Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ATOMIC PHYSICS
RESONANCE|Exercise Exercise-2 part-III one or more than one options correct type|14 VideosATOMIC PHYSICS
RESONANCE|Exercise Exercise-2 Part-III : Comprehension|12 VideosATOMIC PHYSICS
RESONANCE|Exercise Exercise (2) Only one option correct type|30 VideosALTERNATING CURRENT
RESONANCE|Exercise HIGH LEVEL PROBLEMS|11 VideosCAPACITANCE
RESONANCE|Exercise High Level Problems|16 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE-ATOMIC PHYSICS-Exercise-2 part-II Single and double value integer type
- In an experiment on photoelectric effect, the emitter and the collecto...
Text Solution
|
- A light beam of wavelength 400 nm is incident on a metal of work- func...
Text Solution
|
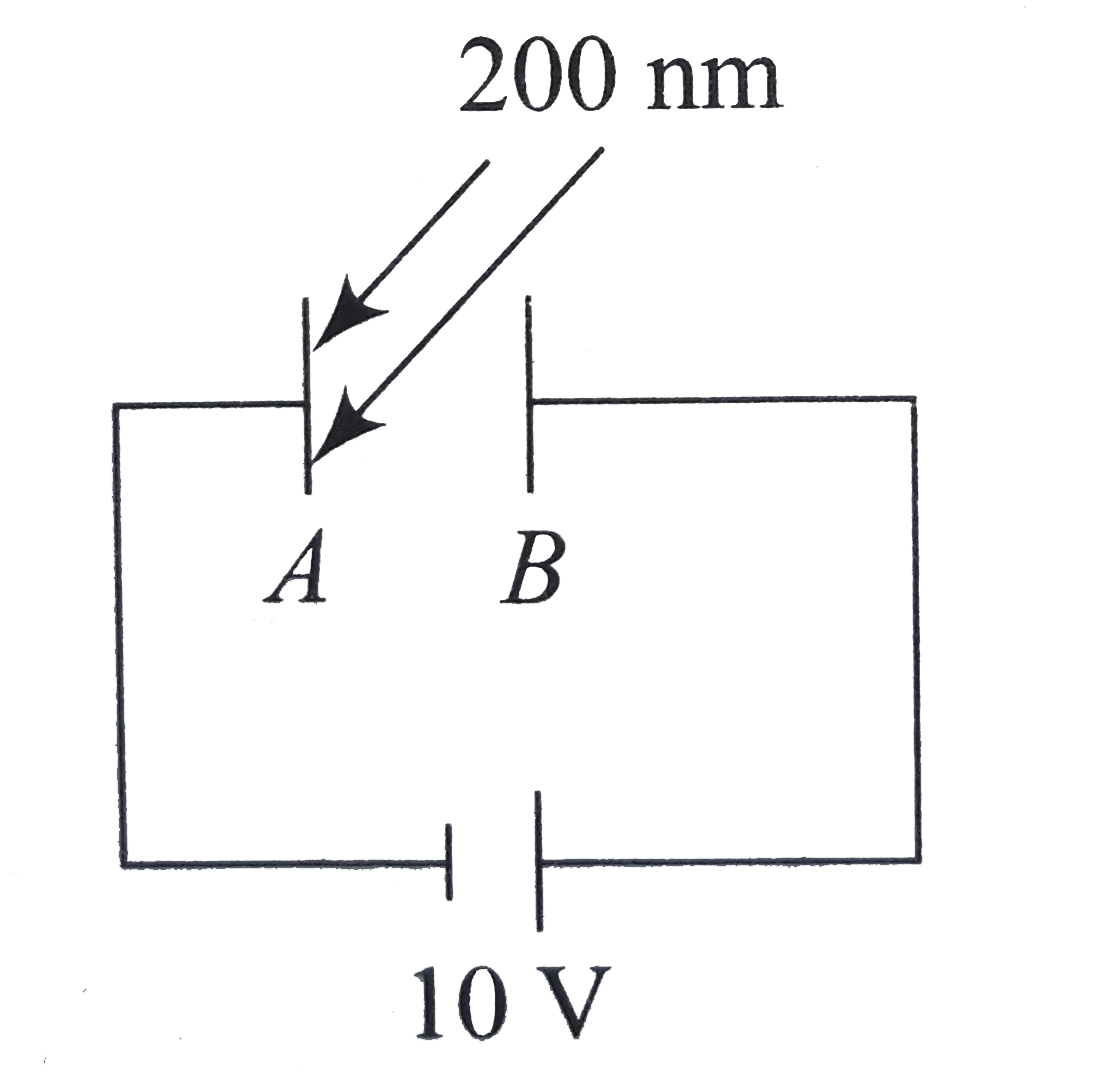
- In Fig. electromagnetic radiations of wavelength 200nm are incident on...
Text Solution
|
- Consider Bohr's theory for hydrogen atom. The magnitude of angular mom...
Text Solution
|
- The first excitation potential of He^(+) ion is n, and the ionization ...
Text Solution
|
- A neutron moving with a speed v strikes a hydrogen atom in ground stat...
Text Solution
|
- The Kbeta X-ray of argon has a wavelength of 0.36 nm. The minimum ener...
Text Solution
|
- Electrons in hydrogen like atom (Z= 3) make transition from the fifth ...
Text Solution
|
- An electron having energy 20 e V collides with a hydrogen atom in the ...
Text Solution
|
- Calcualte the value of X if magnetic field strength at the centre of a...
Text Solution
|
- Radiation from a hydrogen discharge tube ( energy of photons le 13.6 ...
Text Solution
|
- The ionization energy of a hydrogen like Bohr atom is 4 Rydberg. If th...
Text Solution
|