A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
PROPERTIES OF BULK MATTER
PRADEEP|Exercise Integer Type Questions|12 VideosPROPERTIES OF BULK MATTER
PRADEEP|Exercise Asseration - Reason Type Question|18 VideosPROPERTIES OF BULK MATTER
PRADEEP|Exercise Multiple choice questions-II|14 VideosPHYSICAL WORLD AND MEASUREMENT
PRADEEP|Exercise Competiton Focus Jee Medical Entrance|18 VideosRAY OPTICS
PRADEEP|Exercise Problem For Practice(a)|25 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
PRADEEP-PROPERTIES OF BULK MATTER-Multiple choice questions-I
- A thin uniform cylindrical shell, closed at both ends, is partially fi...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform cylinder of length L and mass M having cross-sectional area ...
Text Solution
|
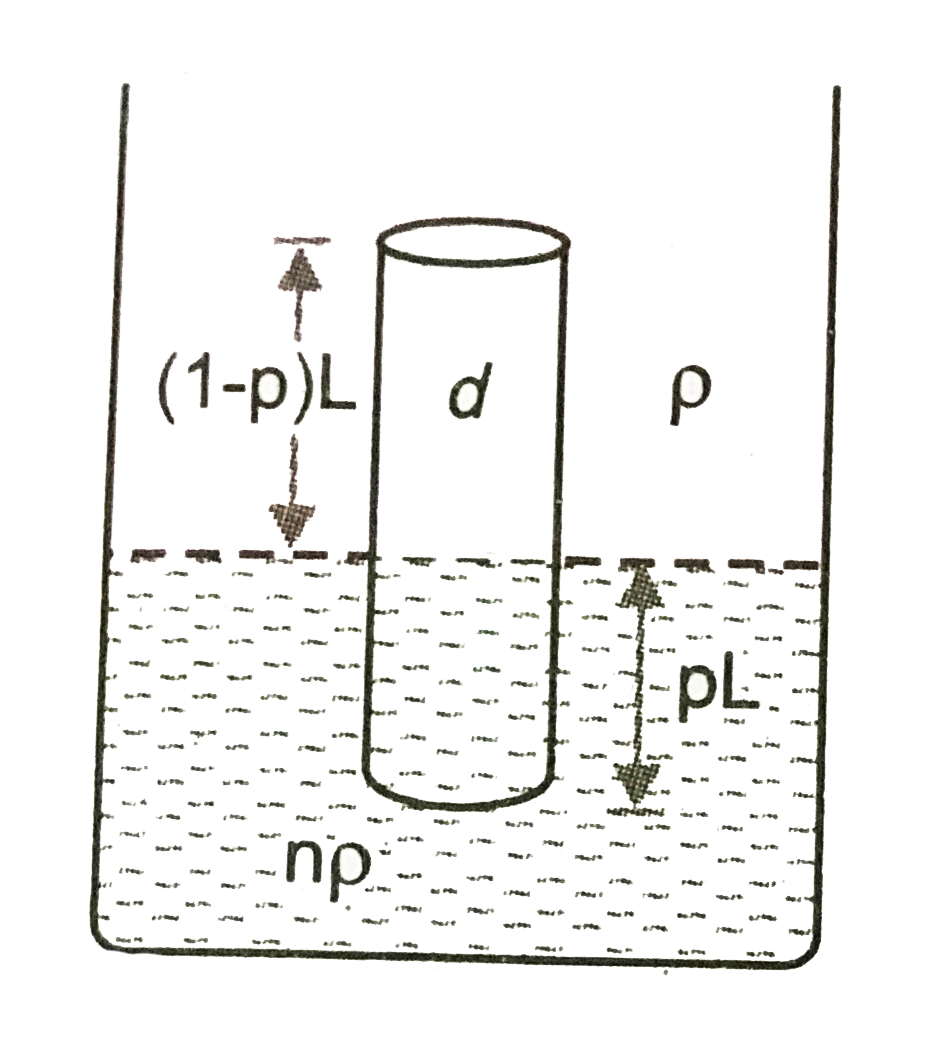
- Two non-mixing liquids of densities rho and (n gt1) are put in a cont...
Text Solution
|
- Pressure inside two soap bubbles are 1.01 and 1.02 atmospheres. Ratio ...
Text Solution
|
- A capillary tube of radius r is immersed in a liquid. The liquid rises...
Text Solution
|
- The work done in increasing the size of a soap film from 10cmxx6cm to ...
Text Solution
|
- Work done in increasing the size of a soap bubble from a radius of 3cm...
Text Solution
|
- Two small drop of mercury, each of radius R coalesce in from a simple ...
Text Solution
|
- Work W is required to form a bubble of volume V from a given solution....
Text Solution
|
- A particle is placed at the origin and a force F=Kx is acting on it (w...
Text Solution
|
- The potential energy function for the force between two atoms in a dia...
Text Solution
|
- A certain number of spherical drops of a liquid of radius r coalesce t...
Text Solution
|
- Assume that a drop of liquid evaporates by decreases in its surface en...
Text Solution
|
- On heating water, bubbles being formed at the bottom of the vessel det...
Text Solution
|
- Under isothermal condition two soap bubbles of radii r(1) and r(2) coa...
Text Solution
|
- The lower end of a capillary tube is dipped in water. Water rises to a...
Text Solution
|
- The lower end of a capillary tube of radius r is placed vertically in ...
Text Solution
|
- A capillary tube of radius r is immersed in water and water rises in t...
Text Solution
|
- A glass capillary tube is of the shape of a truncated cone with an ape...
Text Solution
|
- Water rises to height h in capillary tube. If the length of capillary ...
Text Solution
|