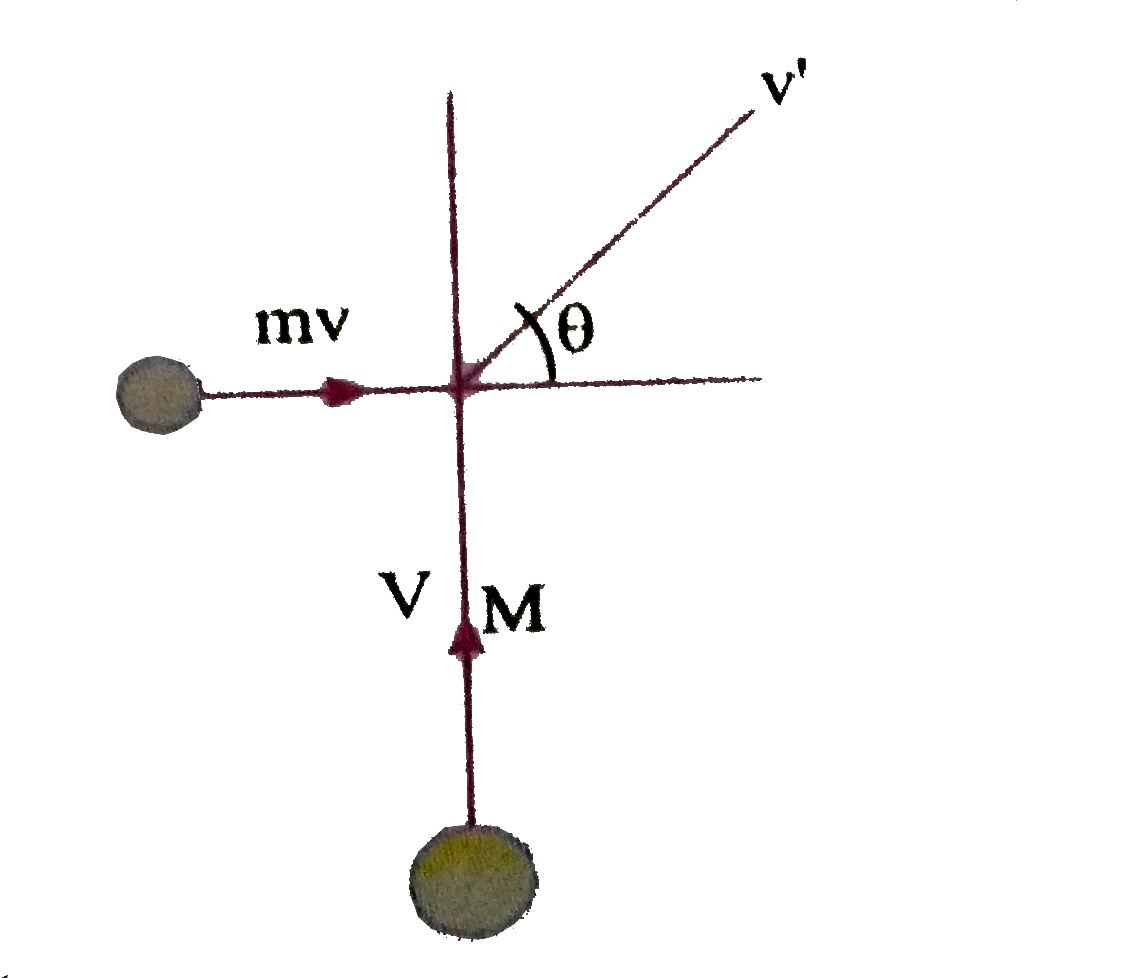
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NARAYNA-COLLISION-Multiple Answer
- Two point masses are connected by a light intextensible string are lyi...
Text Solution
|
- A body moving towards a finite body at rest collides with it. It is po...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass m(1), collides elastically and head on with ball of mas...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks A and B, each of mass m, are connected by a masslesss sprin...
Text Solution
|
- The balls, having linear momenta vecp1=vecpi and vecp22=-vecpi, underg...
Text Solution
|
- If the resultant of all the external forces acting on a system of part...
Text Solution
|
- A pendulum bob of mass m connected to the end of material string of le...
Text Solution
|
- Two equal spheres of mass m are in contact on a smooth horizontal tabl...
Text Solution
|
- A particle (A) of mass m(1) elastically collides with another stationa...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is to be projected horizontally with velocity v from a poin...
Text Solution
|
- A body of mass m moving with a velocity v in the x direction collides ...
Text Solution
|