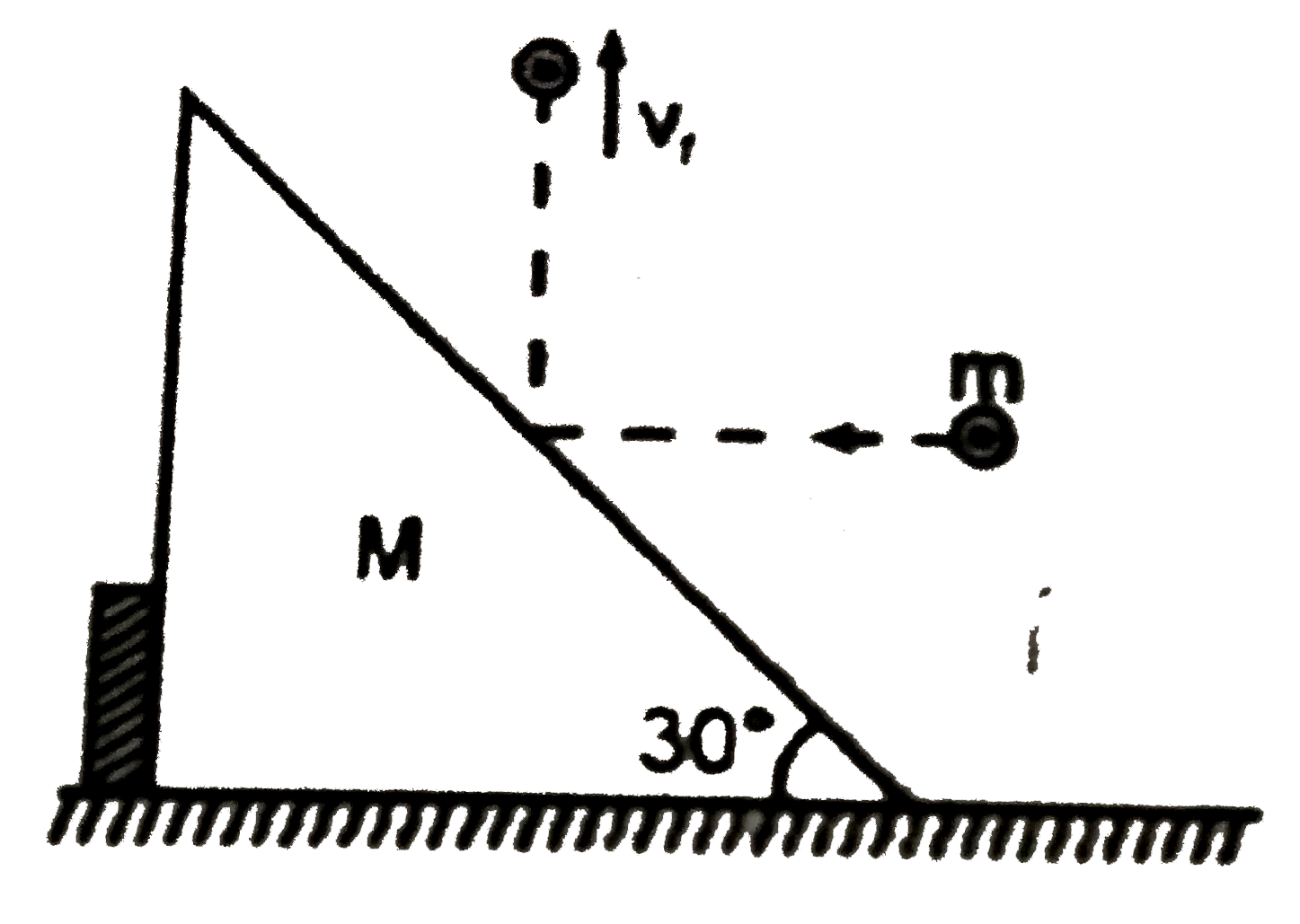
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
DAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMS
RESONANCE|Exercise dpp 56|7 VideosDAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMS
RESONANCE|Exercise dpp 57|7 VideosDAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMS
RESONANCE|Exercise dpp 54|8 VideosCURRENT ELECTRICITY
RESONANCE|Exercise Exercise|54 VideosELASTICITY AND VISCOCITY
RESONANCE|Exercise Advanced Level Problems|9 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE-DAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMS-DPP 55
- A glass ball collides with a smooth horizontal surface (xz plane) with...
Text Solution
|
- As shown in the figure a body of mass m moving horizontally with spee...
Text Solution
|
- A plank of mass m moving with a velocity v along a friction less horiz...
Text Solution
|
- Two friends A and B (each weighing 40 kg) are sitting on a frictionles...
Text Solution
|
- Two friends A and B (each weighing 40 kg) are sitting on a frictionles...
Text Solution
|
- Two friends A and B (each weighing 40 kg) are sitting on a frictionles...
Text Solution
|
- Two friends A and B (each weighing 40 kg) are sitting on a frictionles...
Text Solution
|
- Two friends A and B (each weighing 40 kg) are sitting on a frictionles...
Text Solution
|