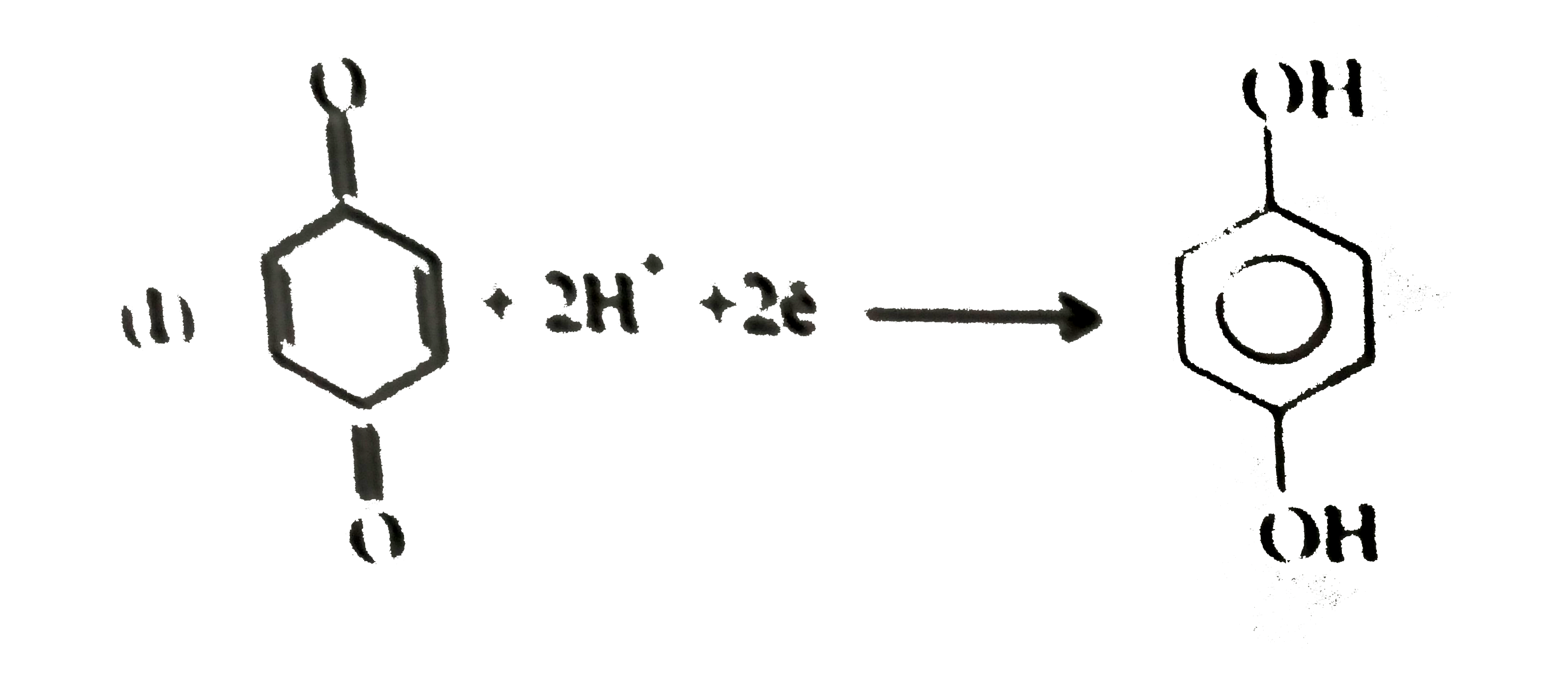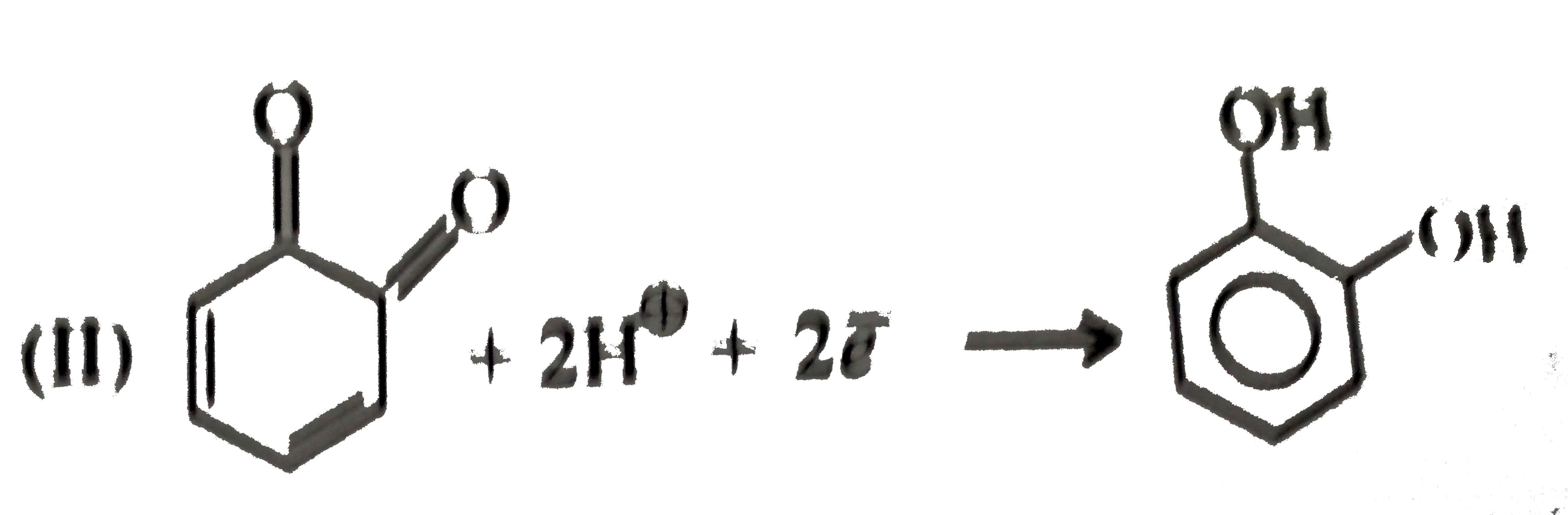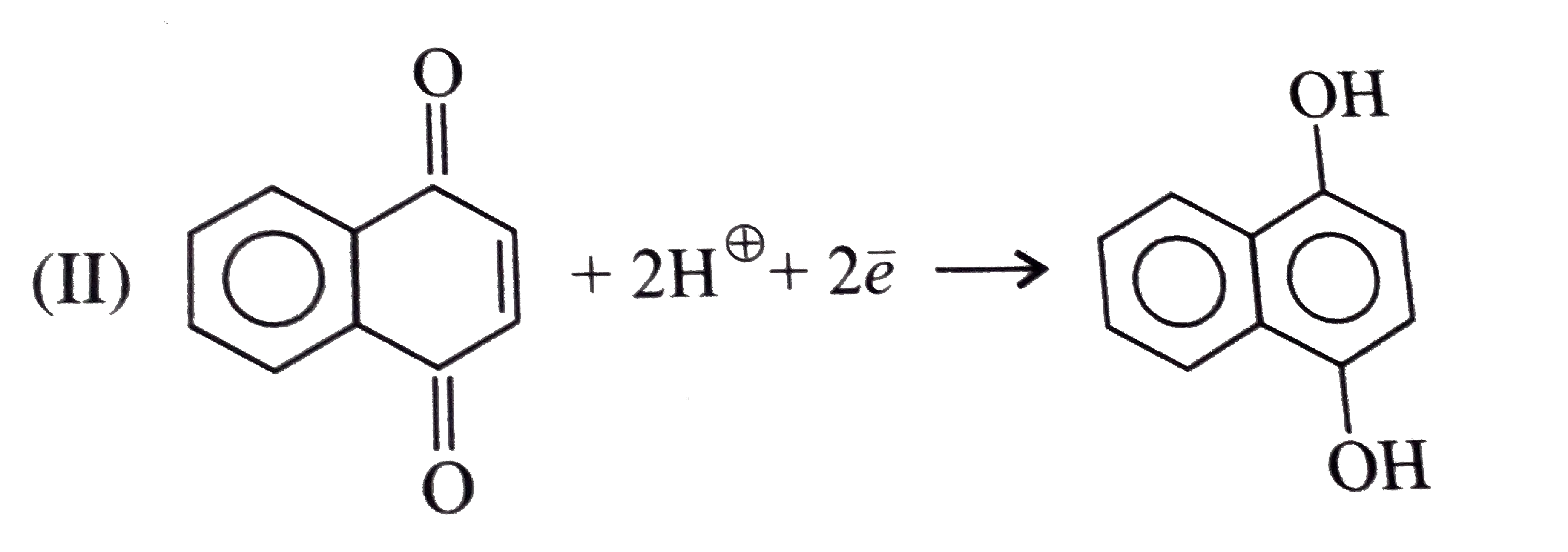Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ALCOHOL,PHENOL AND ETHERS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Exercises Subjective|25 VideosALCOHOL,PHENOL AND ETHERS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Exercises Concept Application|33 VideosALCOHOL,PHENOL AND ETHERS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Archives Analytical And Descriptive|15 VideosALIPHATIC AND AROMATIC ALDEHYDES AND KETONES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Archives Subjective|29 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY-ALCOHOL,PHENOL AND ETHERS-Solved Examples
- Explain why in the synthesis of ether (B) using (A) or A(1) all the th...
Text Solution
|
- Complete the following reactions: a. 2Me(3)C--Br overset (Ag(2)CO(3...
Text Solution
|
- complete the following reactions: a. overset (C(6)H(6) + MeCOCI) un...
Text Solution
|
- a. Calculate the depression in freezing point (Delta T(f)) of 0.1 m s...
Text Solution
|
- Complette the following reactions : a.
Text Solution
|
- Synthesies the following alcohols by using: a. Grignard reagent (G....
Text Solution
|
- a. Write the reaction of EtOH with (i) KNH(2) (ii) aq. KOH (iii) Pot...
Text Solution
|
- Identity the following compounds : a. b. overset (C(5)H(12)O(2)...
Text Solution
|
- Given the stereochemical product of the following reactions:
Text Solution
|
- Give the product of the following reactions: a. b. Given the st...
Text Solution
|
- a. How many conformational isomers are possible of 4-isopropyl cylohe...
Text Solution
|
- Explain which of the following reactions will occur. a. overset (RC...
Text Solution
|
- a. Which is a stronger nucleophile ? C(2)H(5)SH (ethane thiol or ethy...
Text Solution
|
- Distinguish between the following pairs: a. (I)
Text Solution
|
- Distinguish between the following pairs: a. (I) PhOH (II) PhNH(2...
Text Solution
|
- NA (nucleophilic addition) reaction of alcohols with aldehydes gives h...
Text Solution
|
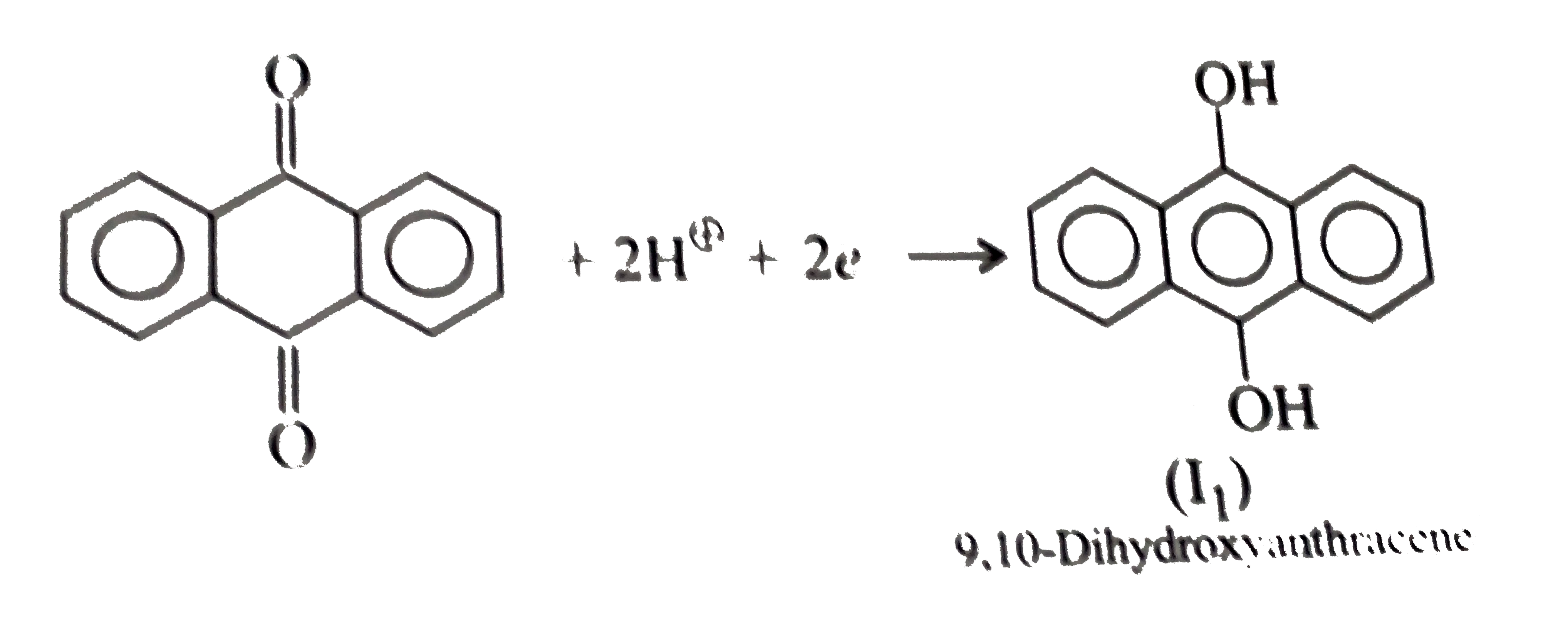
- Give the decreasing order of stability of the following quinones: a....
Text Solution
|
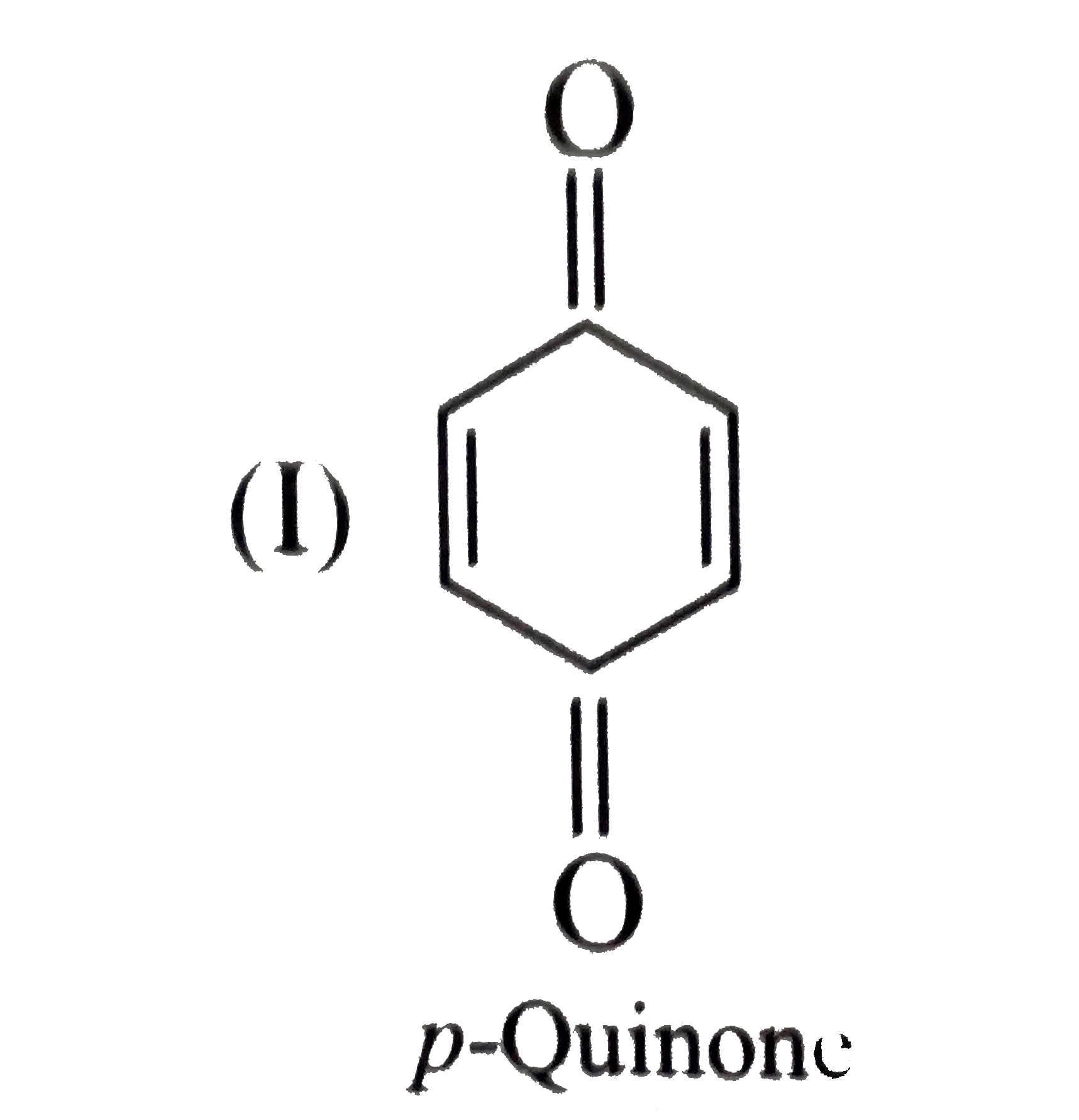
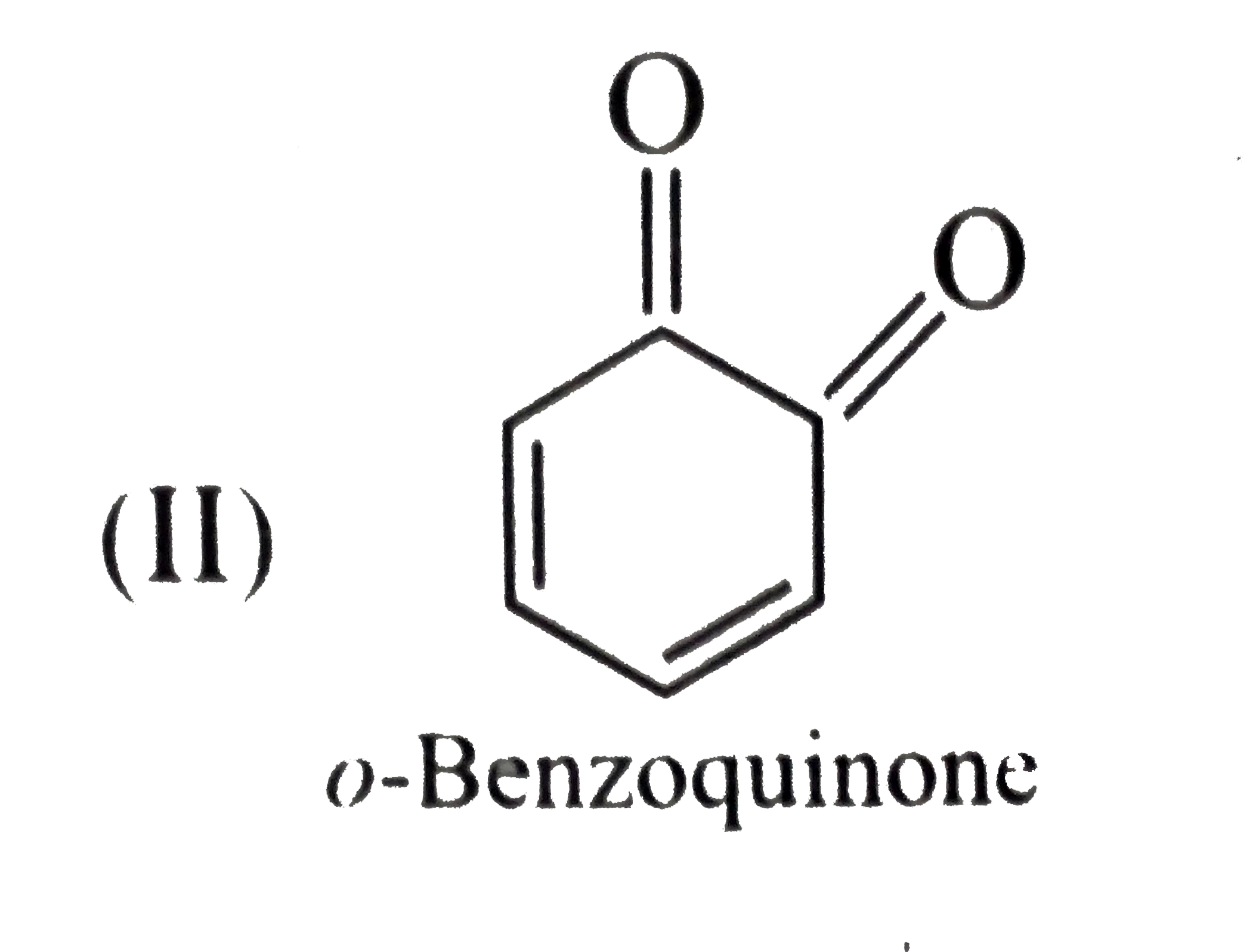
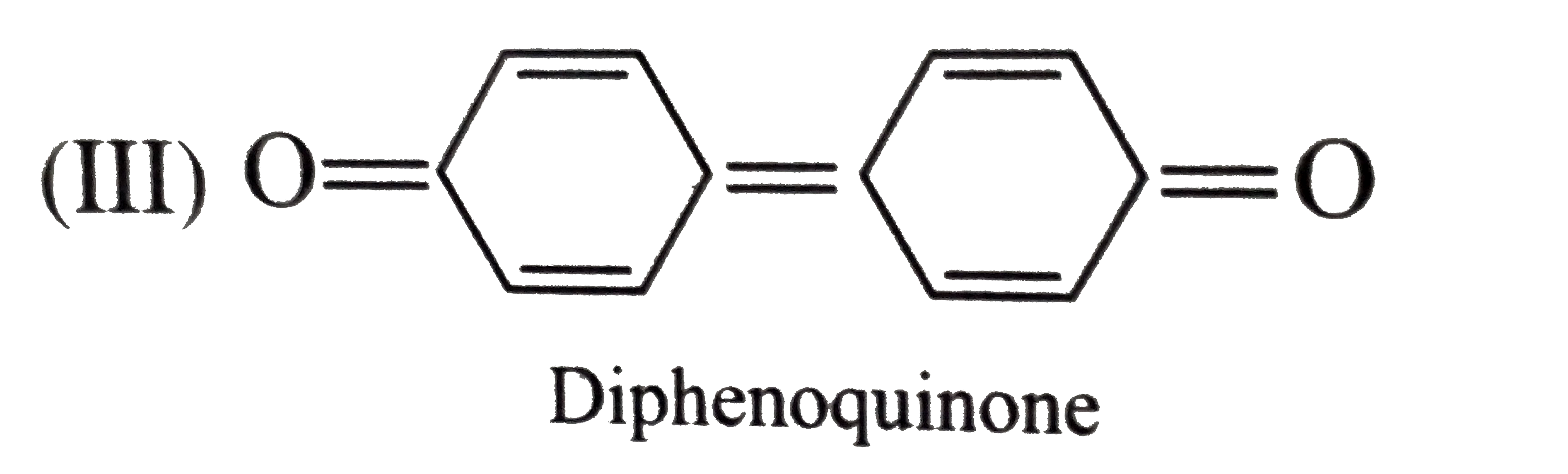
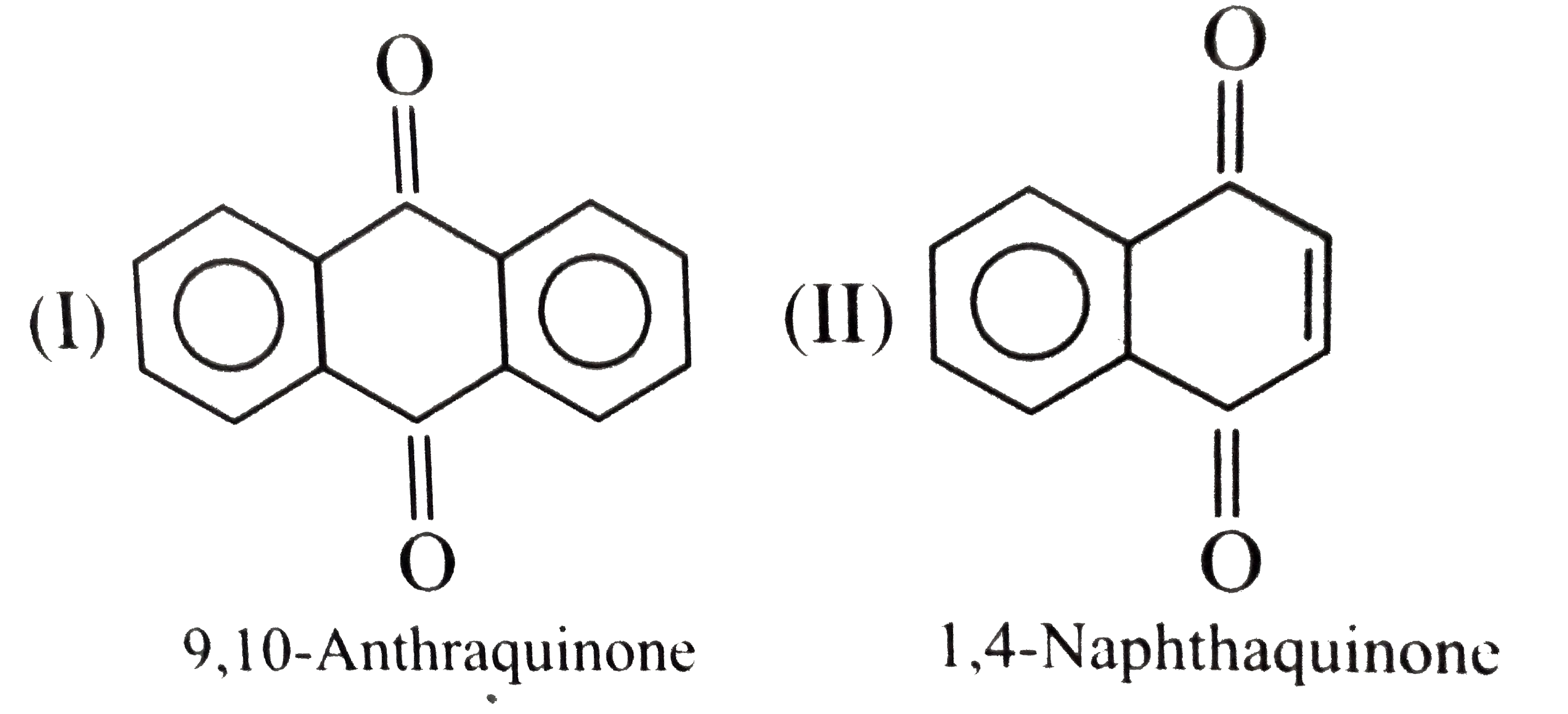
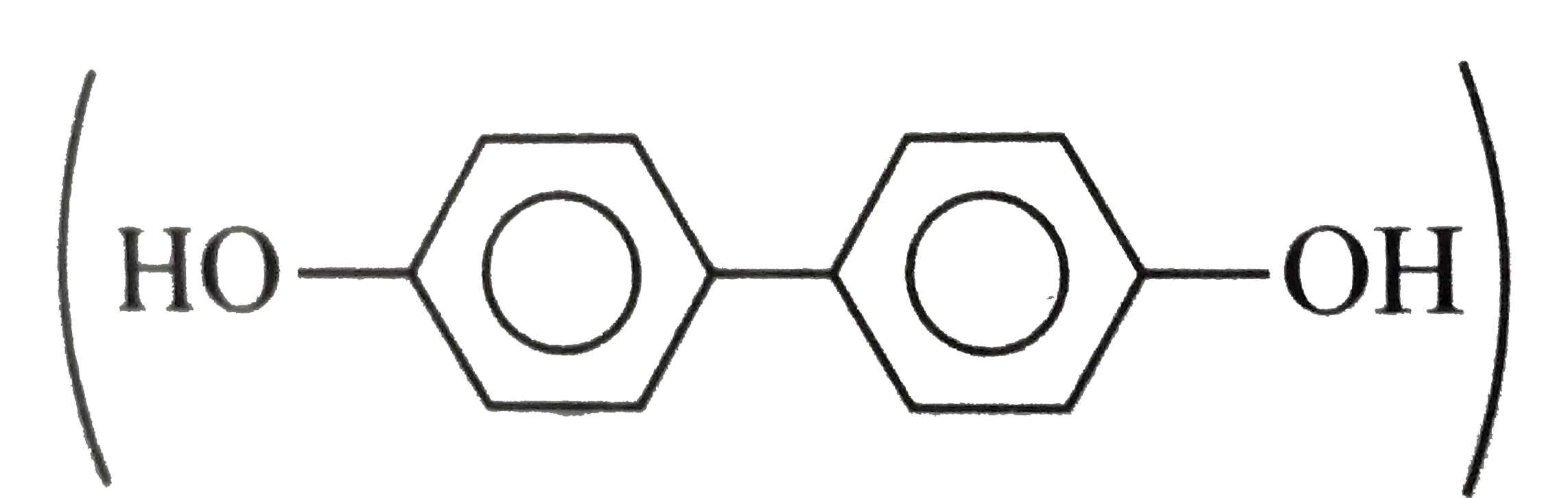 because it generates two aromatic rings which have more reasonance ehergy and greater stability than the reaction of (I) and (II), which would generate only one benzene ring. Both (I) and (II) on reduction give one benzene ring. but (II) is less stable (more reactive) than I because adjacent `(C=O)` groups in (II) make it less stable.
because it generates two aromatic rings which have more reasonance ehergy and greater stability than the reaction of (I) and (II), which would generate only one benzene ring. Both (I) and (II) on reduction give one benzene ring. but (II) is less stable (more reactive) than I because adjacent `(C=O)` groups in (II) make it less stable.