Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
WORK, ENERGY AND POWER
PRADEEP|Exercise Additional Exercises|3 VideosWORK, ENERGY AND POWER
PRADEEP|Exercise higher order thinking skills|10 VideosWORK, ENERGY AND POWER
PRADEEP|Exercise Advanced Problems For Competitions|20 VideosTHERMODYNAMICS
PRADEEP|Exercise Assertion- Reason Type Questions|19 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
PRADEEP-WORK, ENERGY AND POWER-NCERT EXERCISES WITH SOLUTIONS
- A body constrained to move along the z-axis of a co-ordinate system, i...
Text Solution
|
- An electron and a proton are detected in a cosmic ray experiment, the ...
Text Solution
|
- A rain drop of radius 2mm, falls from a height of 500 m above the grou...
Text Solution
|
- A molecules in a gas container hits the wall with speed 200m//s at an ...
Text Solution
|
- A pump on the ground floor of a building can pump of water to fill a ...
Text Solution
|
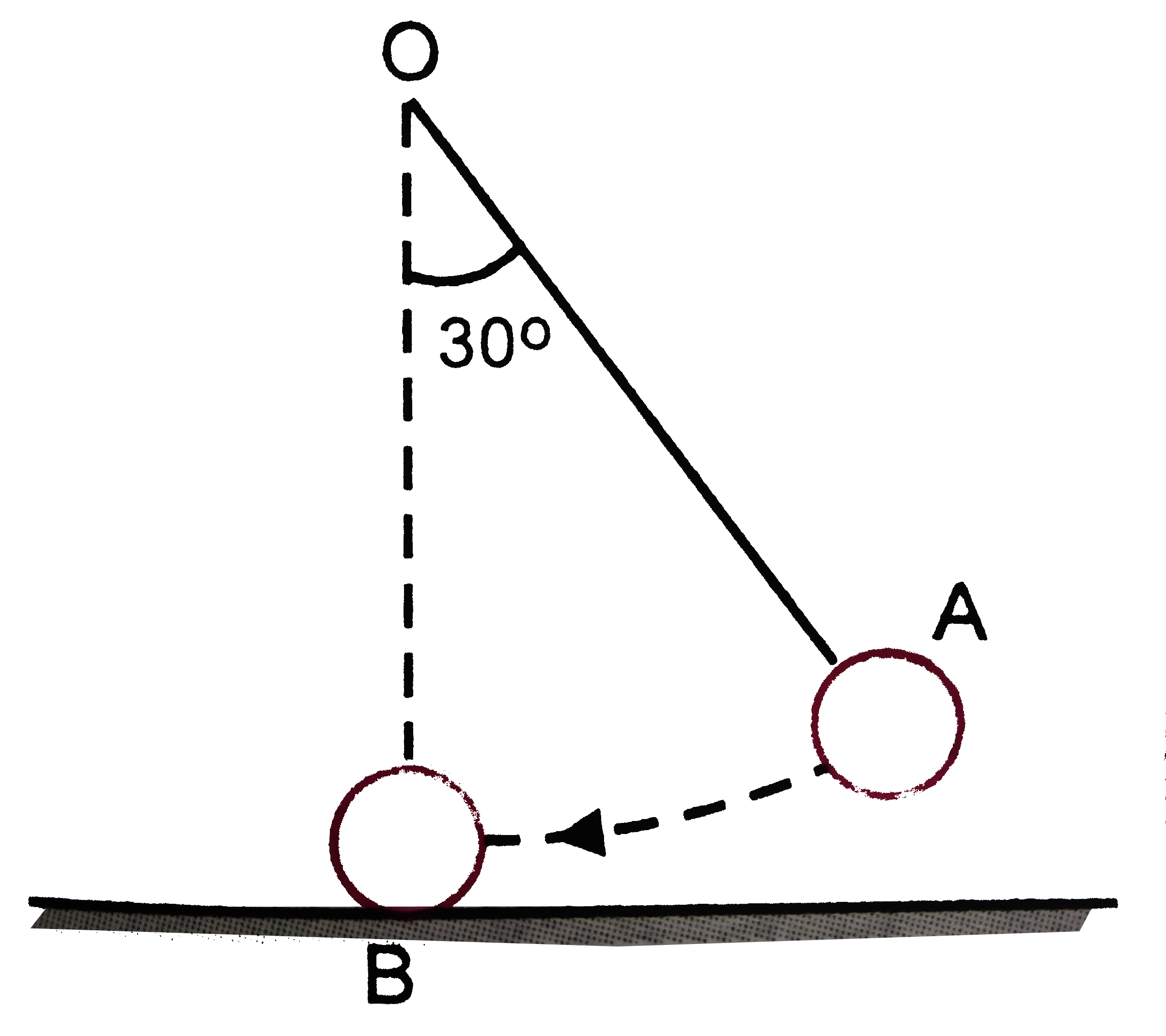
- Two identical ball bearings in contact with each other and resting on ...
Text Solution
|
- The bob A of a simple pendulum released from 30^(@) to the vertical hi...
Text Solution
|
- The bob A of a simple pendulum is released from a horizontal position ...
Text Solution
|
- A trolley of mass 300 ks carrying a sand bag of 25 kg is moving unifor...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass 0.5kg travels in a straight line with velocity v=ax...
Text Solution
|
- The blades of a windmill sweep out a circle of area A. (a) If the wind...
Text Solution
|
- A person trying to lose weight (dieter ) lifts a 10 kg mass through 0....
Text Solution
|
- A family uses 8kW of power. (a) Direct solar energy is incident on the...
Text Solution
|
- A bullet of mass 0.012 kg and horizontal speed 70ms^(-1) strikes a blo...
Text Solution
|
- Two inclined frictionless tracks, one gradual and the other steep meet...
Text Solution
|
- A 1kg block situated on a rough incline is connected to a spring of sp...
Text Solution
|
- A bob of mass 0.3 kg falls from the ceiling of an elevator moving down...
Text Solution
|
- A trolly of mass 200kg moves with a uniform speed of 36 km//h on a fri...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following potential energy curves in figure., cannot poss...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the decay of a free neutron at rest: ntop+e^(-) Show that the...
Text Solution
|