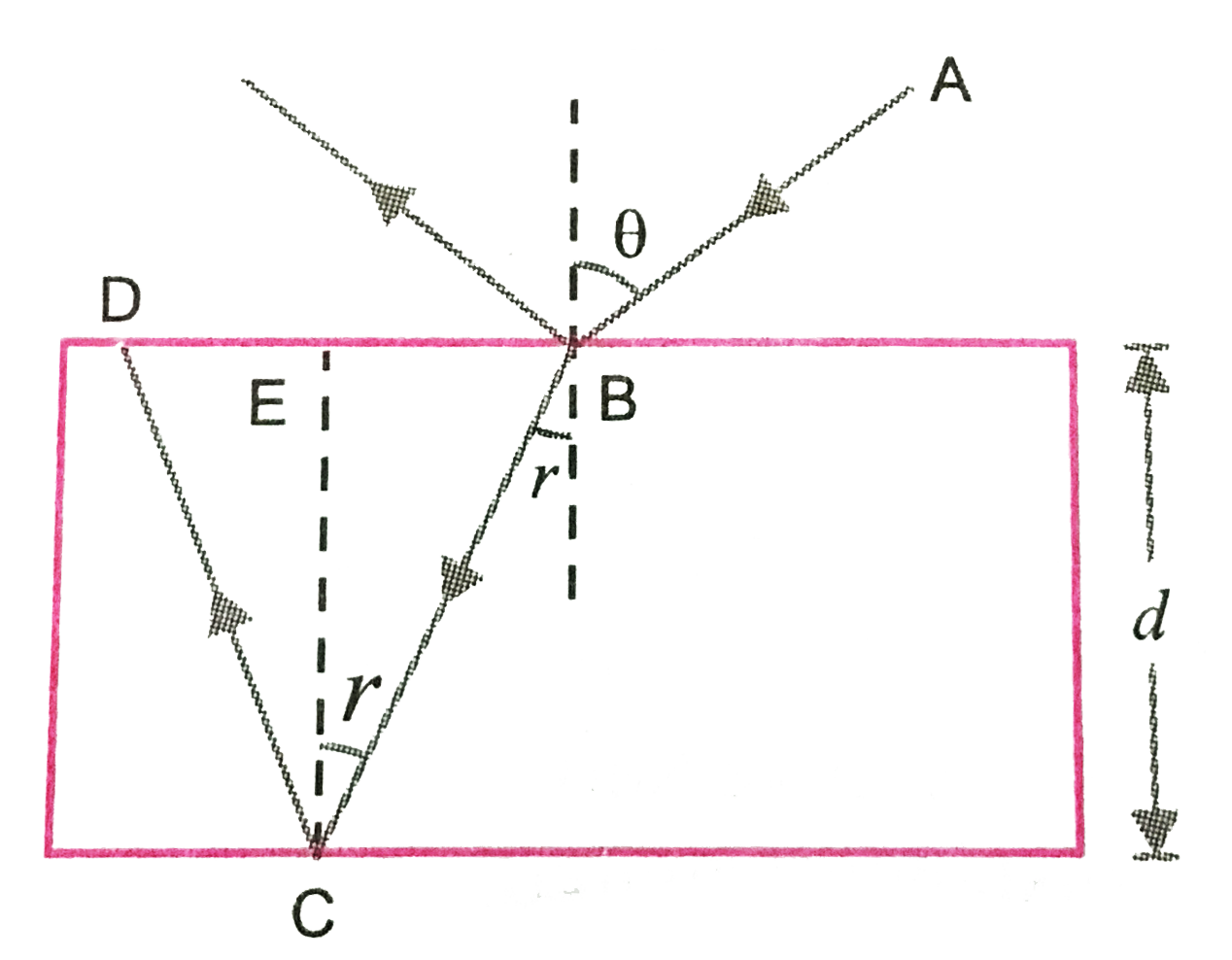
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
PRADEEP-OPTICS-Exercise
- Consider a light beam incident from air to a glass slab at Brewster's ...
Text Solution
|
- Consider sunlight incident on a slit of width 10^(4) Å . The image see...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a ray of light incident from air onto a slab of glass (refrac...
Text Solution
|
- In a Young's double slit experiment, the source is white light. One of...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a standard two slit arrangement with slits S(1), S(2). P(...
Text Solution
|
- Two source S(1) and S(2) of intensity I(1) and I(2) are placed in fron...
Text Solution
|
- Consider sunlight incident on a pinhole of width 10^(3)Å. The image of...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the diffraction pattern for a small pinhole. As the size of t...
Text Solution
|
- For light diverging from a point source
Text Solution
|
- A source of light lies on the angle bisector of two plane mirrors incl...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light travelling in the direction (1)/(2)(hat(i)+sqrt(3)hat(j...
Text Solution
|
- The ratio of the speed of an object to the speed of its real image of ...
Text Solution
|
- The graph in Fig. shows plot of variation of v with change in u for a ...
Text Solution
|
- A beam of light from a source L is incident normally on a plane mirror...
Text Solution
|
- In a concave mirror, an object is placed at a distance d1 from the foc...
Text Solution
|
- A short linear object of length b lies along the axis of a concave mir...
Text Solution
|
- A car is fitted with a convex side-view mirror of focal length 20 cm. ...
Text Solution
|
- A rod of length 10 cm lies along the principal axis of a concave mirro...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a concave mirror and a convex lens (refractive index 1.5) of ...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical glass rods S(1) and S(2) (refractive index=1.5) have one...
Text Solution
|