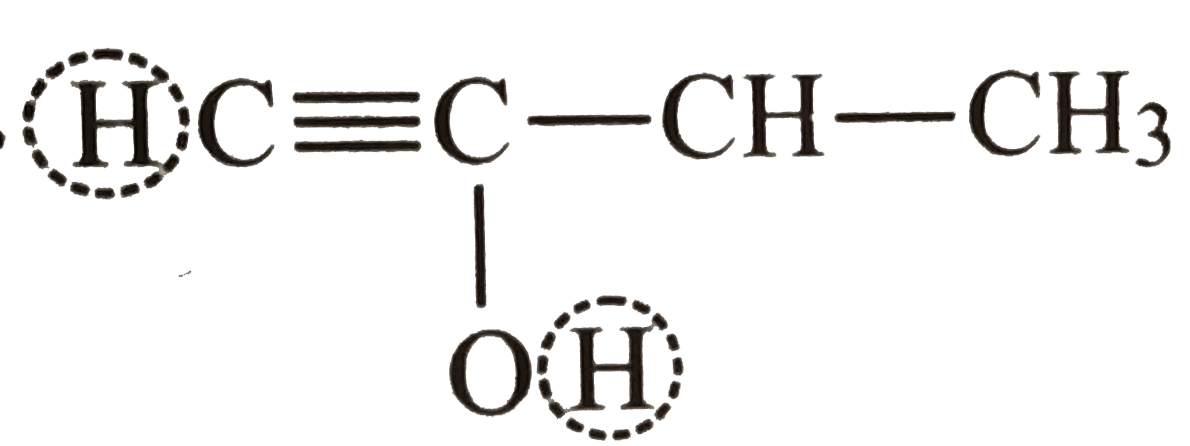Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY-ALKANES AND CYCLOALKANES-Archives
- i. 0.21 gm of but-3-yn-2-ol is treated with excess of C(2)H(5)MgBr at ...
Text Solution
|
- Marsh gas mainly contains:
Text Solution
|
- The compound with the highest boiling point is:
Text Solution
|
- The highest boiling point is expected for:
Text Solution
|
- The compound which has one isopropyl group is -
Text Solution
|
- The (C--H) bond distance is longer in:
Text Solution
|
- When cyclohexane is poured in water, it floats because:
Text Solution
|
- The products obtained at cathode and anode on electrolysis of aqueous ...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the following reaction: Identify the structure of the ma...
Text Solution
|
- How many chiral compounds are possible on monochlorination of 2-Methyl...
Text Solution
|
- What would be the product formed when 1-bromo-3-chlorocylobutane react...
Text Solution
|
- mu observed = Sigma mu(i)X(i) where mu(i) is the dipole moment of th...
Text Solution
|
- The value of N and M are:
Text Solution
|
- The total number of cyclic structure as well as stereoisomers possible...
Text Solution
|