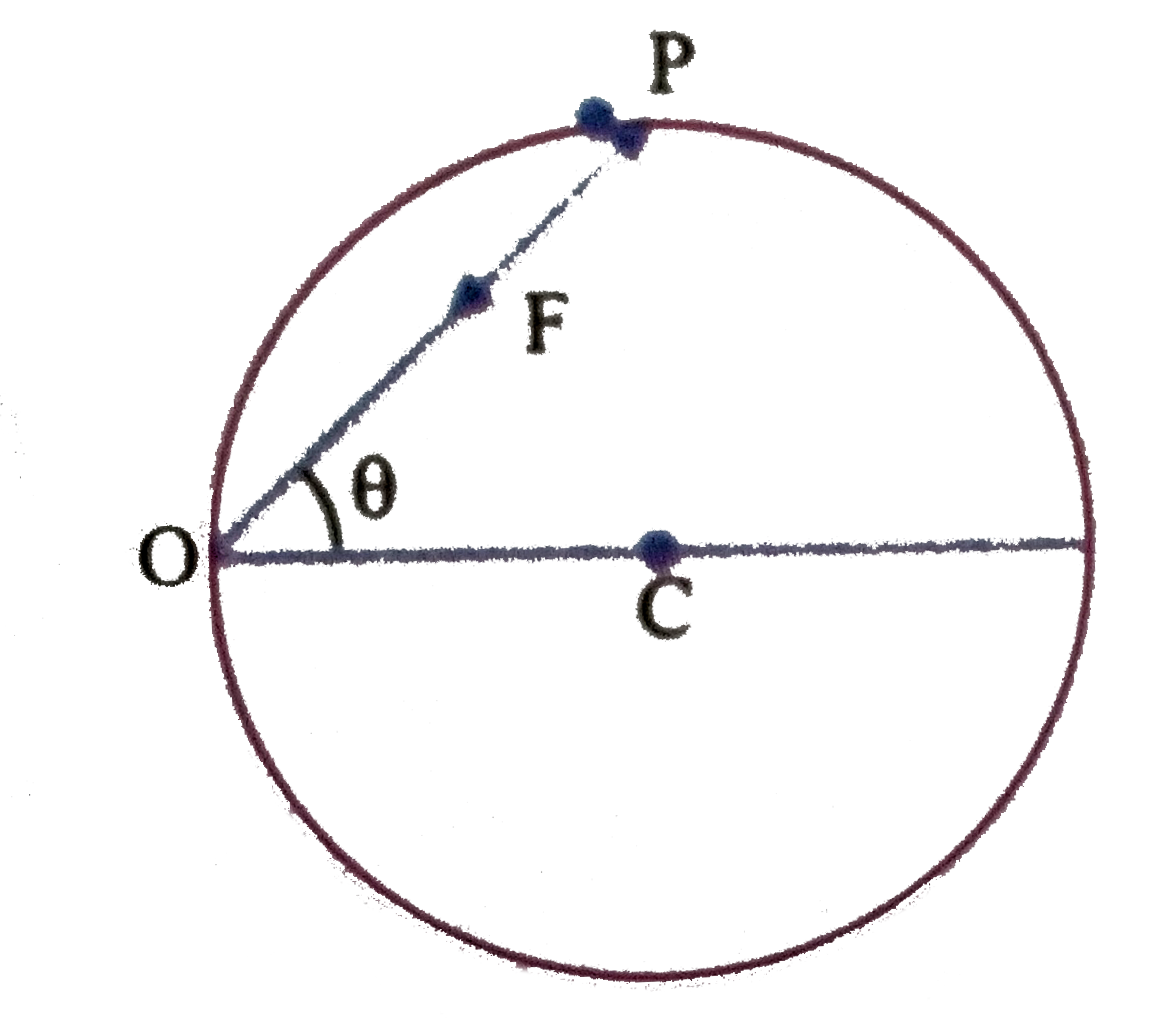
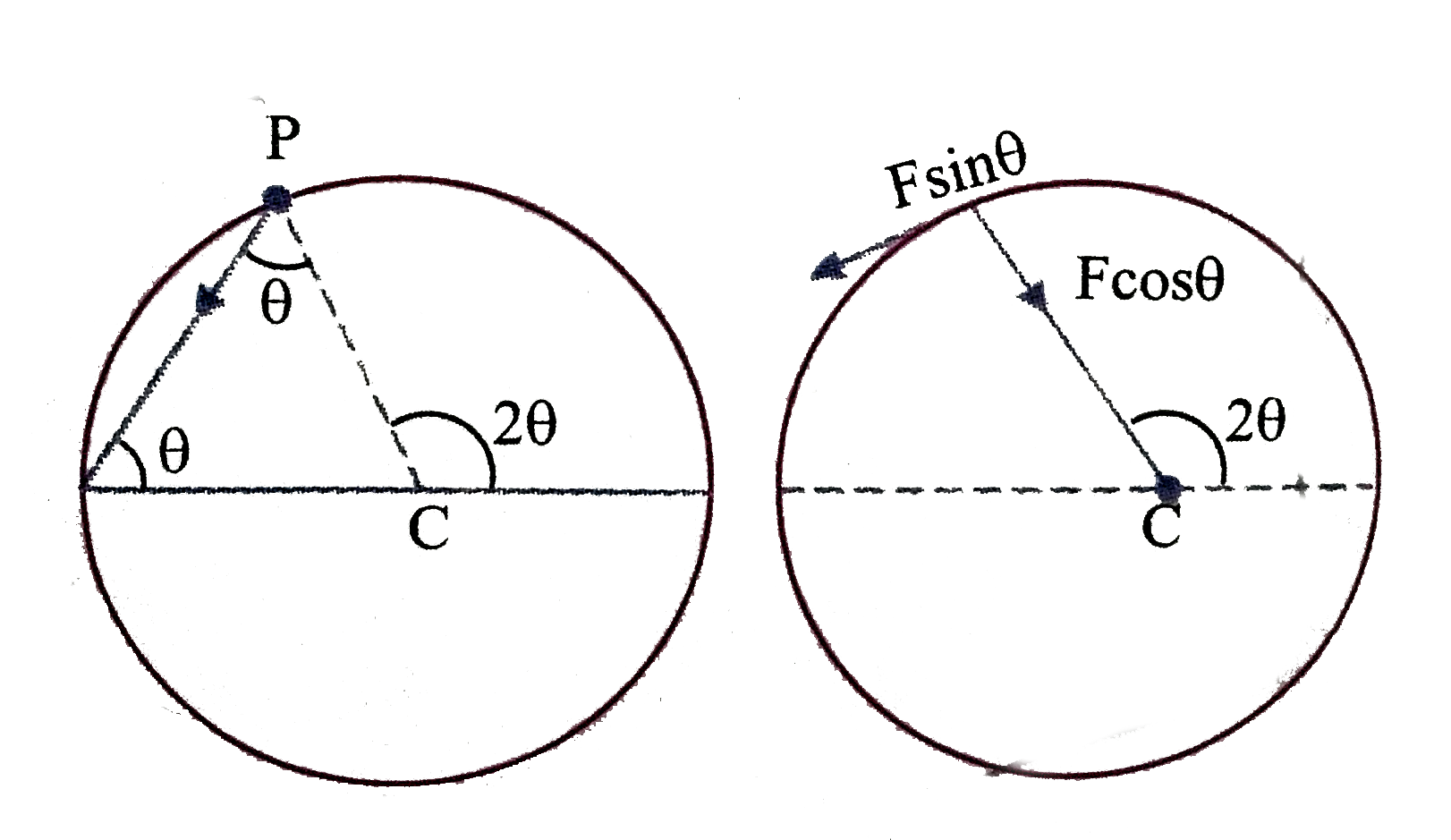
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NARAYNA-CIRCULAR MOTION-IIT QUES.
- A car is moving in a circular horizonta track of radius 10m with a con...
Text Solution
|
- A long horizontal rod has a bead which can slide along its length and ...
Text Solution
|
- A piece of wire is bent in the shape of a parabola y = Kx^(2) (y - axi...
Text Solution
|
- A particle 'P' is moving on a circular under the action of only one fo...
Text Solution
|