Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
THERMODYNAMICS
PRADEEP|Exercise Multiple choice questions (NCERT)|10 VideosTHERMODYNAMICS
PRADEEP|Exercise Multiple choice questions.|96 VideosTHERMODYNAMICS
PRADEEP|Exercise Multiple choice questions|18 VideosSYSTEMS OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION
PRADEEP|Exercise Assertion- Reason Type questions|20 VideosWORK, ENERGY AND POWER
PRADEEP|Exercise Assertion-Reason Type Questions|24 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
PRADEEP-THERMODYNAMICS-Problems for practice
- A sample of gas (gamma = 1.5) is taken through an adiabatic process in...
Text Solution
|
- 200 cm^(3) of a gas is compressed to 100cm^(3) at atmospheric pressure...
Text Solution
|
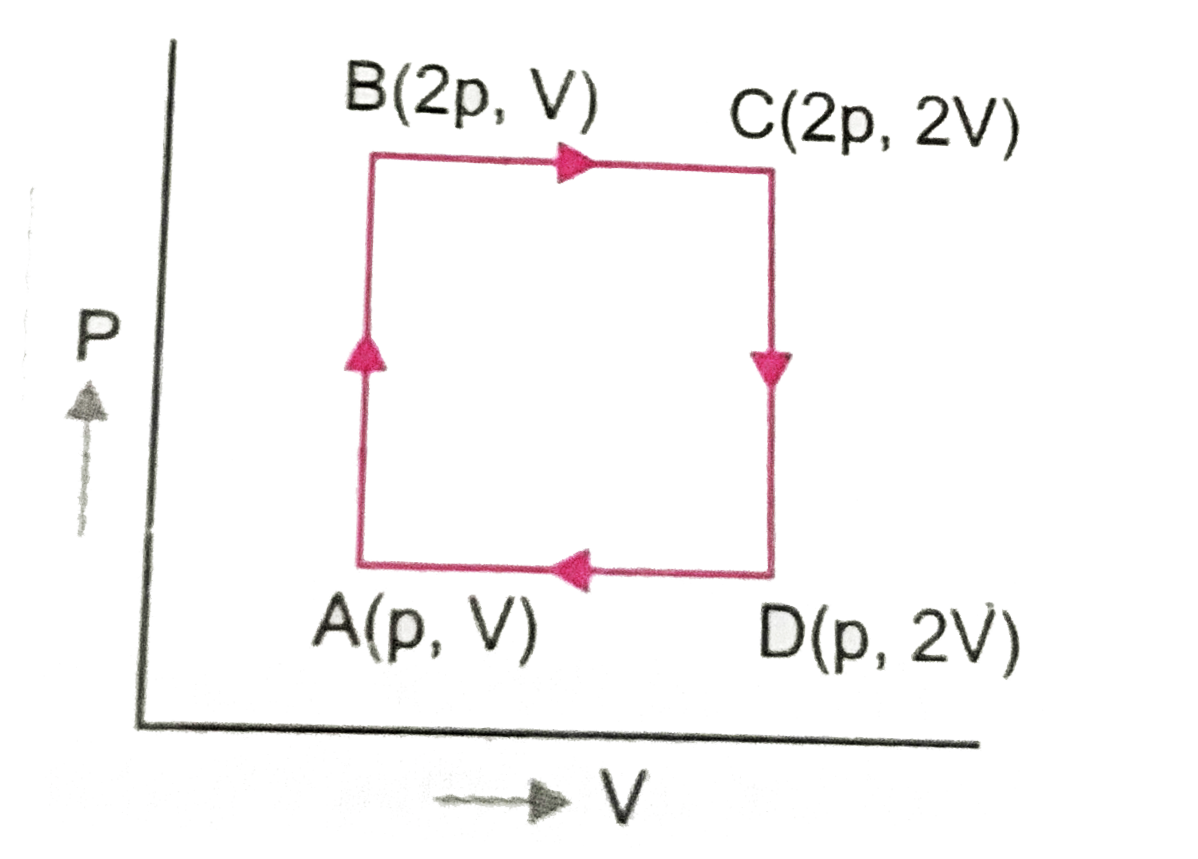
- An ideal monoatomic gas is taken around the cycle ABCDA, wher co-ordin...
Text Solution
|
- A quantity of air at 27^(@)C and atmospheric pressure is suddenly comp...
Text Solution
|
- A cyclinder containing one gram mole of a gas was put on boiling water...
Text Solution
|
- One gram mole of an ideal gas at N.T.P is first expanded isothermally ...
Text Solution
|
- A tyre pumped to a pressure of 6 atmosphere bursts suddenly. Calculate...
Text Solution
|
- Find the final value of a gram molecule of a gas after an isothermal e...
Text Solution
|
- A quantity of air at normal temperature is compressed (a) slowly (b) s...
Text Solution
|
- Two different adiabatic curves for the same gas intersect two isotherm...
Text Solution
|
- If at 50^(@)C and 75 cm of mercury pressure, a definite mass of gas is...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal monoatomic gas is taken around the cycle ABCDA, wher co-ordin...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate net work done by the gas whose thermodynamical behaviour is ...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of an ideal gas is heated from 273K to 546K at constant press...
Text Solution
|
- Three moles of an ideal gas at 127^(@)C expands isothermally untill th...
Text Solution
|
- A volume of 10m^(3) of a liquid is supplied with 100 kal of heat and e...
Text Solution
|
- At 0^(@)C and normal atmospheric pressure, the volume of 1 gram of wat...
Text Solution
|
- A sample of ideal gas (gamma = 1.4) is heated at constant pressure. If...
Text Solution
|
- One kg of water at 373K is converted into steam at the same temperatur...
Text Solution
|
- When a gas is taken from one state a to another state b via one path, ...
Text Solution
|