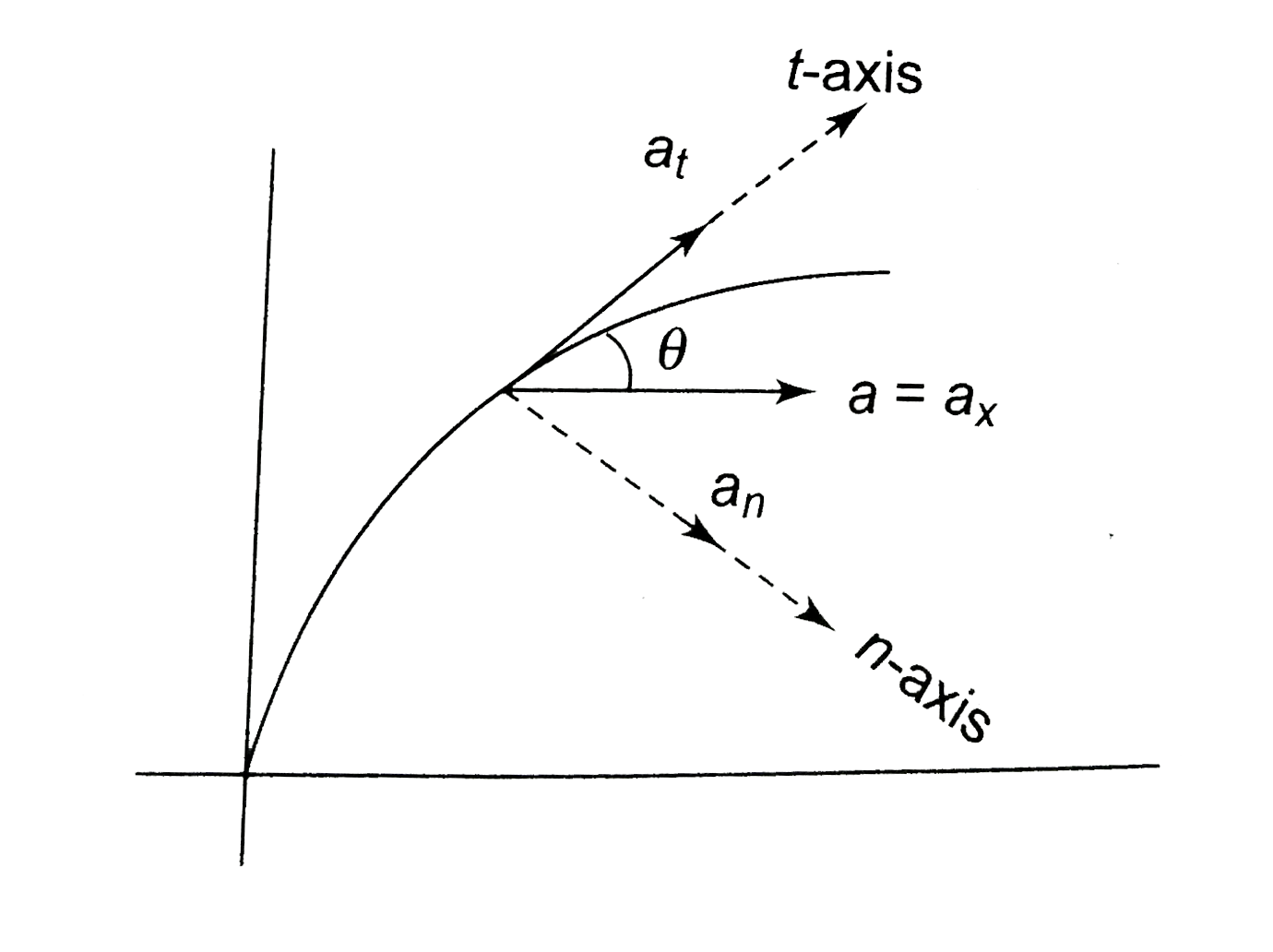
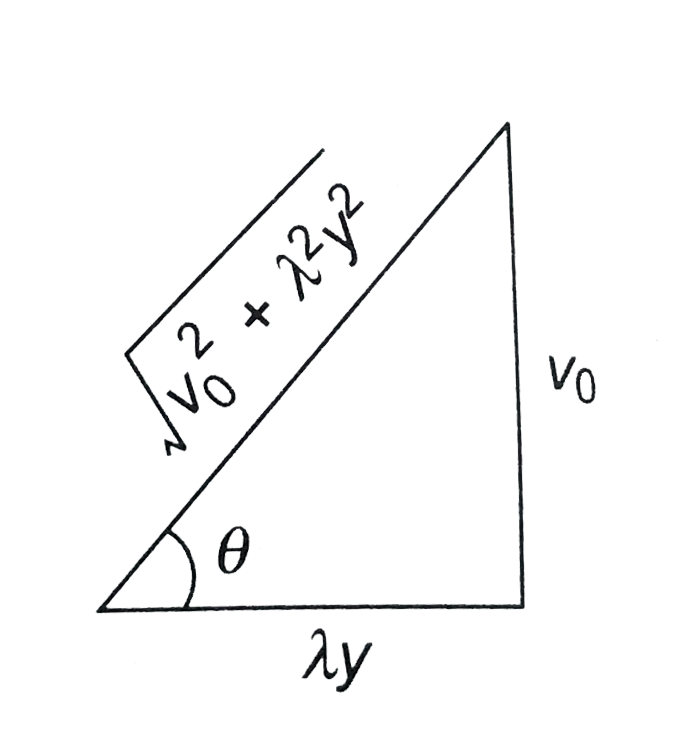
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CP SINGH-CIRCULAR MOTION-Exercise
- A balloon starts rising from the surface of the earth with a verticle ...
Text Solution
|
- A particle revolves round a circular path with a constant speed. (i...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m moves in a circle of radius R with a uniform spee...
Text Solution
|
- A particle moves in a circle of radius 5 cm with constant speed and ti...
Text Solution
|
- A body is whirled in a horizontal circle of radius 20cm. It has an an...
Text Solution
|
- A particle moves in a circular orbit under the action of a central att...
Text Solution
|
- If a body moves with a constant speed in a circle
Text Solution
|
- A car runs at a constant speed on a circular track of radius 100m, tak...
Text Solution
|
- The second's hand of a watch has length 3cm. The speed of the end poin...
Text Solution
|
- For a particle in uniform circular motion , the acceleration vec(a) a...
Text Solution
|
- What is the value of linear velocity, if vecomega =hati-hatj+hatk and ...
Text Solution
|
- An object moves at a constant speed along a circular path in a horizon...
Text Solution
|
- An electric fan has blades of length 30 cm as measured from the axis o...
Text Solution
|
- Two bodies of mass 10kg and 5kg moving in concentric orbits of radii R...
Text Solution
|
- Two cars of mass m(1) and m(2) are moving in circle of radii r(1) an...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is kept fixed on as turntable rotating uniformly. As seen f...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is acted upon by a force of constant magnitude which is alw...
Text Solution
|
- The position vector of a particle in a circular motion about the origi...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following quantities may remain constant during the motio...
Text Solution
|
- When a body is acclerated : (i) its velocity always changes (ii) its s...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following statements is FALSE for a paricle moving in a...
Text Solution
|