A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CP SINGH-KINETIC THEORY OF GASES-Exercises
- Consider the quantity (MkT)/(pV) of an ideal gas where M is the mass o...
Text Solution
|
- Two ballons are filled, one with pure He gas and other by air, repecti...
Text Solution
|
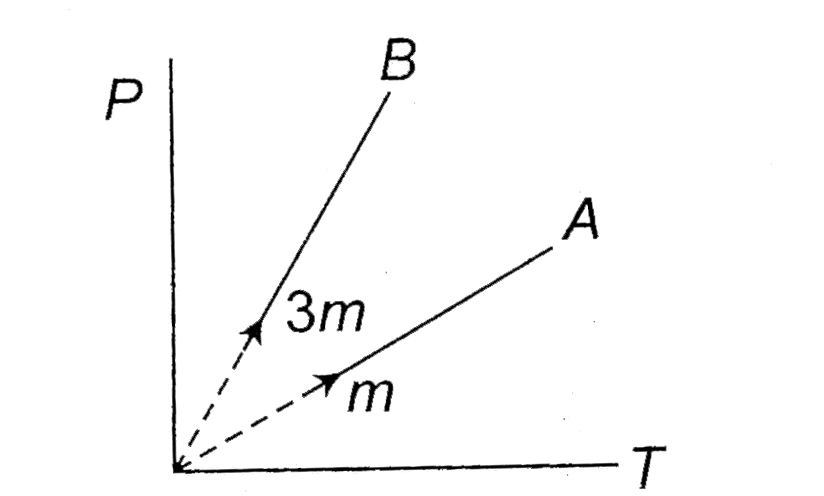
- Two different masses m and 3 m of an ideal gas are heated separately i...
Text Solution
|
- The pressure exterted on the walls of the container by a gas is due to...
Text Solution
|
- At constant volume, temperature is increased. Then
Text Solution
|
- When an ideal gas undergoes an isothermal expansion, the pressure of t...
Text Solution
|
- According to the kinetic theory of gases (i) P prop v(rms) (ii) v(...
Text Solution
|
- The pressure of an ideal gas is written as p=(2E)/(3V).Here E refers t...
Text Solution
|
- Pressure exerted by a perfect gas equal to
Text Solution
|
- At a given temperature, the pressure of an ideal gas of density rho is...
Text Solution
|
- According to the kinetic theory of gases, at absolute temperature
Text Solution
|
- Gas at a pressure P(0) in contained as a vessel. If the masses of all ...
Text Solution
|
- Three containes of the same volume contain three different gases. The ...
Text Solution
|
- Four molecules have speeds 2 m//s, 3 km//s, 4 km//s and 5 km//s. The r...
Text Solution
|
- Speed of sound in a gas is v and rms velocity of the gas molecules is ...
Text Solution
|
- The mean square speed of the molecules of a gas at absolute temperatur...
Text Solution
|
- At room temperature, the rms speed of the molecules of a certain diato...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following gases has maximum rms speed at a given temperat...
Text Solution
|
- The temperature at which the rms speed of air molecules is double of t...
Text Solution
|
- The curve between absolute temperature and v(rms)^(2) is
Text Solution
|