Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
OSCILLATIONS AND WAVES
IE IRODOV, LA SENA & SS KROTOV|Exercise Elastic Waves|39 VideosOSCILLATIONS AND WAVES
IE IRODOV, LA SENA & SS KROTOV|Exercise Electromagnetic Waves, Radiation|36 VideosOSCILLATIONS AND WAVES
IE IRODOV, LA SENA & SS KROTOV|Exercise Electromagnetic Waves, Radiation|36 VideosOPTICS
IE IRODOV, LA SENA & SS KROTOV|Exercise Exercise|2 VideosPHYSICAL FUNDAMENTALS OF MECHANICS
IE IRODOV, LA SENA & SS KROTOV|Exercise Relativistic Mechanics|49 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
IE IRODOV, LA SENA & SS KROTOV-OSCILLATIONS AND WAVES-Electric Oscillations
- An oscillating circuit consisting of a coil and a capacitor connected ...
Text Solution
|
- A series circuit consisting of a capacitor and a coil with active res...
Text Solution
|
- Demonstrate thatat low damping the quality factor Q of a circuit maint...
Text Solution
|
- A circuit consisting of a capacitor and a coil connected in seried if ...
Text Solution
|
- It takes t(0) hours for a direct current I(0) to charge a storage batt...
Text Solution
|
- Find the effective value of current if its mean value is I(0) and its ...
Text Solution
|
- A solenoid with inductance L=7 m H and active resistance R=44 Omega is...
Text Solution
|
- A coil with inductive resistance X(L)=30 Omega and impedance Z=50 Omeg...
Text Solution
|
- A coil with inductance L=0.70 H and active resistance r=20 Omega is co...
Text Solution
|
- A circuit consisting of a capacitor and a coil in series is connected ...
Text Solution
|
- A source of sinusoidal emf with constant voltage is connected in serie...
Text Solution
|
- A series circuit consisting of an inductance - free resistance R=0.16 ...
Text Solution
|
- A coil and an inductance - free resistance R=25 Omega are connected i...
Text Solution
|
- An alternating current of frequency omega=314s^(-1) is fed to a circui...
Text Solution
|
- Draw the approcimate vector diagrams of currents in the circuits shown...
Text Solution
|
- A capacitor with capacitance C=1.0 muF and a coil with active resitan...
Text Solution
|
- A capacitor with capacitance C and a coil with active resistance R and...
Text Solution
|
- A circuit consists of a capacitor with capacitance C and a coil with a...
Text Solution
|
- A ring of thin wire with active resistance R and inductance L rotates ...
Text Solution
|
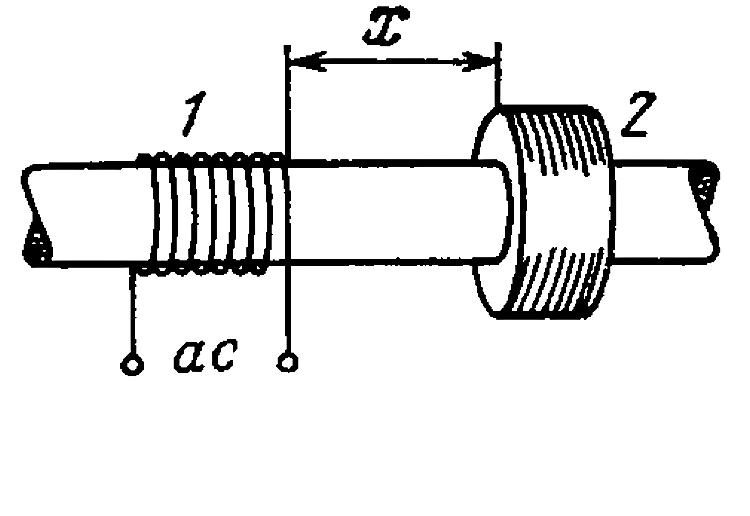
- A wooden core ( figure ) supports two coils : coil 1 with inductance ...
Text Solution
|