Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
WORK, ENERGY AND POWER
PRADEEP|Exercise Long Answer Question|24 VideosWORK, ENERGY AND POWER
PRADEEP|Exercise Advanced Problems For Competitions|20 VideosWORK, ENERGY AND POWER
PRADEEP|Exercise Very Short Anwer Question.|54 VideosTHERMODYNAMICS
PRADEEP|Exercise Assertion- Reason Type Questions|19 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
PRADEEP-WORK, ENERGY AND POWER-Short Answer Question
- A bullet of mass 0.01J kg and travelling at a speed of 500m//s strikes...
Text Solution
|
- In any perfectly inelastic collision, is whole of KE lost ?
Text Solution
|
- Throwinig mud on a wall is an example of perfectly inelastic collisio...
Text Solution
|
- What is meant by zero work ? State the conditions under which a force ...
Text Solution
|
- Two bodies of unequal masses have same linear momentum. Which one has ...
Text Solution
|
- Tow bodies of unequal masses have same K.E. Which one has greater line...
Text Solution
|
- How do potential energy and K.E. of a spring vary with displacement ?...
Text Solution
|
- What is meant by mass energy equivalence ? Discuss its significance in...
Text Solution
|
- Hydrogenic materials are used as moderators in nuclear reactors to slo...
Text Solution
|
- How do you justify energy conservation from the vibrations of a simple...
Text Solution
|
- A graph of potential energy V(x) verses x is shown in figure. A partic...
Text Solution
|
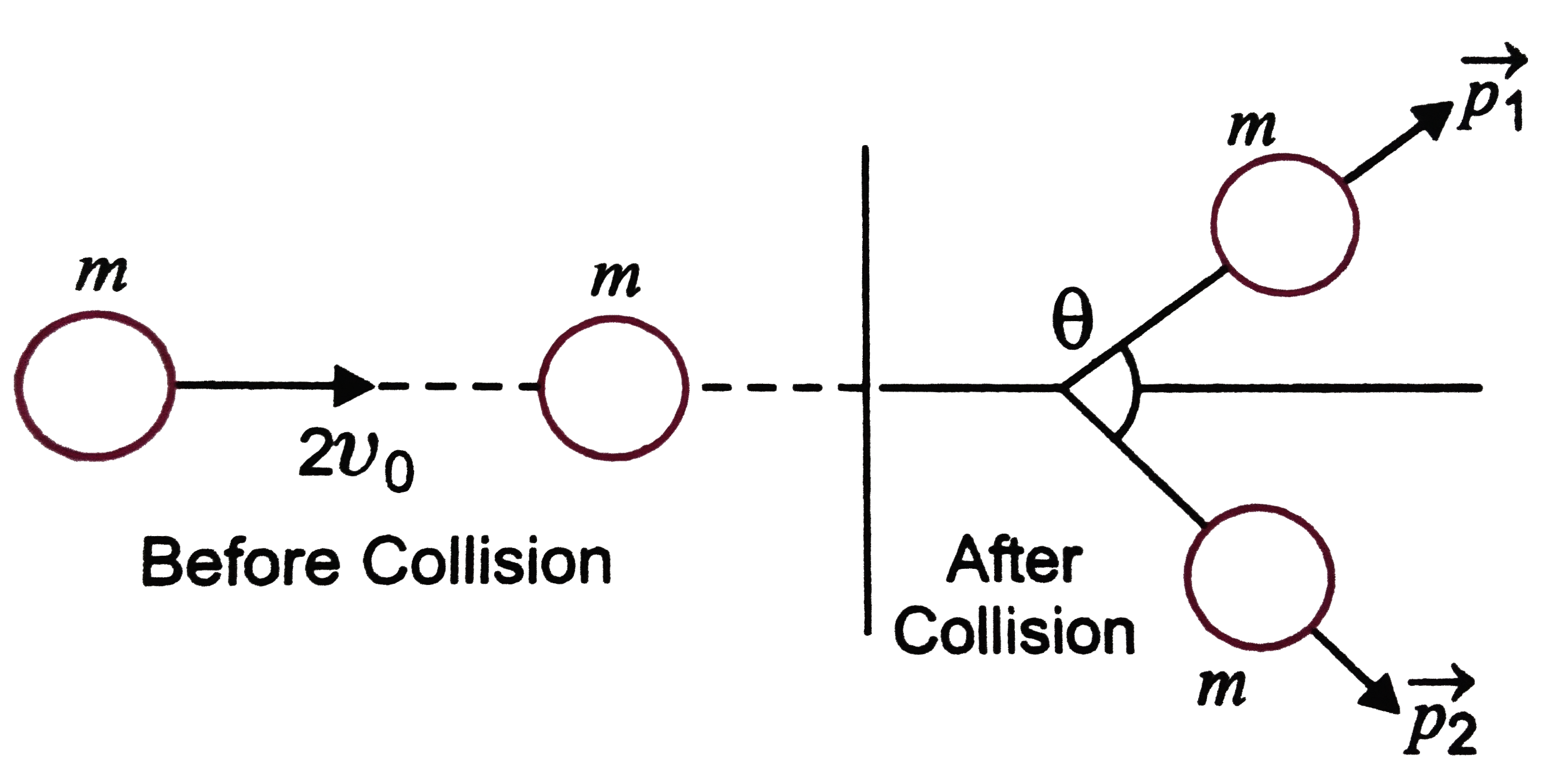
- A ball of mass mm, moving with a speed 2upsilon(0), collides inelastic...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a one-dimensional motion of a particle with total energy E. T...
Text Solution
|
- The bob A of a pendulum released from horizontal to the vertical hits ...
Text Solution
|
- A raindrop of mass 1g falling from a height of 1km hits is the ground ...
Text Solution
|
- Two pendulums with identical bobs and lengths are suspended from a com...
Text Solution
|
- Suppose the average mass of raindrops is 3.0xx10^(-5)kg and their aver...
Text Solution
|
- An engine is attahed to a wagon through a shock absorber of length 1.5...
Text Solution
|
- An adult weighing 600N raises the centre of gravity of his body by 0.2...
Text Solution
|
- On complete combustion , a litre of petrol gives off heat equivalent t...
Text Solution
|