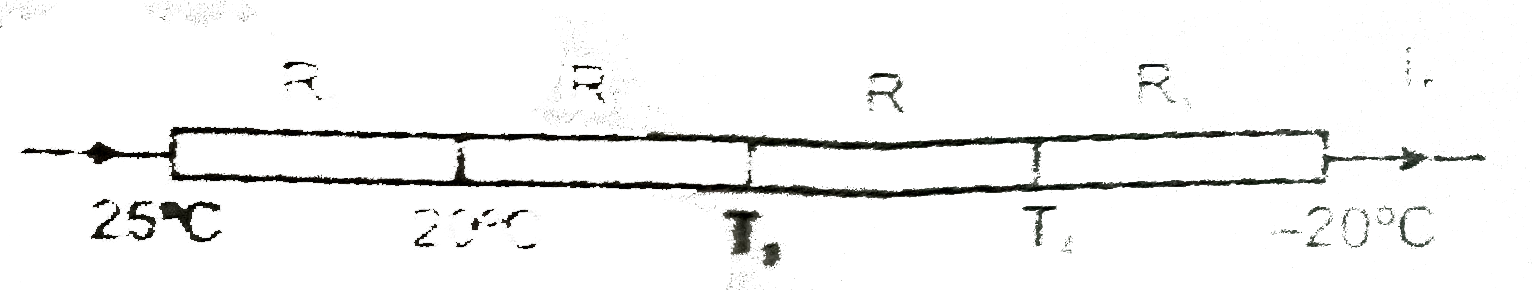Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE-HEAT TRANSFER-Example
- Three identical rods of length 1 m each, having cross-sectional area o...
Text Solution
|
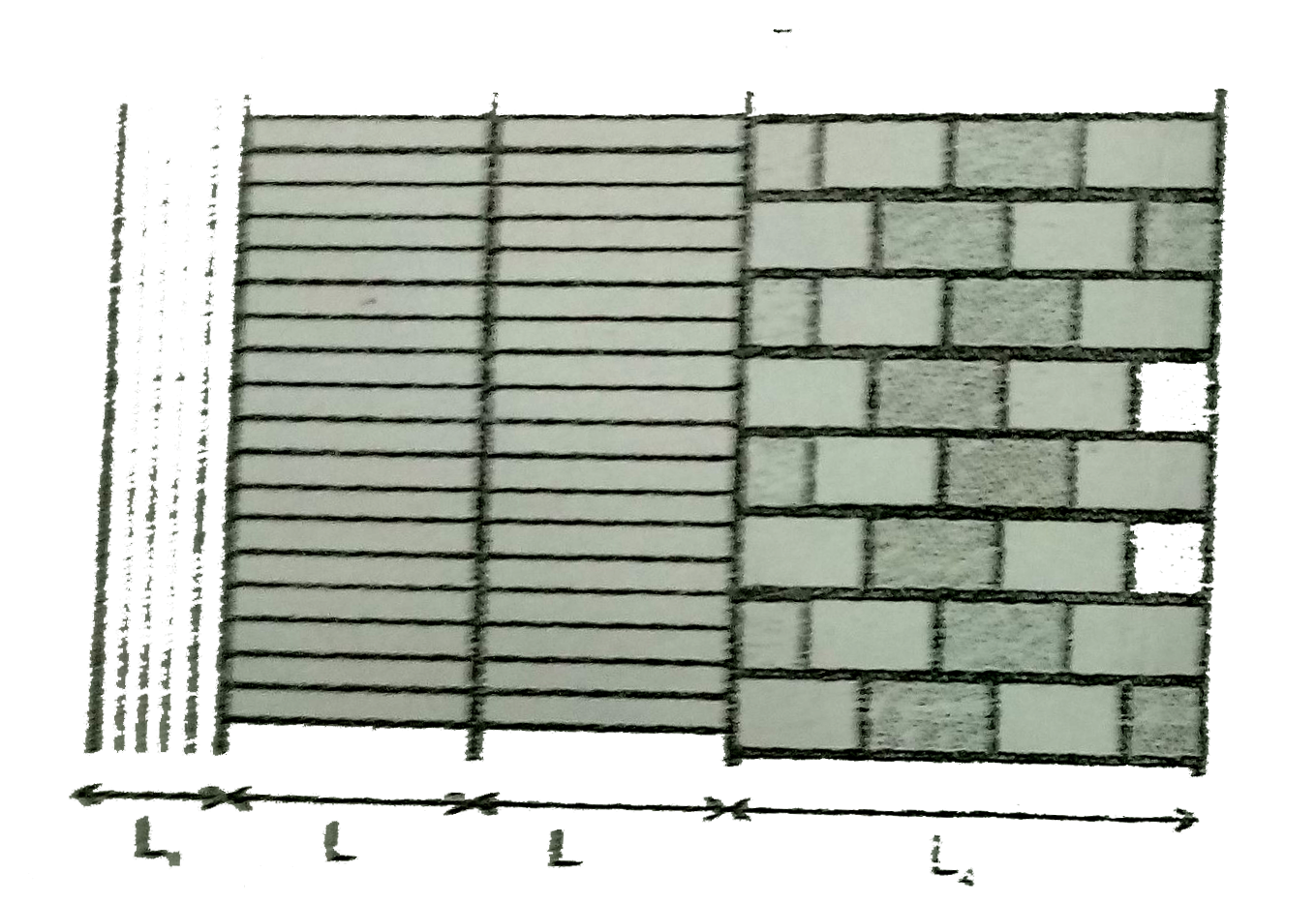
- The figure shows the cross-section of the outer wall of a house buit i...
Text Solution
|
- In example 3, K(1) = 0.125 W//m-.^(@)C, K(2) = 5K(1) = 0.625 W//m-.^(@...
Text Solution
|
- Three copper rods and three steel rods each of length l = 10 cm and ar...
Text Solution
|
- Two thin conectric shells made of copper with radius r(1) and r(2) (r(...
Text Solution
|
- A container of negligible heat capacity contains 1kg of water. It is c...
Text Solution
|
- Solar radiation is found to have an intensity maximum near the wavelen...
Text Solution
|
- A body of emissivity (e = 0.75), surface area of 300cm^(2) and tempera...
Text Solution
|
- A hot black body emits the enegy at the rate of 16 Jm^-2s^-1 and its m...
Text Solution
|
- A body at temperature 40^(@)C is kept in a surrounding of constant tem...
Text Solution
|