Expression for E due to a charged conducting spherical shell :
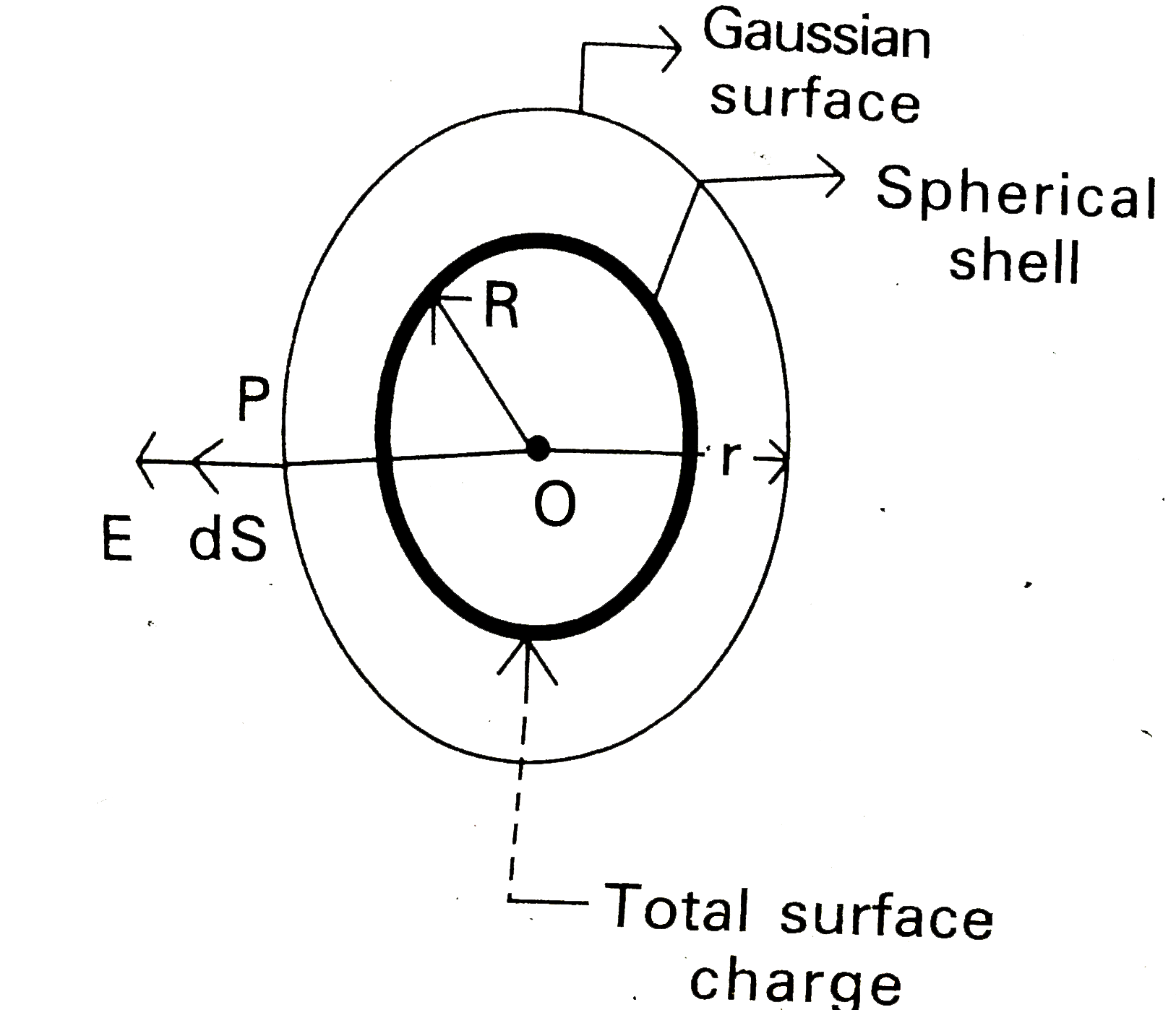
(1) Consider a uniformly charged spherical shell. Let total charge on it is 'q' and its radius is R.
Surface charge density `sigma =("Total charge")/("Surface area")=q/(4pi R^(2))` ...(1)
(2) Since the shell is uniformly charged, the intensity of electric field at any point depends on radial distance 'r' from centre 'O'. The direction of E is aways from the centre along the radius.
(i) E at a point outside the shell :
(1) Consider a point at a distance 'r' outside the sphere. Construct a Gaussian surface with 'r' as radius (where `r gt R`).
(2) Total flux coming out of this sphere is `phi=underset(oint)vec(E).d vec(s)=E oint ds=q/epsi_(0)`.
But `underset(S)(oint)dS=` Area of sphere `=4pi r^(2)`
`:. E.4pi r^(2)=q/epsi_(0)`
But `q=4pi R^(2) sigma` (from equation 1)
`:. E=1/(4pi r^(2) (4pi R^(2) sigma)/epsi_(0)`
(3) Therefore at any point outside the sphere, `E=sigma/epsi_(0) R^(2)/r^(2)`
(ii) E at a point on the surface of shell :
(1) Construct a Gaussian surface with radius `r=R`.
(2) Total flux through this sphere `phi=oint vec(E). d vec(S)=E underset(S)(oint) dS=q/epsi_(0)`.
But `oint dS` of sphere `=4pi R^(2)` and `q=4pi R^(2) sigma`
`implies E.4pi R^(2) =(4pi R^(2) sigma)/epsi_(0)=(4pi R^(2) sigma)/epsi_(0) implies E=sigma/epsi_(0)`
(3) Therefore intensity at any point on surface of the sphere `E=sigma/epsi_(0)`

(iii) E at a point inside the shell :
(1) Consider a point P inside the shell. Construct a Gaussian surface with radius r (where `r lt R`). There is no charge inside the shell. So form Gauss's law `underset(S)(oint) vec(E).dvec(S)=q/epsi_(0)`.
But `q=0implies underset(S)(oint)vec(E).dvec(S)=E.4pi r^(2)=0`.
(2) Therefore, intensity of electric field at any point inside a charged shell is zero.

