bo...
Text Solution
|
- A certain salt (X) gives the following tests : (a) Its aqueous solut...
Text Solution
|
- A white crystalline compound (X) swells open heating and gives violet-...
Text Solution
|
- The metallic salt (XY) is soluble in water. (a) When the aqueous sol...
Text Solution
|
- An inorganic compound (X) shows the following reactions : (a) It is ...
Text Solution
|
- Compound (X) on reduction with LiAlH(4) gives a hydride (Y) containing...
Text Solution
|
- An inorganic Lewis acid (X) shows the following reactions : (a) It f...
Text Solution
|
- (a) On bolining a minerak (A) with NaCO(3) solution, a white precipirt...
Text Solution
|
- Identify (A) + N(2) overset(Delta) rarr (B) overset(H(2) O) rarr unde...
Text Solution
|
- A colourless mixture of two salts (A) and (B) (excess) is soluble in H...
Text Solution
|
- B(10)C(2)H(12) is isoelectronic with
Text Solution
|
- Draw possible structures of B(4)H(10) and B(5) H(11) molecules, showin...
Text Solution
|
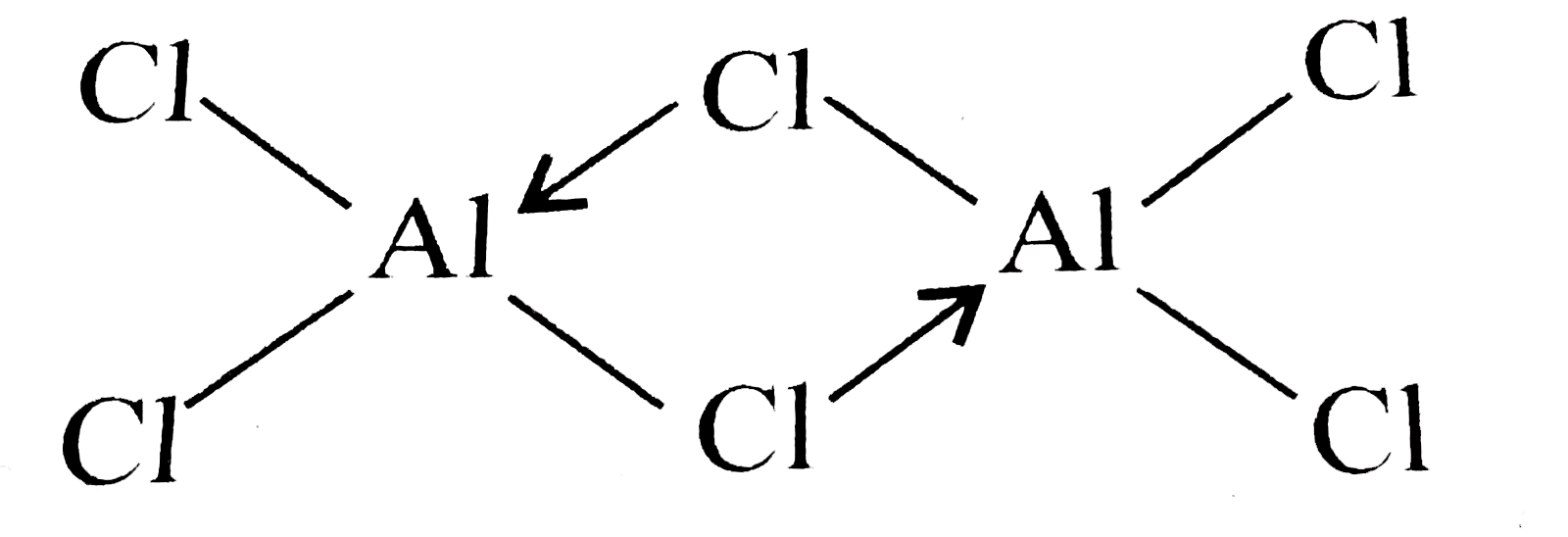
- How many the electrical conductivity of Al(2)Cl(6) changes on heating ...
Text Solution
|
- Complete the following : (a) (b) .
Text Solution
|