A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CP SINGH-KINETIC THEORY OF GASES-Exercises
- A gas has volume V and pressure p. The total translational kinetic ene...
Text Solution
|
- The average translational energy and the rms speed of molecules in a s...
Text Solution
|
- A polyatomic gas with (n) degress of freedom has a mean energy per mol...
Text Solution
|
- Three perfect gases at absolute temperature T(1), T(2) and T(3) are mi...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a mixture of oxygen and hydrogen kept at room temperature, As...
Text Solution
|
- The temperature of argon, kept in a vessel, is raised by 1^(@)C at a c...
Text Solution
|
- A vessel contains a mixture of one mole of oxygen and two moles of nit...
Text Solution
|
- A gas mixture consists of 2 moles of oxygen and 4 moles of argon at te...
Text Solution
|
- A gas is enclosed in a container which is then placed on a fast moving...
Text Solution
|
- Mean free path of a gas molecule is
Text Solution
|
- If the mean free path of atoms is doubled then the pressure of gas wil...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows two flasks connected to each other. The volume of the fla...
Text Solution
|
- Two containers of equal volume contain the same gas at pressure P(1) a...
Text Solution
|
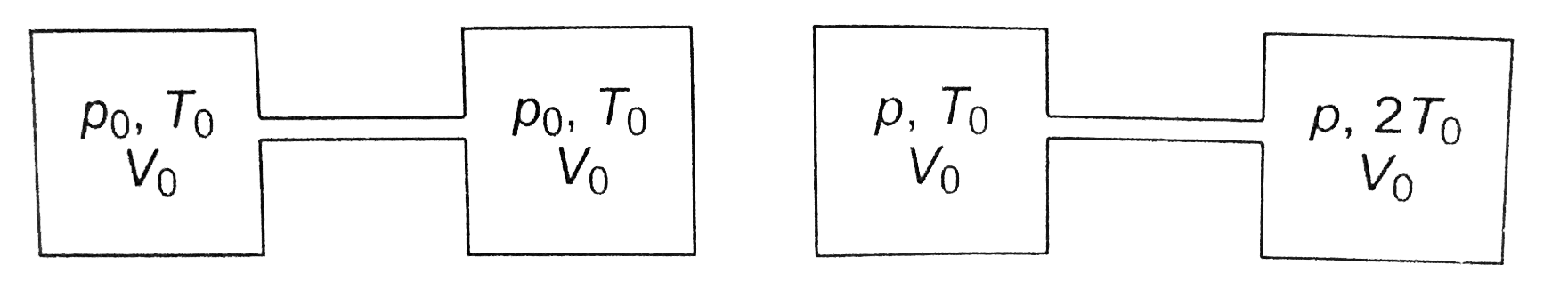
- Two idential container joined by a small pipe initially contain the sa...
Text Solution
|
- In the previous question let V(0) be the volume of each container. All...
Text Solution
|
- The temperature at the bottom of a 40 cm deep lake is 12^(@)C and that...
Text Solution
|
- An air bubble doubles in radius on string from the bottom of a lake to...
Text Solution
|
- When an air bubble of radius 'r' rises from the bottom to the surface ...
Text Solution
|
- If pressure of CO(2) (real gas ) in a container is given by P = (RT)/...
Text Solution
|
- The equation of state of gas is given (P + (aT^(2))/(V))V^( c) = (RT +...
Text Solution
|