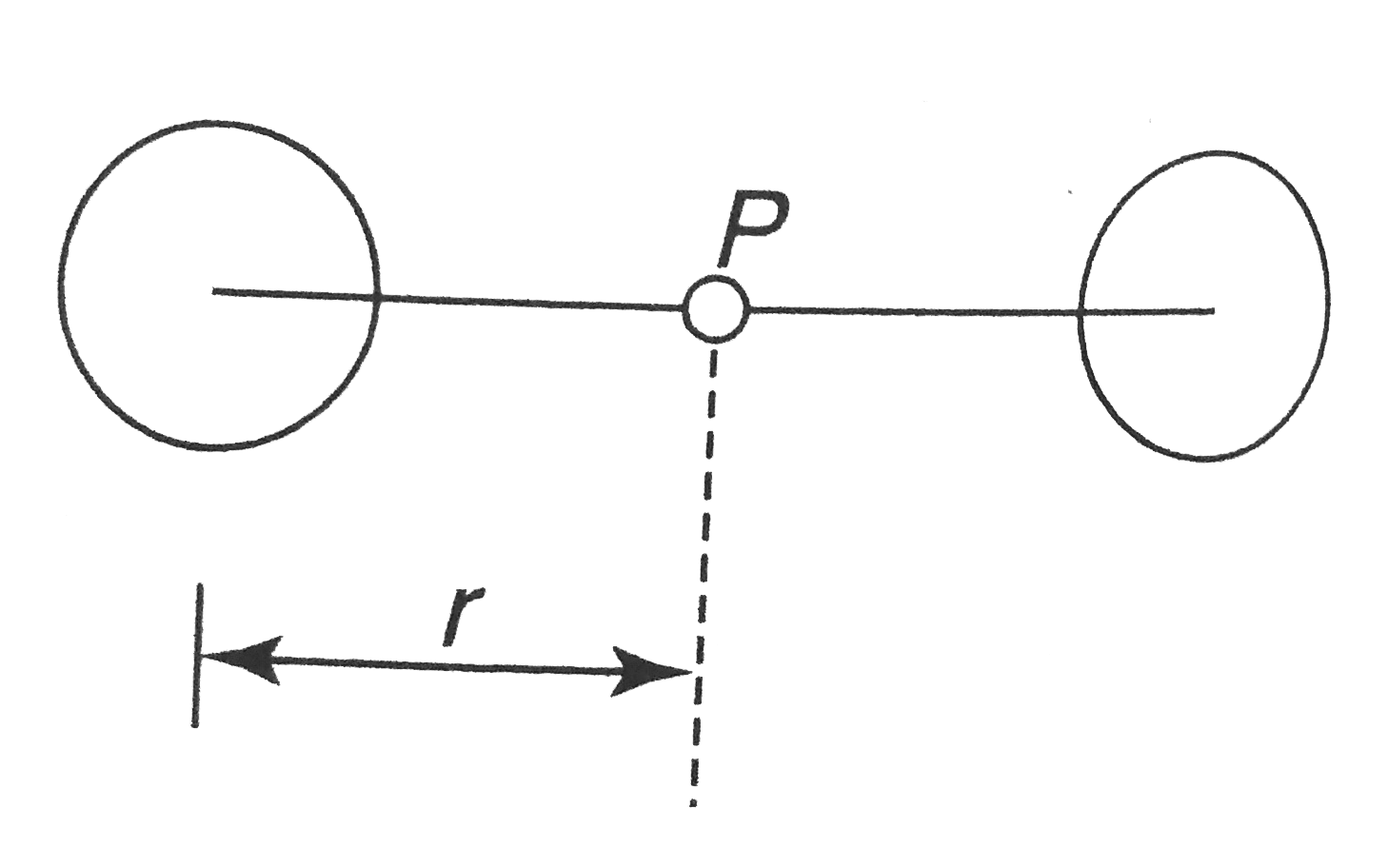
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
GRAVITATION
A2Z|Exercise Assertion Reasoning|16 VideosGRAVITATION
A2Z|Exercise NEET Questions|42 VideosGRAVITATION
A2Z|Exercise Motion Of Satellite|33 VideosGENERAL KINEMATICS AND MOTION IN ONE DIMENSION
A2Z|Exercise Chapter Test|30 VideosKINETIC THEORY OF GASES AND THERMODYNAMICS
A2Z|Exercise Chapter Test|29 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
A2Z-GRAVITATION-Problems Based On Mixed Concepts
- If radius of the earth contracts to half of its present value without ...
Text Solution
|
- Find the escape velocity of particle of mass m which is situated at a ...
Text Solution
|
- If a particles of mass m is projected with minimum velocity form the s...
Text Solution
|
- The mass of a satellite is M//81 and radius is R//4 where M and R are ...
Text Solution
|
- The orbital velocity of a satellite at point B with radius r(B) and n....
Text Solution
|
- An asteroid of mass m is approaching earth, initially at a distance 10...
Text Solution
|
- A projectile rises upto a maximum height of R//(1-K^(2)) where K is a ...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is projected from the surface of one star towards other sta...
Text Solution
|
- Two stars of mass m(1) and m(2) are parts of a binary star system. Th...
Text Solution
|
- Binary stars of comparable masses rotates under the influence of each ...
Text Solution
|
- The ratio of cube of circumferences of the orbit of a satellite to th...
Text Solution
|
- Two planets revolve with same angular velocity about a star. The radiu...
Text Solution
|
- What would be the projections velocity of a satellite so that interste...
Text Solution
|
- A satellite in equatorial plane is rotating in the direction of earth'...
Text Solution
|
- A satellite is orbiting with areal velocity v(a). At what height form ...
Text Solution
|
- The magnitude of the gravitational field at distance r(1) and r(2) fro...
Text Solution
|
- A spherical planet has uniform density pi/2xx10^(4)kg//m^(3). Find out...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is projected from point A, that is at a distance 4R form th...
Text Solution
|
- Three identical stars, each of mass M, from an equilateral triangle (s...
Text Solution
|
- A satellite can be in a geostationary orbit around earth in an orbit o...
Text Solution
|