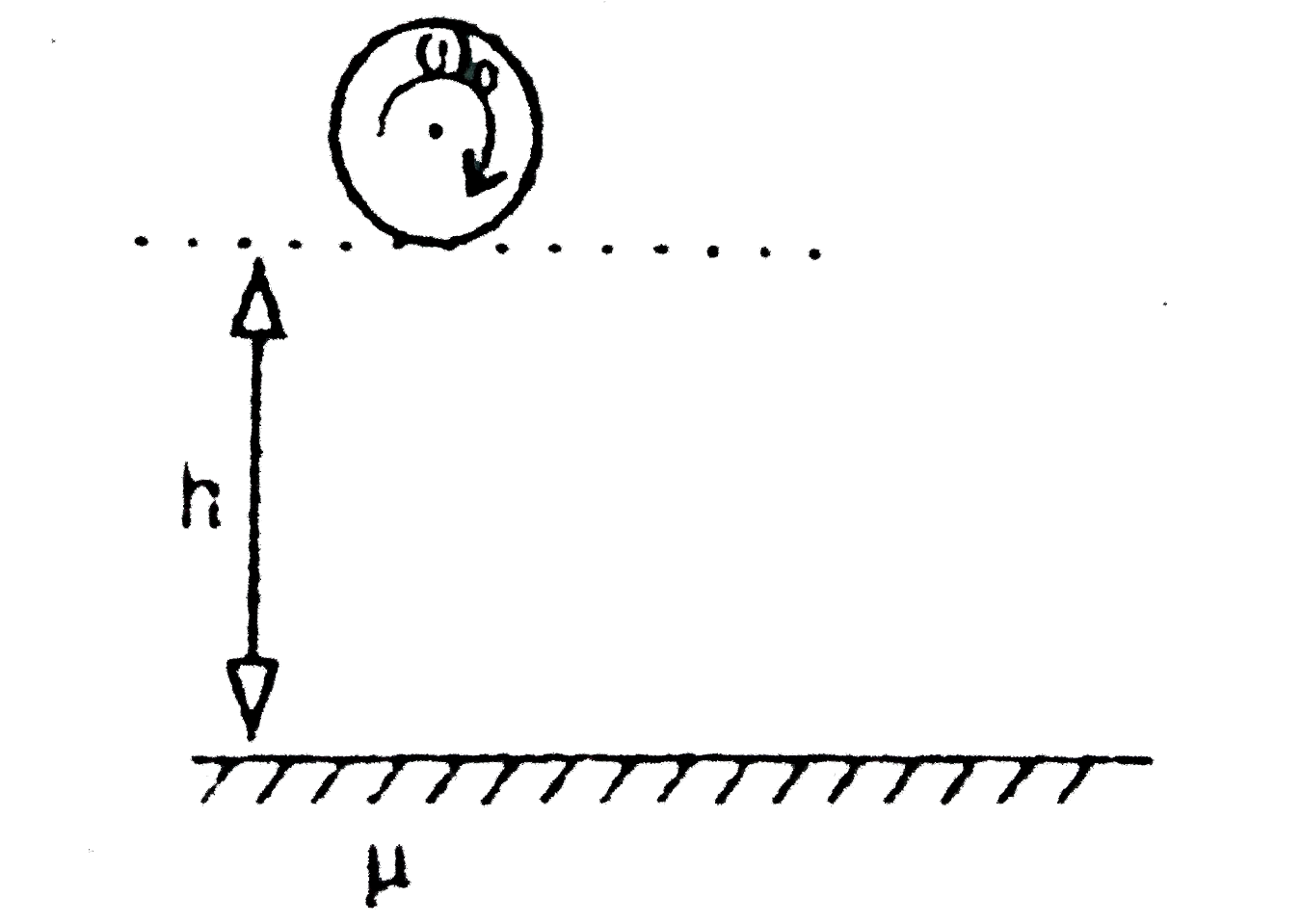Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE-TEST PAPERS-PART - II PHYSICS
- A unifrom rod AB of length 4m and mass 12 kg is thrown such that just ...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m = 2 kg is connected to a spring of force constant k ...
Text Solution
|
- A solid sphere with angular velocity omega(0) is dropped on a rough su...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass 5 kg is held against a wall with a force of 100 N. as ...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown a thin light inextensible string is wrapped around...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the following redox reaction : H(2)O + AX + BY rarr HA + YO...
Text Solution
|
- 1 mol of an ideal gas undergoes different thermodynamical process in P...
Text Solution
|
- 1 mol of an ideal gas undergoes different thermodynamical process in P...
Text Solution
|
- Boyle's temperature (T(B)) : It is the temperature at which a real gas...
Text Solution
|
- Boyle's temperature (T(B)) : It is the temperature at which a real gas...
Text Solution
|
- The degree of polarity of a convalent compound is measured by the dipo...
Text Solution
|
- The degree of polarity of a convalent compound is measured by the dipo...
Text Solution
|
- Identification of +m & -m groups : If the first atom of the group has ...
Text Solution
|
- Identification of +m & -m groups : If the first atom of the group has ...
Text Solution
|
- 1 mol of a real gas obeys P(V(m) - b) = RT , where 'b' and 'R' are con...
Text Solution
|
- One gram of a metallic chloride was found to contain 0.835 g of chlori...
Text Solution
|
- The graph of compressibility factor (Z) vs. P for one mole of a real g...
Text Solution
|
- N(2) undergoes photochemical dissociation into one normal N-atom and o...
Text Solution
|
- Four moles of an ideal diatomic gas (gamma = 1.4) at 300 K and 12 atm ...
Text Solution
|
- The vapour density of the mixture at equilibrium is 38.3 at 33^(@)C ...
Text Solution
|