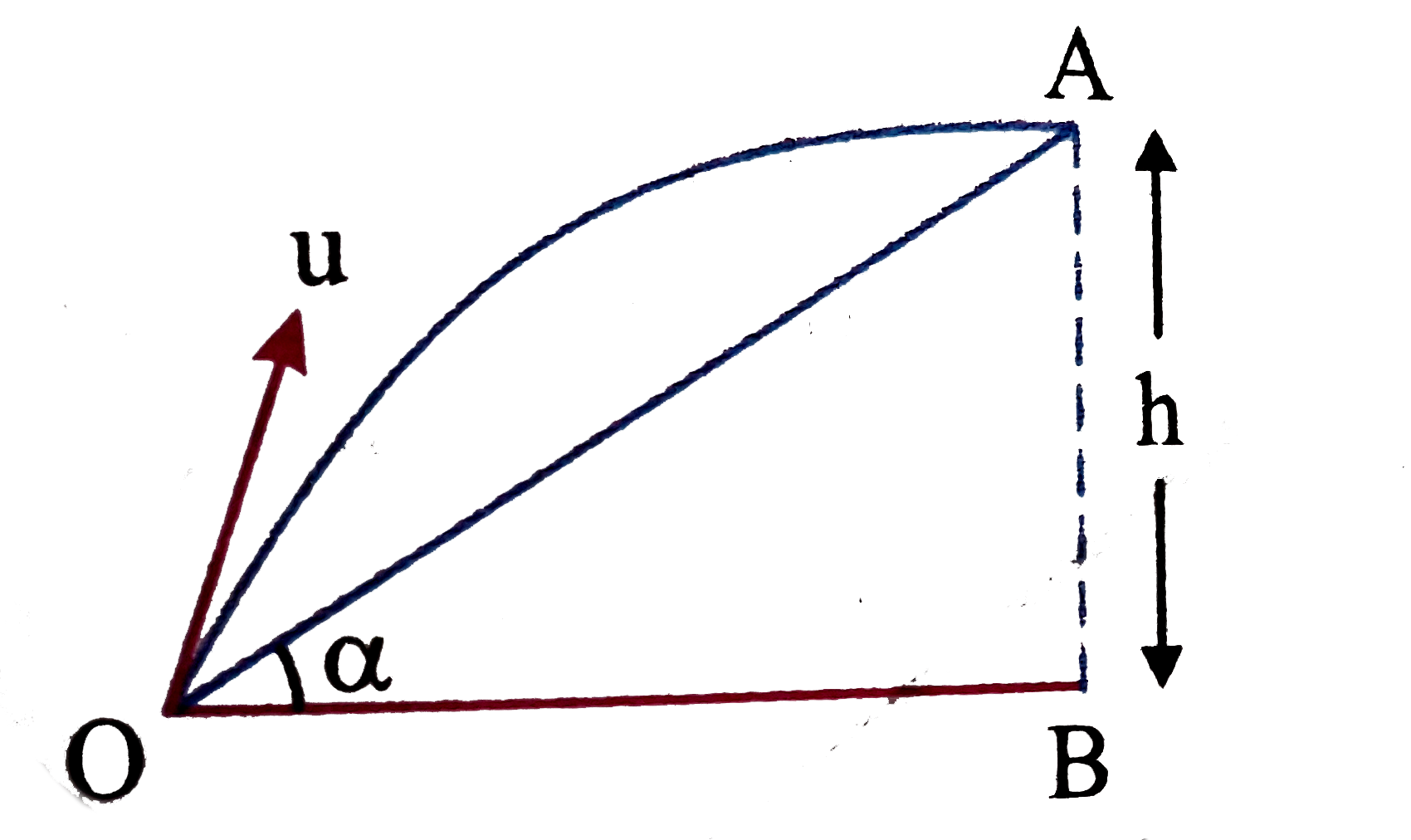
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
MOTION IN A PLANE
NARAYNA|Exercise Level -V Multi answer|18 VideosMOTION IN A PLANE
NARAYNA|Exercise Level -V Passage|15 VideosMOTION IN A PLANE
NARAYNA|Exercise NCERT BASED QUES. PASSAGE|8 VideosMECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS
NARAYNA|Exercise LEVEL-II (H.W)|24 VideosMOTION IN A STRAIGHT LINE
NARAYNA|Exercise Level 2 H.W|29 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NARAYNA-MOTION IN A PLANE-Level -V Single answer
- A block of mass m in floating in a river flowing with a velocity of 2m...
Text Solution
|
- From a point on the ground at a distance a from the foot of a pole, a ...
Text Solution
|
- A heavy particle is projected with a velocity at an angle with the hor...
Text Solution
|
- A fixed morter fires a bomb at an angle of 53^@ above the horizontal w...
Text Solution
|
- The angular elevation of an enemy's position on a hill 'h' ft height i...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles are projected simultaneously with the same speed v in th...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a sphere moving in a steady flow of air in the x-directio...
Text Solution
|
- A very broad elevator is going up vertically with a constant accelerat...
Text Solution
|
- A boy throws a ball upward with velocity v(0)=20m//s. The wind imparts...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is projected from an inclined plane OP1 from A with velocit...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is projected with a certain velocity at an angle prop above...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is projected at an angle 60^@ with speed 10(sqrt3)m//s, fro...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is projected from a point A with velocity usqrt2 at an angl...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is dropped from point P at time t = 0. At the same time an...
Text Solution
|
- Shots are fired simultaneously from the top and bottom of a vertical c...
Text Solution
|
- Two projectiles are projected simultaneously from two towers as shwon ...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown, the two projectiles are fired simultaneously. The...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles A and B are projected simultaneously in the directins sh...
Text Solution
|
- A particle starts from the origin of coordinates at time t = 0 and mov...
Text Solution
|
- Motion of a particle is governed by following relations y=x/alpha,V(x)...
Text Solution
|