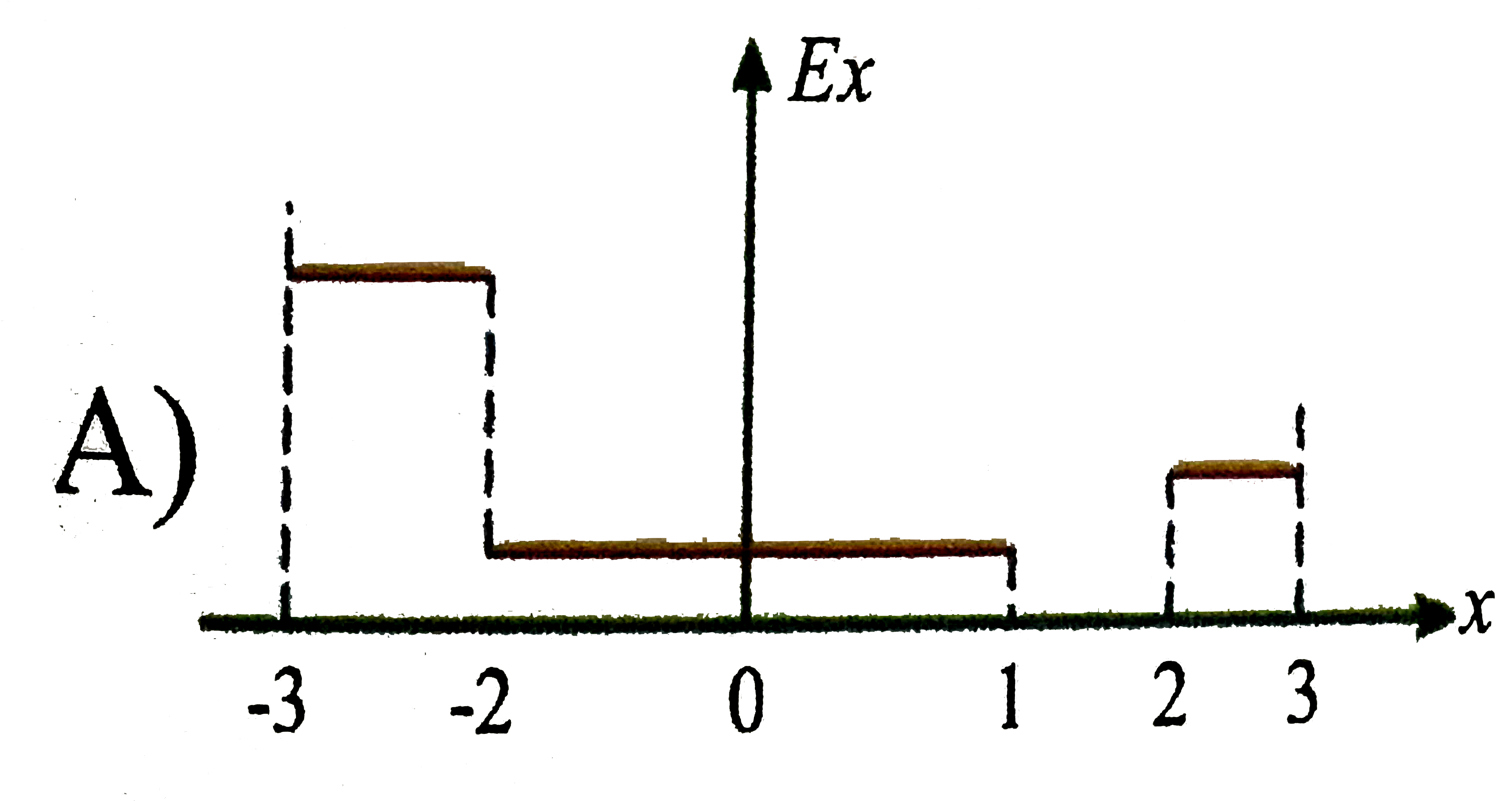
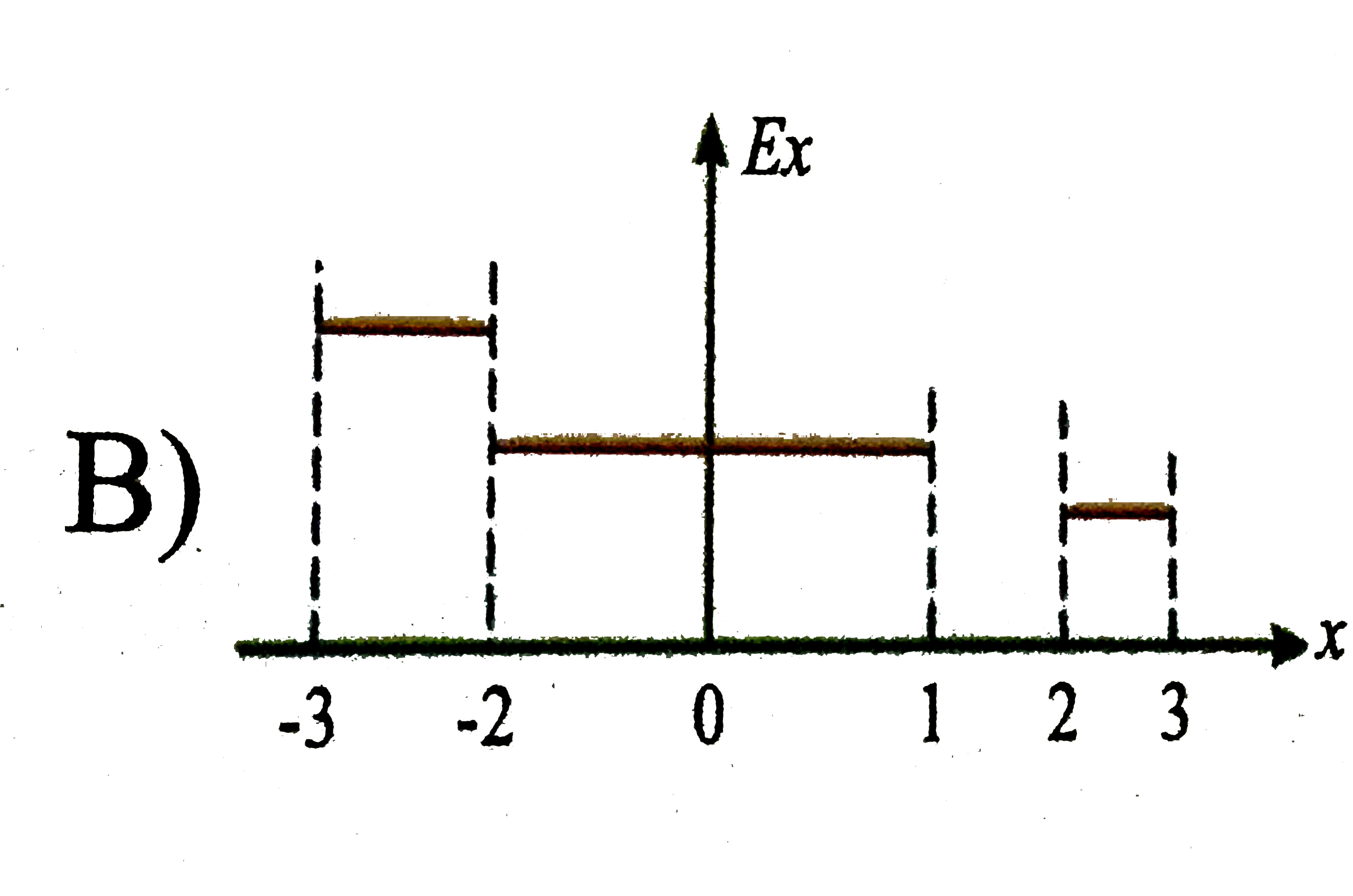A
B
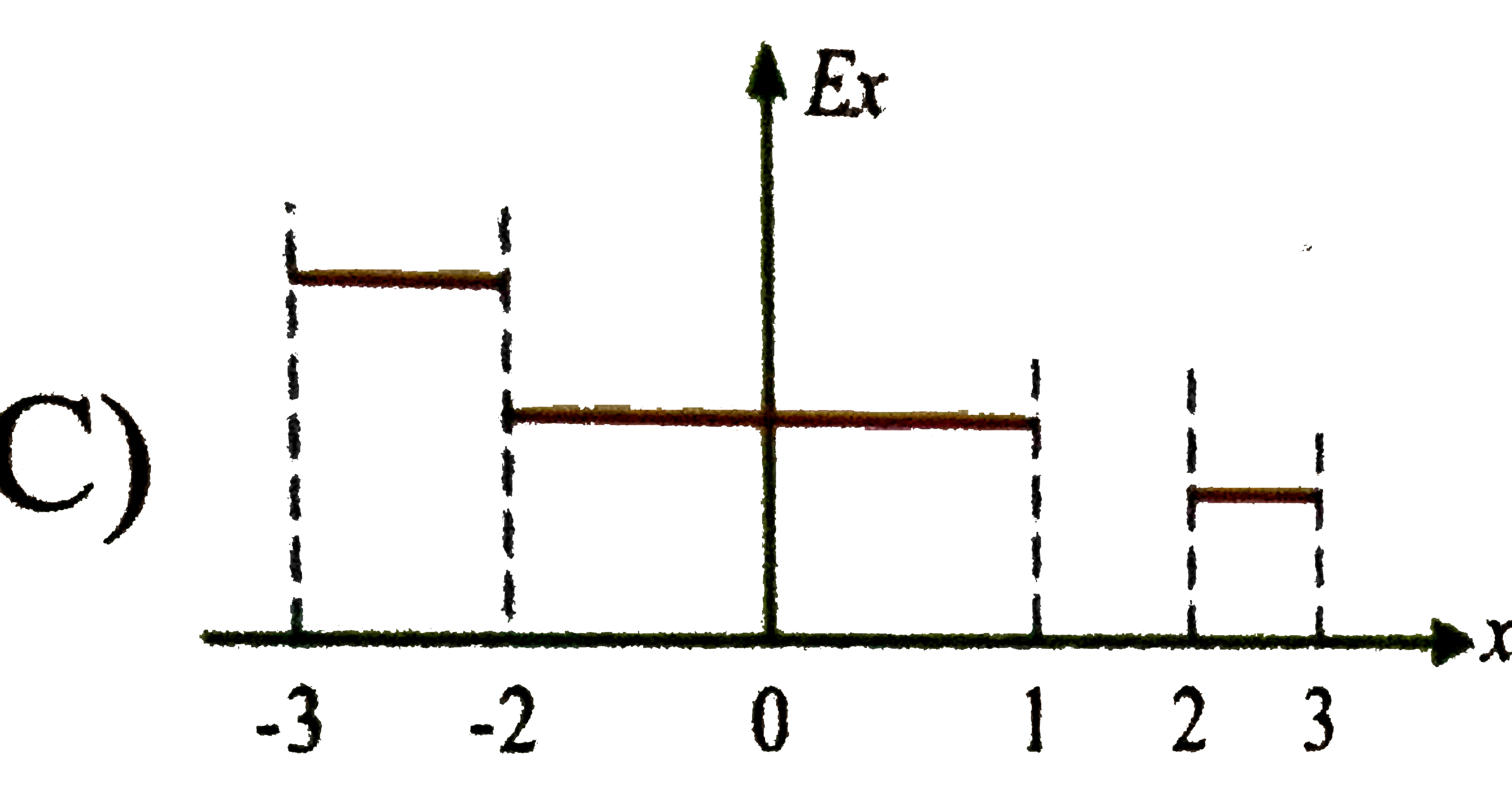
C
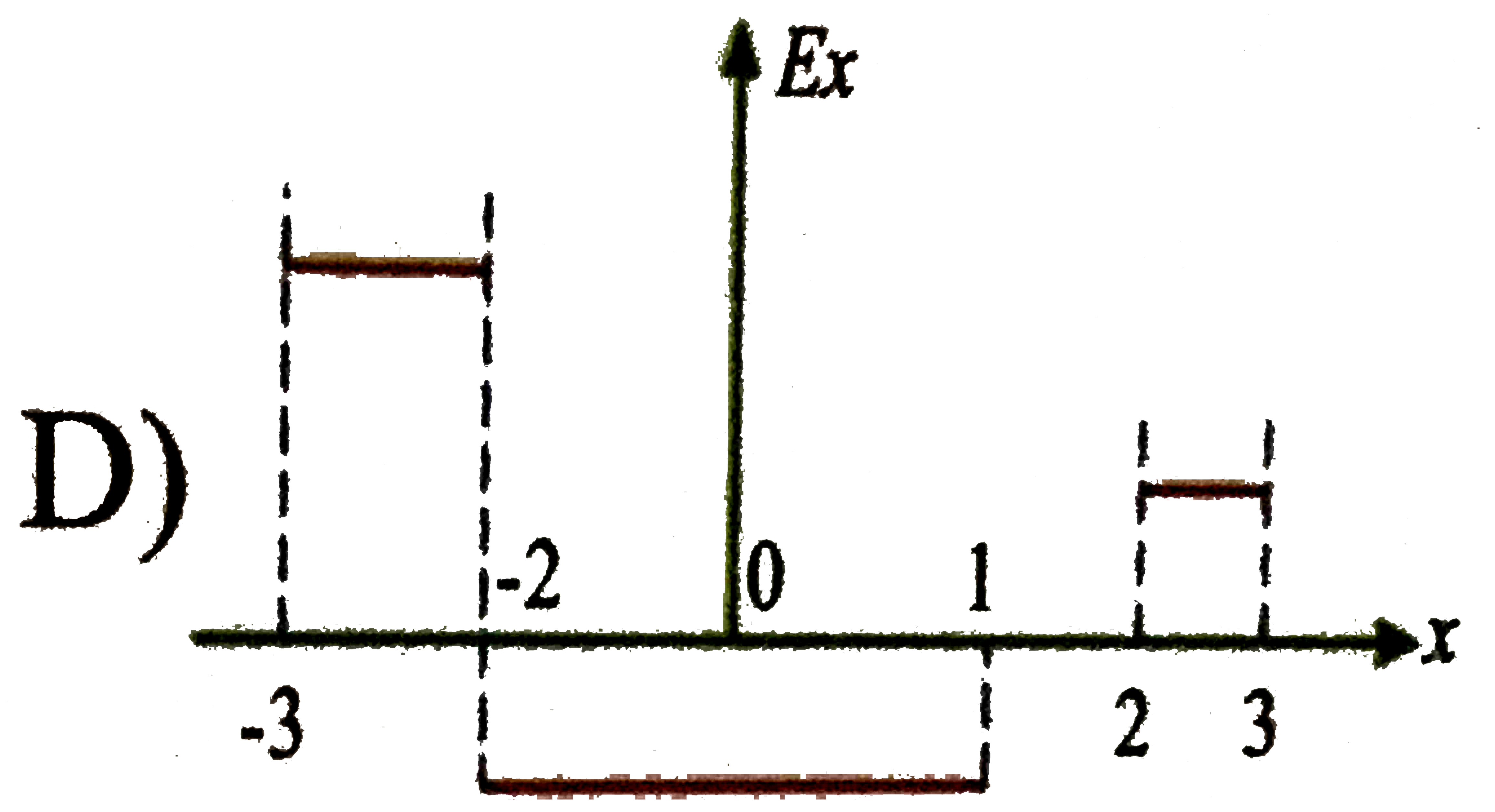
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTROSTATICS AND GAUSS LAW
NARAYNA|Exercise Passage V|3 VideosELECTROSTATICS AND GAUSS LAW
NARAYNA|Exercise Passage VI|3 VideosELECTROSTATICS AND GAUSS LAW
NARAYNA|Exercise Passage III|3 VideosELECTROSTATIC POTENTIAL AND CAPACITANCE
NARAYNA|Exercise ADDITIONAL PROBLEMS|14 VideosEXPERIMENTAL PHYSICS
NARAYNA|Exercise Comprehension type|6 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NARAYNA-ELECTROSTATICS AND GAUSS LAW-Passage IV
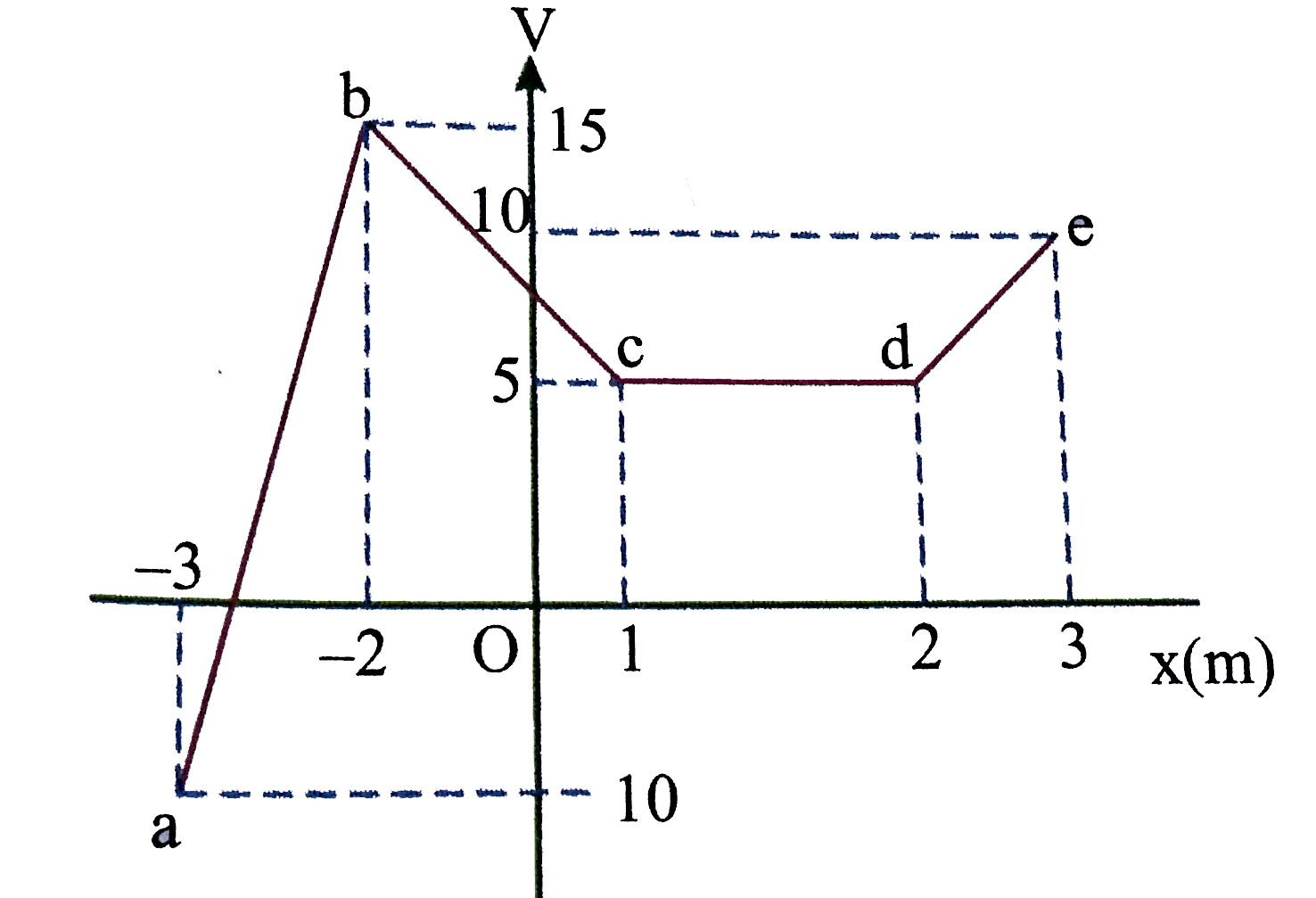
- Suppose electric potential varies along the x-axis as shown in the abo...
Text Solution
|
- Suppose electric potential varies along the x-axis as shown in the abo...
Text Solution
|
- Suppose electric potential varies along the x-axis as shown in the abo...
Text Solution
|
- Suppose electric potential varies along the x-axis as shown in the abo...
Text Solution
|
- Suppose electric potential varies along the x-axis as shown in the abo...
Text Solution
|
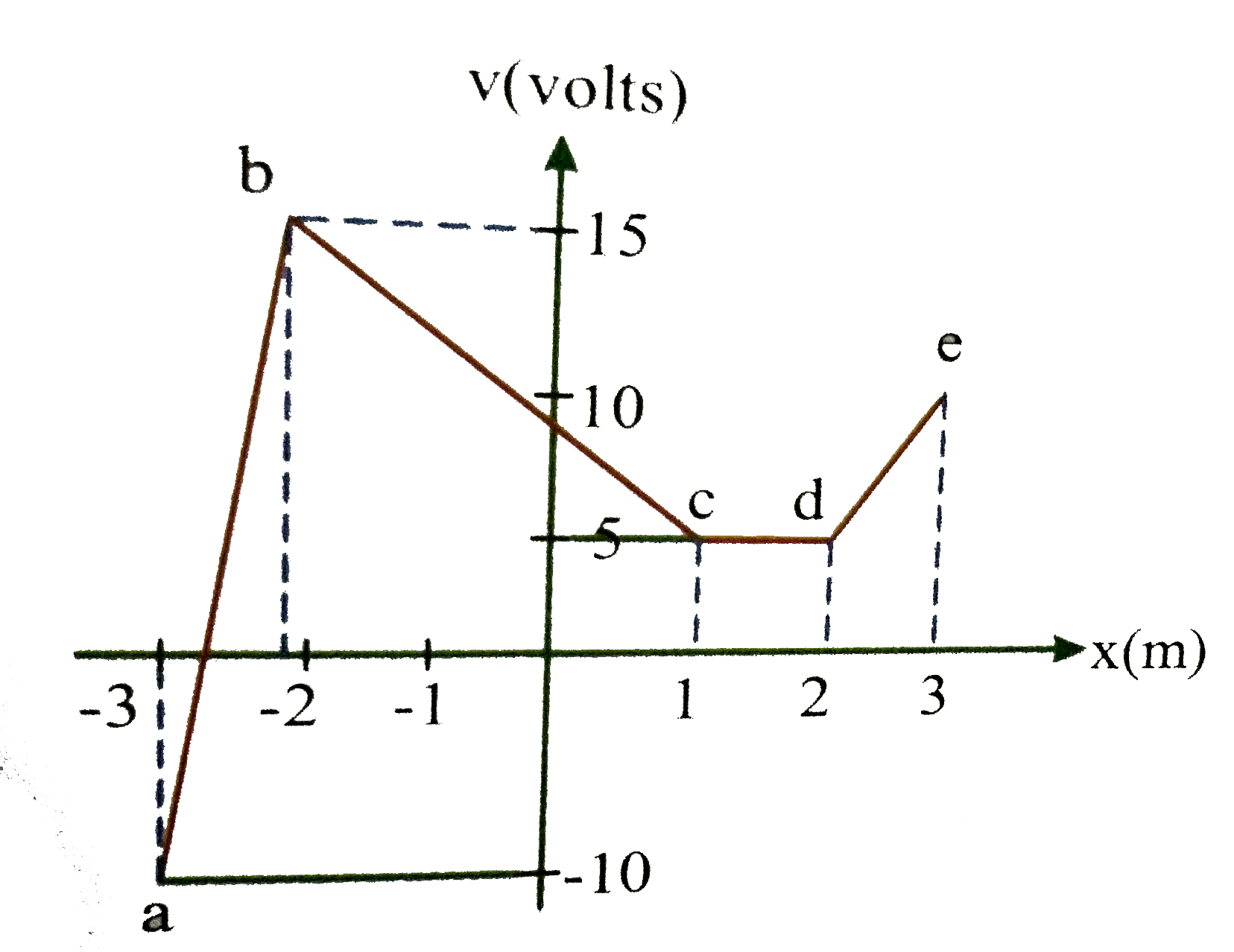 Suppose electric potential varies along the x-axis as shown in the above figure the potential doesnot vary in `y or z` direction of the intervals shown (ignore the behaviour at the end points of the intervals) the field `E_(x)` has a maximum absolute value `"FB_(1)"Vm^(-1)` in the region `"FB_(2)"` its value in the region cd is `"FB_(3)"Vm^(-1)` then
Suppose electric potential varies along the x-axis as shown in the above figure the potential doesnot vary in `y or z` direction of the intervals shown (ignore the behaviour at the end points of the intervals) the field `E_(x)` has a maximum absolute value `"FB_(1)"Vm^(-1)` in the region `"FB_(2)"` its value in the region cd is `"FB_(3)"Vm^(-1)` then