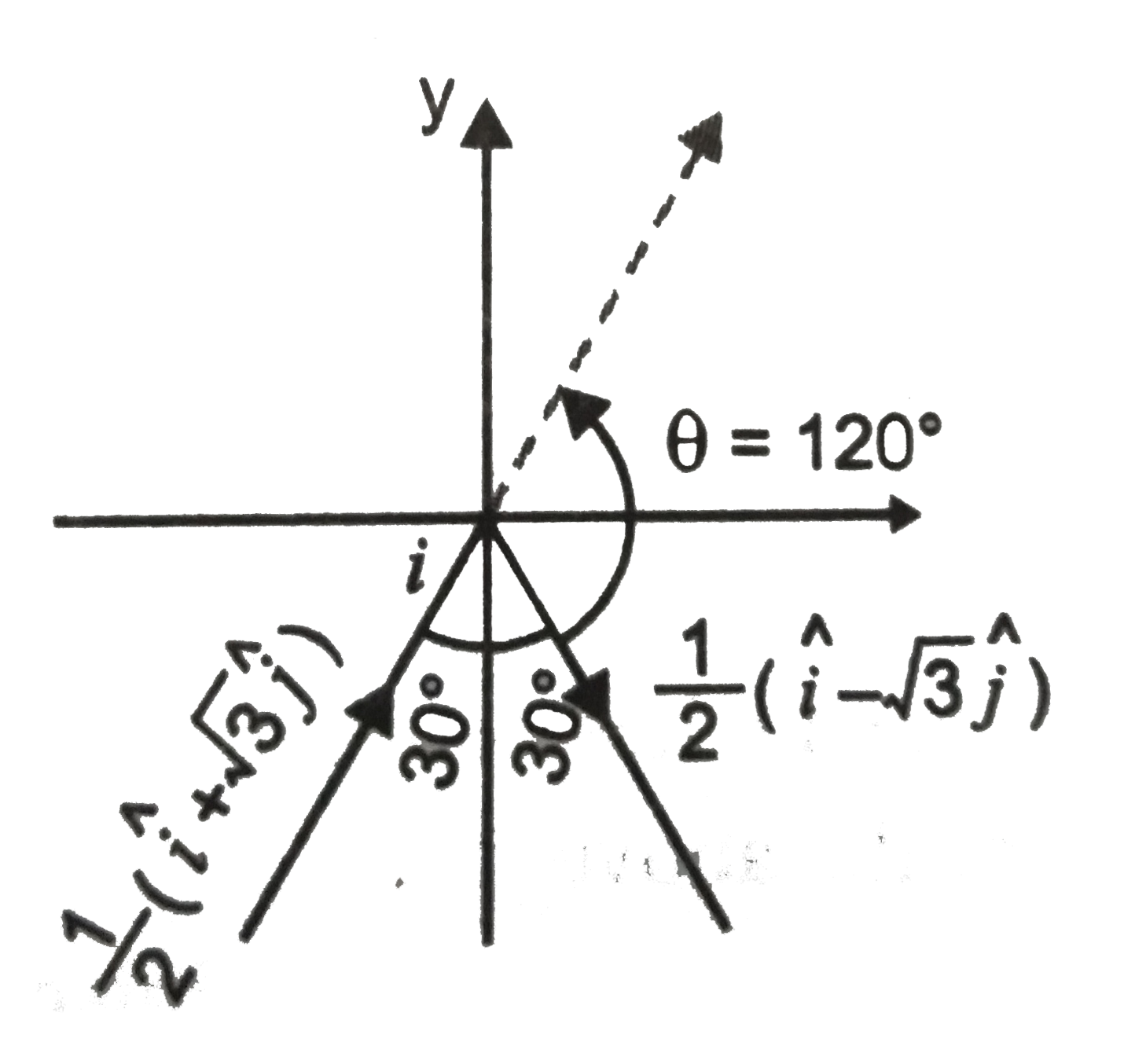A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
PRADEEP-OPTICS-Exercise
- For light diverging from a point source
Text Solution
|
- A source of light lies on the angle bisector of two plane mirrors incl...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light travelling in the direction (1)/(2)(hat(i)+sqrt(3)hat(j...
Text Solution
|
- The ratio of the speed of an object to the speed of its real image of ...
Text Solution
|
- The graph in Fig. shows plot of variation of v with change in u for a ...
Text Solution
|
- A beam of light from a source L is incident normally on a plane mirror...
Text Solution
|
- In a concave mirror, an object is placed at a distance d1 from the foc...
Text Solution
|
- A short linear object of length b lies along the axis of a concave mir...
Text Solution
|
- A car is fitted with a convex side-view mirror of focal length 20 cm. ...
Text Solution
|
- A rod of length 10 cm lies along the principal axis of a concave mirro...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a concave mirror and a convex lens (refractive index 1.5) of ...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical glass rods S(1) and S(2) (refractive index=1.5) have one...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical thin planoconvex glass lenses (refractive index 1.5) eac...
Text Solution
|
- A diverging lens with magnitude of focal length 25 cm is placed at a d...
Text Solution
|
- An observer can see through a pin-hole the top end of a thin rod of he...
Text Solution
|
- For a given incident ray as shown in Fig., the condition of total inte...
Text Solution
|
- Considering normal incidence of ray, the equivalent refractive index o...
Text Solution
|
- The graph in Fig. shows how the inverse of magnification 1//m produced...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the ray diagram for the refraction given Fig. The maximum va...
Text Solution
|
- A luminous object is placed at a distance of 30 cm from the convex len...
Text Solution
|