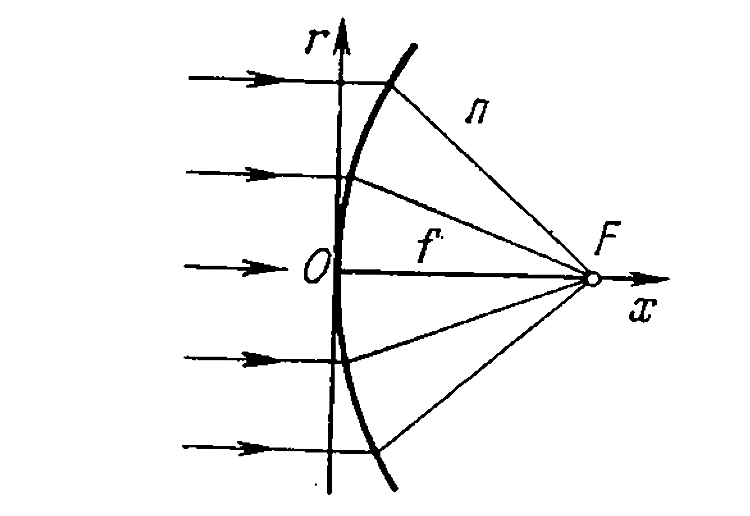
All rays focusing at a point must have traversed the same optical path. Thus

`x + n sqrt(r^(2) + (f - x)^(2)) = nf` or `(nf - x)^(2) = n^(2) r^(2) + n^(2) (f - x)^(2)`
or, `n^(2)r^(2) = (nf - x)^(2) -[n(f - x)]^(2) = (nf - x + nf -nx) (nf - x - nf + nx)`
`= x(n - 1) (2n f - (n + 1)x)`
`= 2n (n -1) fx - (n + 1) (n - 1)x^(2)`
Thus, `(n + 1) (n - 1)x^(2) - 2n (n - 1) fx + n^(2) r^(2) = 0`
so, `x = (n(n - 1)f+-sqrt(n^(2)(n -1)^(2) f^(2) - n^(2) (n + 1) (n - 1)))/((n + 1) (n - 1))`
`= (nf)/(n + 1) 1+= sqrt(1 -(n + 1)/(n - 1)(r^(2))/(f^(2)))`
Ray must move forward so `x lt f`, for `+` sing `x gt f` fro small `r`, so -sign
(Also `x rarr 0` as `r rarr 0`)
`(x gt f` means ray turning back in the direction of incidence. (see Fig.)
Hence `x = (nf)/(n + 1) [1-sqrt(1 -(n + 1)/(n - 1)(r^(2))/(f^(2)))]`
For the maximum value of `r`,
`sqrt(1 -(n + 1)/(n - 1)(r^(2))/(f^(2))) = 0` (A)
beacuse the expression under the radical sign must be non-negative, which gives the maximum value of `r`.
Hence from Eqn .(A), `r_(max) = f sqrt((n - 1)//(n + 1))`