Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ALLEN-SOLUTIONS-EXERCISE-04 [A]
- The vapour pressure of ethanol and methanol ate 44.5 mm Hg and 88.7 mm...
Text Solution
|
- The vapour pressure of pure benzene at a certain temperature is 640 mm...
Text Solution
|
- Addition of 0.643g of a compound to 50mL of benzene (density: 0.879g m...
Text Solution
|
- A solution containing 30g of a nonvolatile solute in exactly 90g water...
Text Solution
|
- The freezing point of ether was lowered by 0.60^(@)Con dissolving 2.0g...
Text Solution
|
- The addition of 3g of a substance to 100g C CI(4)(M = 154 g mol^(-1)) ...
Text Solution
|
- To 500cm^(3) of water, 3.0 xx 10^(-3) kg acetic acid is added. If 23% ...
Text Solution
|
- A 0.01m aqueous solution of K(3)[Fe(CN)(6)] freezes ar -0.062^(@)C. Wh...
Text Solution
|
- The degree of dissociation of Ca(NO(3))(2) in a dilute aqueous solutio...
Text Solution
|
- A solution containing 0.11kg of barium nitrate in 0.1kg of water boils...
Text Solution
|
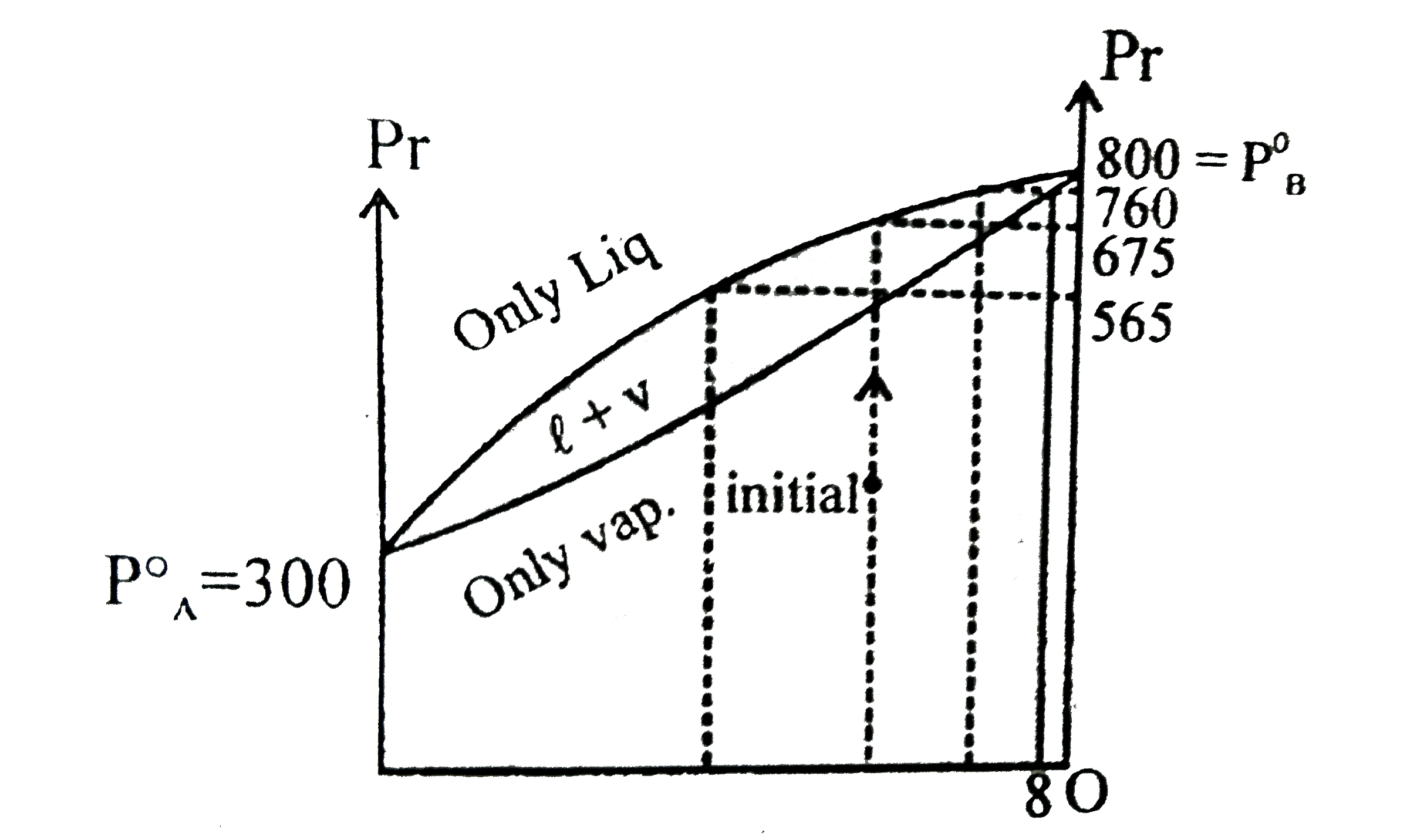
- The vapour pressure of two pure liquids, A and B that form an ideal so...
Text Solution
|
- Sea water is found to contain 5.85% NaCI and9.50% MgCI(2) by weight of...
Text Solution
|
- Find the freezing point of a glucose solution whose osmotic pressure a...
Text Solution
|
- The latent heat of fusion of ice is 80 calories per gram at 0^(@)C. Wh...
Text Solution
|
- At 300K, two solutions of glucose in water of concentration 0.01M and ...
Text Solution
|
- At 10^(@)C, the osmotic pressure of urea solution is 500 mm.The soluti...
Text Solution
|
- A 0.1M solution of potassiu ferrocyanide is 46% dissociated at 18^(@)C...
Text Solution
|