Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
R SHARMA-CHEMICAL KINETICS-Archives
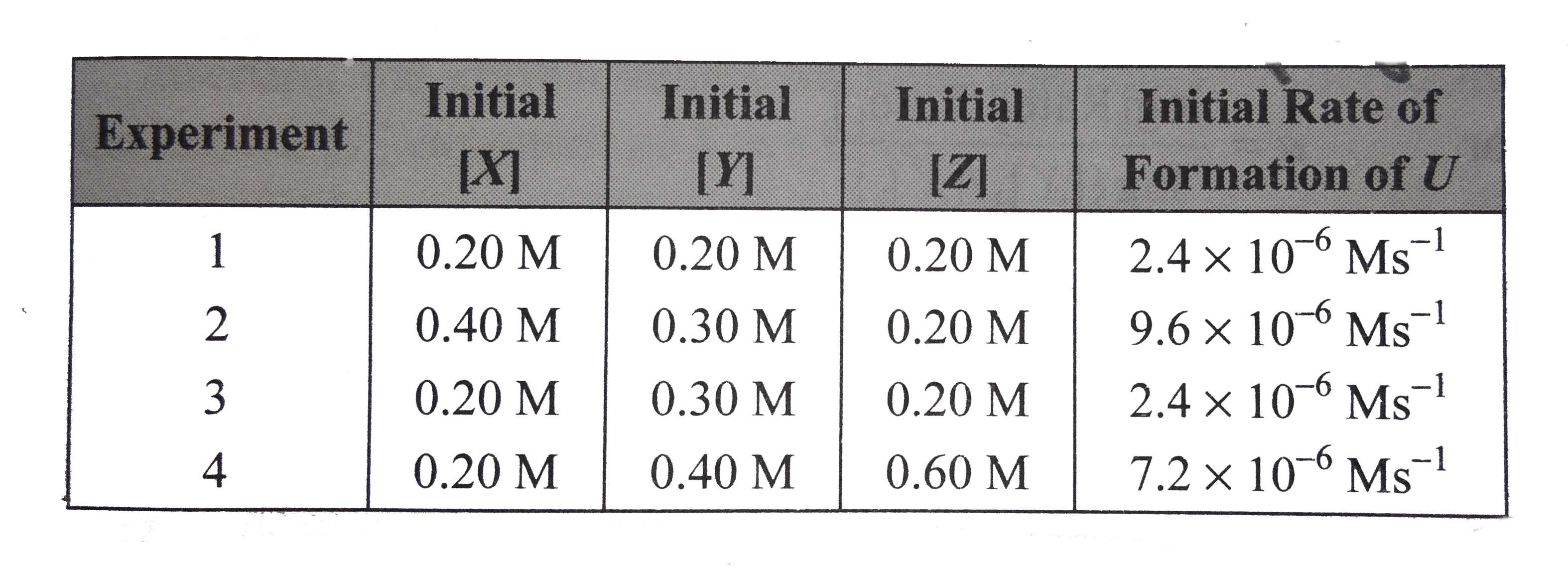
- Method of intial rates: Given the following data, determine the rate l...
Text Solution
|
- The addition of a catallystic during a chemical reaction alters which ...
Text Solution
|
- The rate of a first-order reaction is 0.04 "mol L"^(-1) s^(-1) at 10 s...
Text Solution
|
- The rate constant of the reaction A rarr B is 0.6 xx 10^(-3) mole per ...
Text Solution
|
- The activation energy of a reaction can be determined from the slope o...
Text Solution
|
- When initial concentration of a reactant is doubled in a reaction, its...
Text Solution
|
- What is the activation energy for a reaction if its rate doubles when ...
Text Solution
|
- A reaction having equal energies of activation for forward and reverse...
Text Solution
|
- In a reaction , A + B rarr Product, rate is doubled when the concentra...
Text Solution
|
- In a zero-order reaction for every 10^(@) rise of temperature, the rat...
Text Solution
|
- Activation energy (E(a)) and rate constants (k(1) and k(2)) of a chemi...
Text Solution
|
- Which one of the following statements for the order of a reaction is i...
Text Solution
|
- The unit of rate constant for a zero order reaction is s^(-1).
Text Solution
|
- The half life of a substance in a certain enzyme catalyzed reaction is...
Text Solution
|
- 2N(2)O(5) rarr 4NO(2) + O(2) If (-d[N(2)O(5)])/(dt) = k(1)[N(2)O(5)]...
Text Solution
|
- For the reaction N(2)O(5) rarr 2NO(2) + (1)/(2) O(2), the rate of disa...
Text Solution
|
- During the kinetic study of the reaction 2A +B rarr C + D following ...
Text Solution
|
- For an endothermic reaction, where Delta H represents the enthalpy of ...
Text Solution
|
- The rate of the reaction 2NO+CI(2)rarr 2NOCI is given by the rate ...
Text Solution
|
- For the reaction, N(2) + 3H(2) rarr 2NH(3), if (d[NH(3)])/(d t) = 2 xx...
Text Solution
|
- In the reaction BrO^(-3)(aq) + 5Br^(-) (aq) + 6H^(+) rarr 3Br(2)(1) ...
Text Solution
|