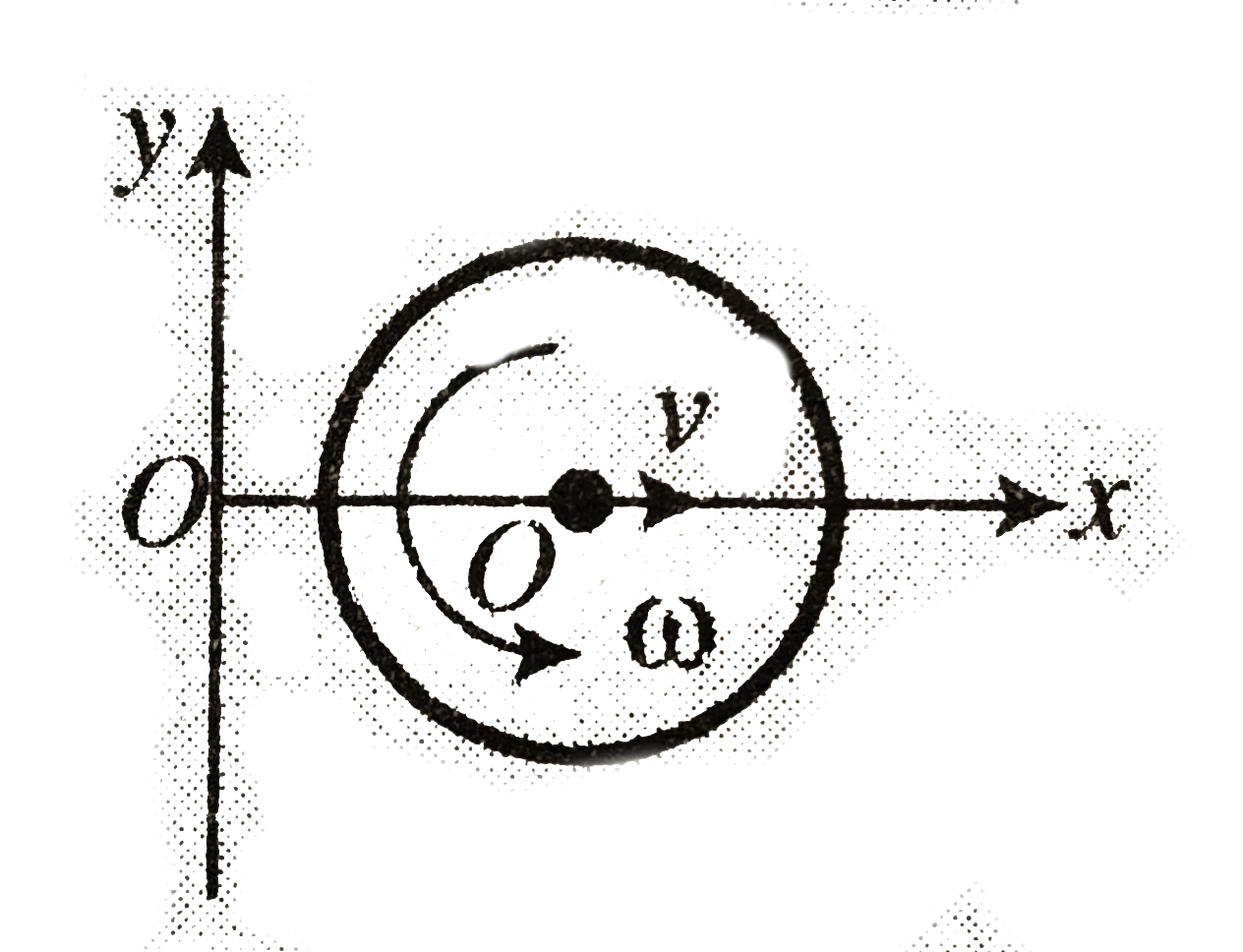Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
PHYSICAL FUNDAMENTALS OF MECHANICS
IE IRODOV, LA SENA & SS KROTOV|Exercise The Fundamental Equation Of Dynamics|59 VideosPHYSICAL FUNDAMENTALS OF MECHANICS
IE IRODOV, LA SENA & SS KROTOV|Exercise Laws Of Conservation Of Energy, Momentum And Angular Momentum|82 VideosOSCILLATIONS AND WAVES
IE IRODOV, LA SENA & SS KROTOV|Exercise Electromagnetic Waves, Radiation|36 VideosTHERMODYNAMICS AND MOLECULAR PHYSICS
IE IRODOV, LA SENA & SS KROTOV|Exercise Transport Phenomena|38 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
IE IRODOV, LA SENA & SS KROTOV-PHYSICAL FUNDAMENTALS OF MECHANICS-Relativistic Mechanics
- A rotating disc moves in the positive direction of x-axis as shown. Fi...
Text Solution
|
- A rod moves lengthwise with a constant velocity v relative to the iner...
Text Solution
|
- In a traingle the proper length of each side equals a. Find the perime...
Text Solution
|
- Find the proper length of a rod if in the laboratory frame of referenc...
Text Solution
|
- A stationary upright cone has a taper angle theta=45^@, and the area o...
Text Solution
|
- With what velocity (relative to the reference frame K) did the clock m...
Text Solution
|
- A rod flies with constant velocity past a mark which is stationary in ...
Text Solution
|
- The proper lifetime of an unstable particle is equal to Deltat0=10ns. ...
Text Solution
|
- In the reference frame K a muon moving with a velocity v=0.990c travel...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles moving in a laboratory frame of reference along the same...
Text Solution
|
- A rod moves along a ruler with a constant velocity. When the positions...
Text Solution
|
- Two rods of the same proper length l0 move toward each other parallel ...
Text Solution
|
- Two unstable particles move in the reference frame K along a straight ...
Text Solution
|
- A rod AB oriented along the x axis of the reference frame K moves in t...
Text Solution
|
- The rod A^'B^' moves with a constant velocity v relative to the rod AB...
Text Solution
|
- There are two groups of mutually synchronized clocks K and K^' moving ...
Text Solution
|
- The reference frame K^' moves in the positive direction of the x axis ...
Text Solution
|
- At two points of the reference frame K two events occurred separated b...
Text Solution
|
- The space-time diagram, shows three events A, B, and C which occurred ...
Text Solution
|
- The velocity components of a particle moving in the xy plane of the re...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles move toward each other with velocities v1=0.50c and v2=0...
Text Solution
|