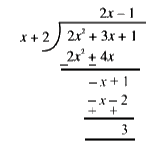Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
PROBABILITY
AAKASH INSTITUTE|Exercise TRY YOURSELF|36 VideosPROBABILITY
AAKASH INSTITUTE|Exercise ASSIGNMENT (SECTION - A Competition Level Questions)|114 VideosPRINCIPLE OF MATHEMATICAL
AAKASH INSTITUTE|Exercise Section-D:(Assertion-Reason Type Questions)|12 VideosRELATIONS AND FUNCTIONS
AAKASH INSTITUTE|Exercise Assignment (Section - J) Aakash Challengers Questions|8 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
AAKASH INSTITUTE-PROBABILITY-ASSIGNMENT SECTION-J (aakash challengers questions)
- A is a set having n elements. A subset P of A is chosen at random. The...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a twon with n people. A person spreads a rumour to a second, ...
Text Solution
|
- Two players P1, and P2, are playing the final of a chase championship,...
Text Solution
|
- If a and b are chosen randomly from the set consisting of number 1, 2,...
Text Solution
|
- Two dice are thrown simultaneously to get the co-ordinates of a point ...
Text Solution
|
- A function f is such that f(x)=x^3+ax^2+bx+c, where a, b, c are chosen...
Text Solution
|
- Two point P, Q are taken at random on a straight line OA of length a....
Text Solution
|
- A point P is taken at random on a straight line AB. The chance that th...
Text Solution
|
- If two points are taken at random on the circumference of circle, the ...
Text Solution
|
- Three points P, Q and R are selected at random from the cirumference o...
Text Solution
|
- 3 six faced dice are thrown. One die bears numbers 0 to 5, second bear...
Text Solution
|
- A bag contains (2n+1) coins. It is known that n of these coins have a ...
Text Solution
|
- If three squares of dimension 1xx1 are selcted at random from the ch...
Text Solution
|
- Every person in the room has shake hands with a certain number of othe...
Text Solution
|