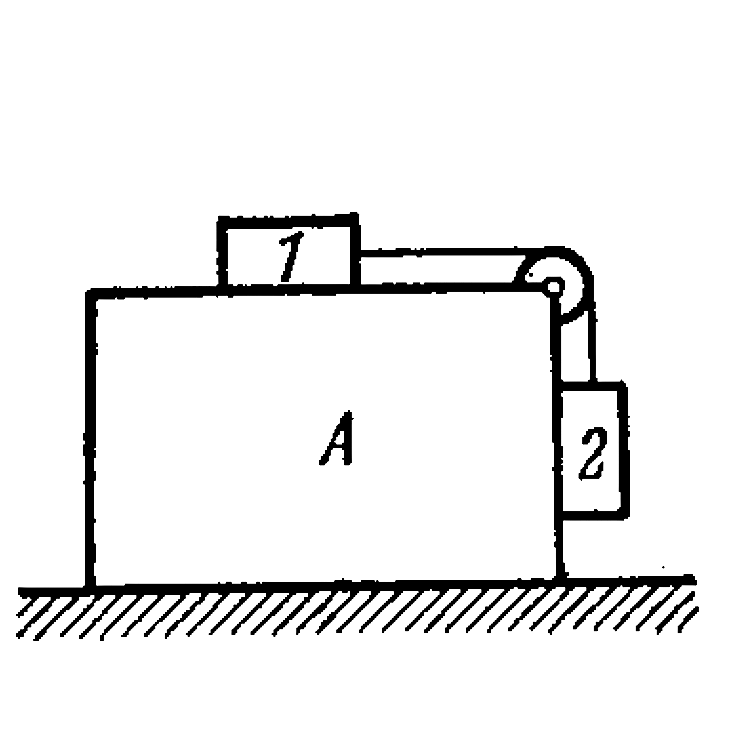
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
PHYSICAL FUNDAMENTALS OF MECHANICS
IE IRODOV, LA SENA & SS KROTOV|Exercise Laws Of Conservation Of Energy, Momentum And Angular Momentum|82 VideosPHYSICAL FUNDAMENTALS OF MECHANICS
IE IRODOV, LA SENA & SS KROTOV|Exercise Universal Gravitation|34 VideosPHYSICAL FUNDAMENTALS OF MECHANICS
IE IRODOV, LA SENA & SS KROTOV|Exercise Relativistic Mechanics|49 VideosOSCILLATIONS AND WAVES
IE IRODOV, LA SENA & SS KROTOV|Exercise Electromagnetic Waves, Radiation|36 VideosTHERMODYNAMICS AND MOLECULAR PHYSICS
IE IRODOV, LA SENA & SS KROTOV|Exercise Transport Phenomena|38 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
IE IRODOV, LA SENA & SS KROTOV-PHYSICAL FUNDAMENTALS OF MECHANICS-The Fundamental Equation Of Dynamics
- Find the accelerations of rod A and wedge B in the arrangement shown i...
Text Solution
|
- In the arrangement shown in figure the masses of the wedge M and the b...
Text Solution
|
- What is the minimum acceleration with which bar A (figure) should be s...
Text Solution
|
- Prism 1 with bar 2 of mass m placed on it gets a horizontal accelerati...
Text Solution
|
- Prism 1 of mass m1 and width angle alpha (see figure) rests on a horiz...
Text Solution
|
- In the arrangement shown in figure the masses m of the bar and M of th...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m moves along a circle of radius R. Find the modulu...
Text Solution
|
- An aircraft loops the loop of radius R=500m with a constant velocity v...
Text Solution
|
- A small sphere of mass m suspended by a thread is first taken aside so...
Text Solution
|
- A ball suspended by a thread swings in a vertical plane so that its ac...
Text Solution
|
- A small body A starts sliding off the top of a smooth sphere of radius...
Text Solution
|
- A device (figure) consists of a smooth L-shaped rod located in a horiz...
Text Solution
|
- A cyclist rides along the circumference of a circular horizontal plane...
Text Solution
|
- A car moves with a constant tangential acceleration wtau=0.62m//s^2 al...
Text Solution
|
- A car moves uniformly along a horizontal since curvey = a sin (x//alph...
Text Solution
|
- A chain of mass m forming a circle of radius R is slipped on a s...
Text Solution
|
- A fixed pulley carries a weightless thread with masses m(1) and m(2) a...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m moves along the internal smooth surface of a vert...
Text Solution
|
- Find the magnitude and direction of the force acting on the particle o...
Text Solution
|
- A body of mass m is thrown at an angle to the horizontal with the init...
Text Solution
|