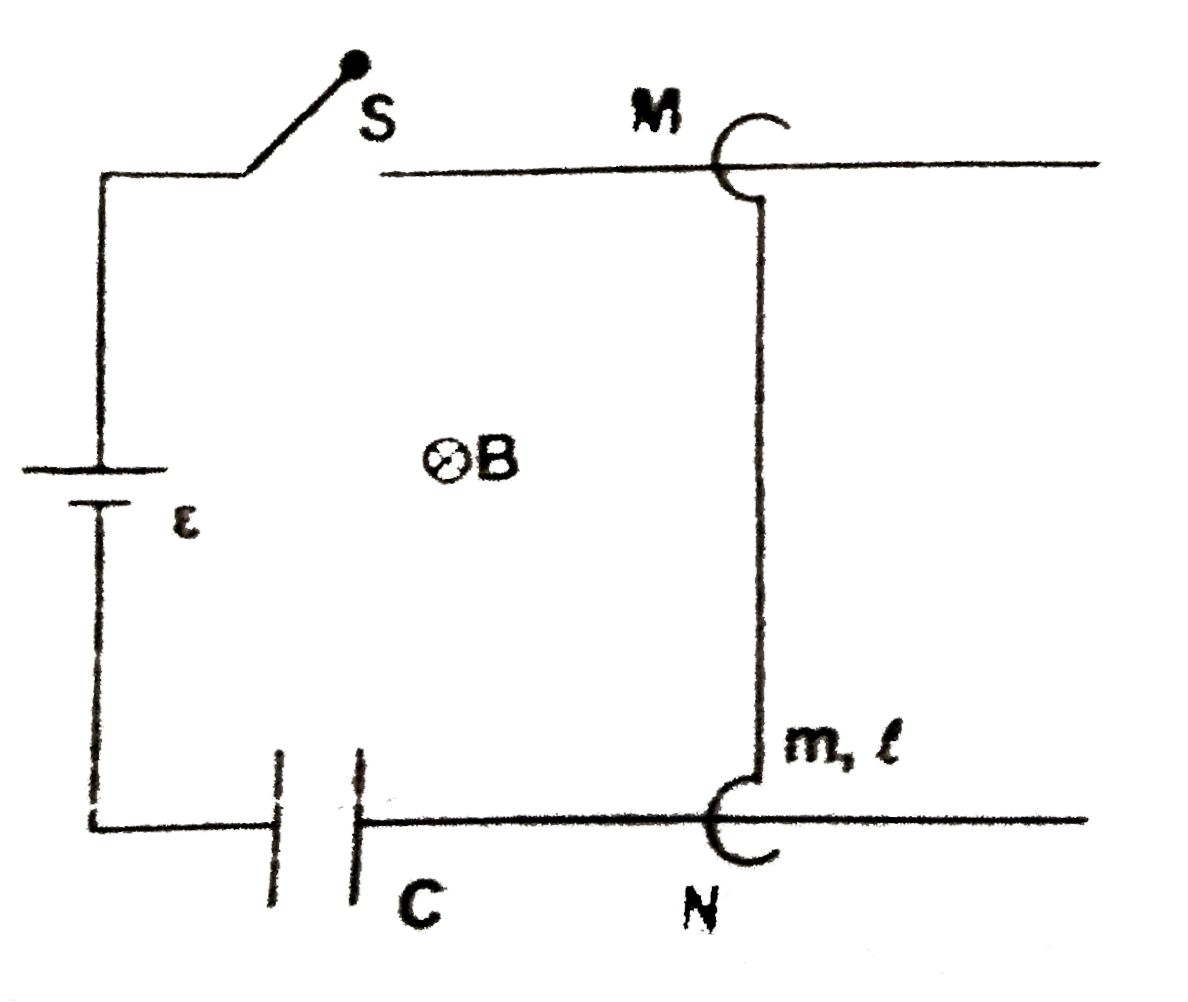
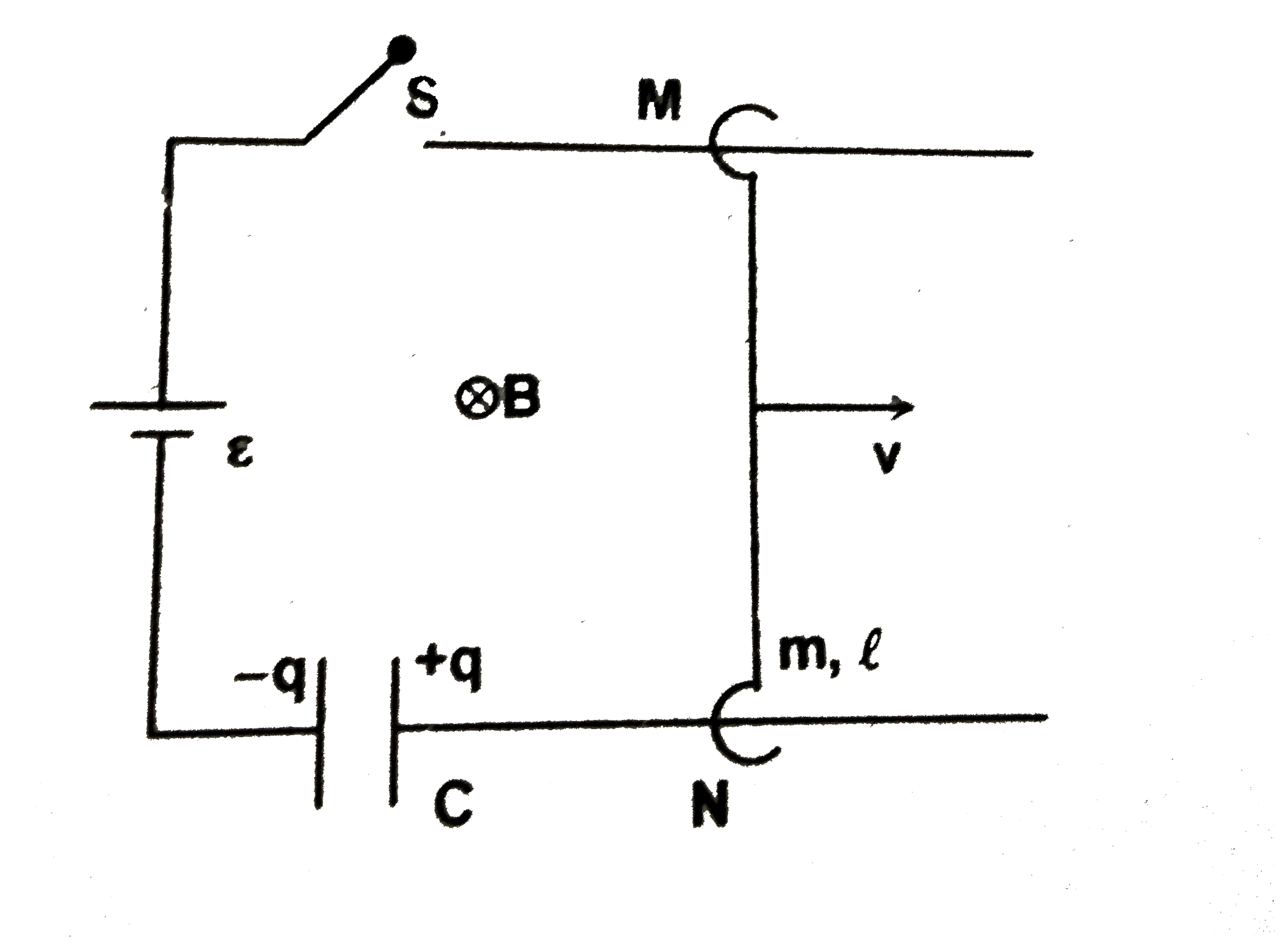
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
FIITJEE-TEST PAPERS-PHYSICS
- A circular conducting ring of radius 'a' is rolling with slipping on a...
Text Solution
|
- A time varying magnetic field B=krt (where k is a constant r is the ra...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting rod MN of mass m and length 'l' is placed on parallel sm...
Text Solution
|
- Charge 'q' is uniformly distributed along the length of a non-coductin...
Text Solution
|
- Initially capacitor 'A' is charged to a potential drop epsilon and cap...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit shown, switch's is closed at t=0. then the ratio (U(1))...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit shown the average power developed in the resistor R(1) ...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform potentiometer wire AB of length 100 cm has a resistance of 5...
Text Solution
|
- A small spherical conductor 'A' of radias 'a' is initially charged to ...
Text Solution
|
- Two moles of an ideal diatomic gas is taken through a process VT^(2)= ...
Text Solution
|
- A sperical ball of mass m, radiua r is connected to string of length (...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal diode is connected in a circuit with resistance R=5Omega and ...
Text Solution
|
- A vessel is quarter filled with a liquid of refractive index mu. The r...
Text Solution
|
- A spring block system with mass of block m and spring constant K (all ...
Text Solution
|
- What should be the approzimate kinetic energy of an electron so that i...
Text Solution
|
- A 2 kg block moving with 10m//s strikes a spring of constant pi^(2)N//...
Text Solution
|
- Unpolarised light of intensity 32 watt m^(-2) passes through three pol...
Text Solution
|
- Choose the incorrect statements.
Text Solution
|
- In a radio receiver, the short wave and medium wave station are tuned ...
Text Solution
|
- A string of length 2L, obeying Hooke's Law, is stretched so that its e...
Text Solution
|