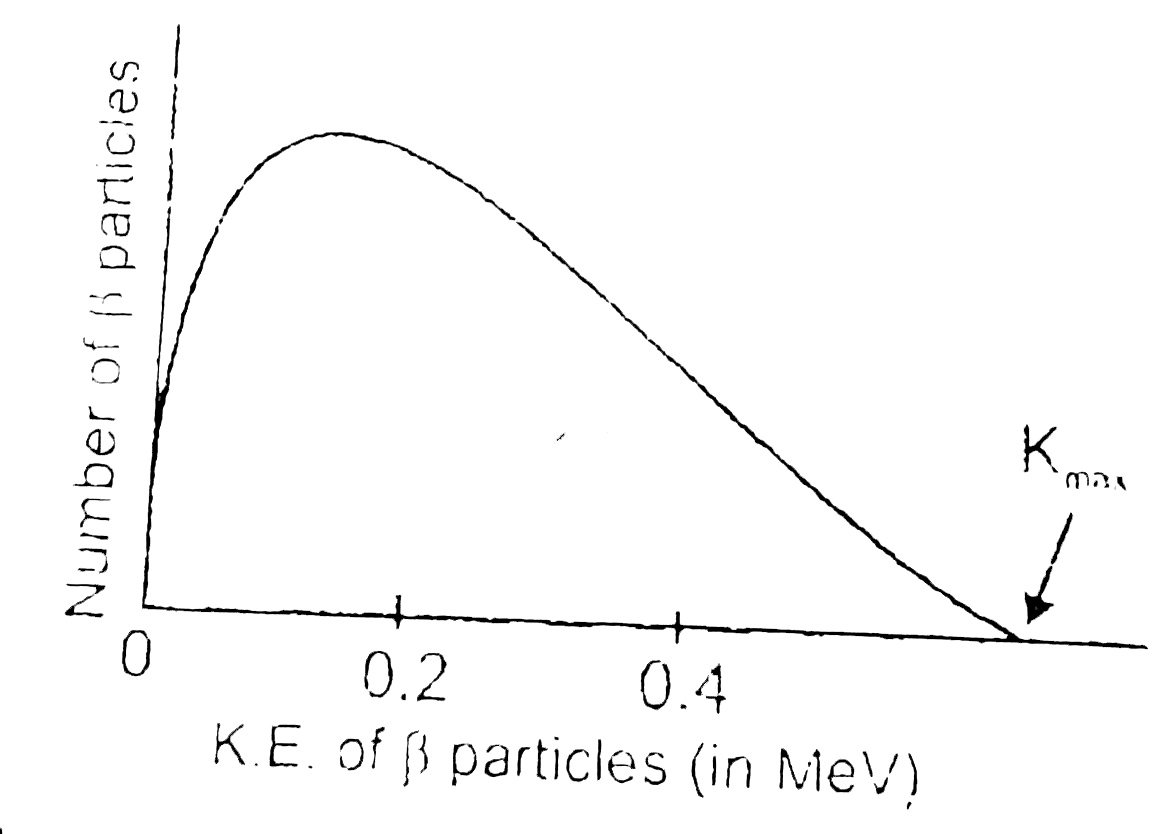
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE-NUCLEAR PHYSICS-Exercise -3 Part-III CBSE PROBLEMS (LAST 10 YEARS)
- Draw the graph showing thervariation of binding energy per nucleon wit...
Text Solution
|
- Name the reaction which takes place when a slow neutron beam strikes ....
Text Solution
|
- (a) Draw the energy level diagram showing the emission of beta-particl...
Text Solution
|
- A raioactive sample contains 2.2 mg of pure .(6)^(11)C which has half-...
Text Solution
|
- Define decay constant
Text Solution
|
- Define the term half-life period and decay constant of a radioactive s...
Text Solution
|
- The sequence of decay of radioactive nucleus is D overset alphato D1ov...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the concept of nuclear forces. Discuss their characterstic pro...
Text Solution
|
- State and explain the laws of radioactive disintergration. Hence defin...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the binding energy per nucleon of .(20)^(40)Ca. Given that ...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the amount of energy released during the alpha-decay of .(...
Text Solution
|
- A neutron is absorbed by a .(3)^(6)Li nucleus with the subsequent emis...
Text Solution
|
- What do you understand by isotopes, isobars and isotones? Explain with...
Text Solution
|
- The nucleus .^(23)Ne deacays by beta-emission into the nucleus .^(23)...
Text Solution
|
- Two nuclie have mass numbers in the ratio 1:2. What is the ration of t...
Text Solution
|
- A radiactive nucleus 'A' undergoes a series of decays according to the...
Text Solution
|
- Define the activity of a radionuclide. Write its SI unit. Give a plot ...
Text Solution
|
- Draw a plot of potential energy of a pair of nucleons as a function of...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Write symbolically the beta-decay process of ""(15)^(32)P. (b) ...
Text Solution
|
- How is the size of nucleus experimentally determined ? Write the relat...
Text Solution
|