A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
BIOMOLECULES
RESONANCE|Exercise Ex-2(Subjective)Part-I|20 VideosBIOMOLECULES
RESONANCE|Exercise Ex-2(Single correct)Part-II|17 VideosBIOMOLECULES
RESONANCE|Exercise Ex-1(sec-E)Part-II|14 VideosBASIC CONCEPTS
RESONANCE|Exercise ORGANIC CHEMISTRY(BASIC CONCEPTS)|27 VideosBIOMOLECULES & POLYMER
RESONANCE|Exercise ORGANIC CHEMISTRY(Biomolecules & Polymer)|33 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE-BIOMOLECULES-Ex-1(Assertion/Reasoning)Part-III
- Statement-1 : Gly-Ala is a structural isomer pf Ala-Gly. Statement-2...
Text Solution
|
- Statement-1 : Methyl alpha-D-fructofuranoside (I) undergoes acid catal...
Text Solution
|
- Statement-1 : D-glucose (I) yields an optically active saccharic acid ...
Text Solution
|
- Statement-1 : Arginine (I), is the most basic out of twenty common ami...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : 1,3- Butadiene is the monomer for natural rubber. Reason...
Text Solution
|
- Statement-1 : Glucose and fractose cannot give similar osazone on reac...
Text Solution
|
- Statement-1 : All monosaccharides are sweet in taste. Statement-2 : ...
Text Solution
|
- Statement I: Cellulose is not diagested by human beings. Statement I...
Text Solution
|
- Statement-1 : Bakelite is copolymer Statement-2 : Bakelite is a ther...
Text Solution
|
- Statement-1 : Polybutadiene is an example of chain growth polymer. S...
Text Solution
|
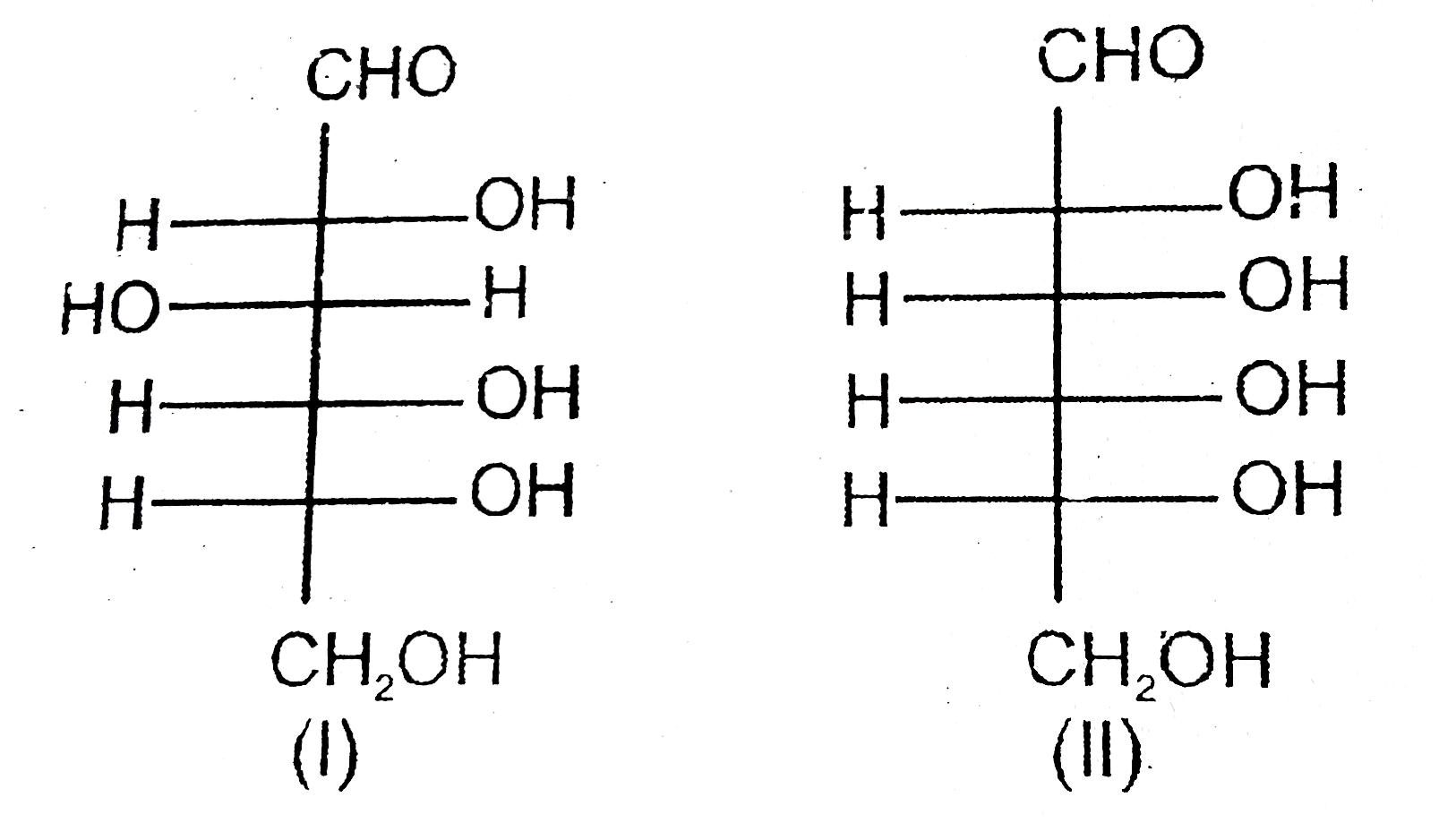
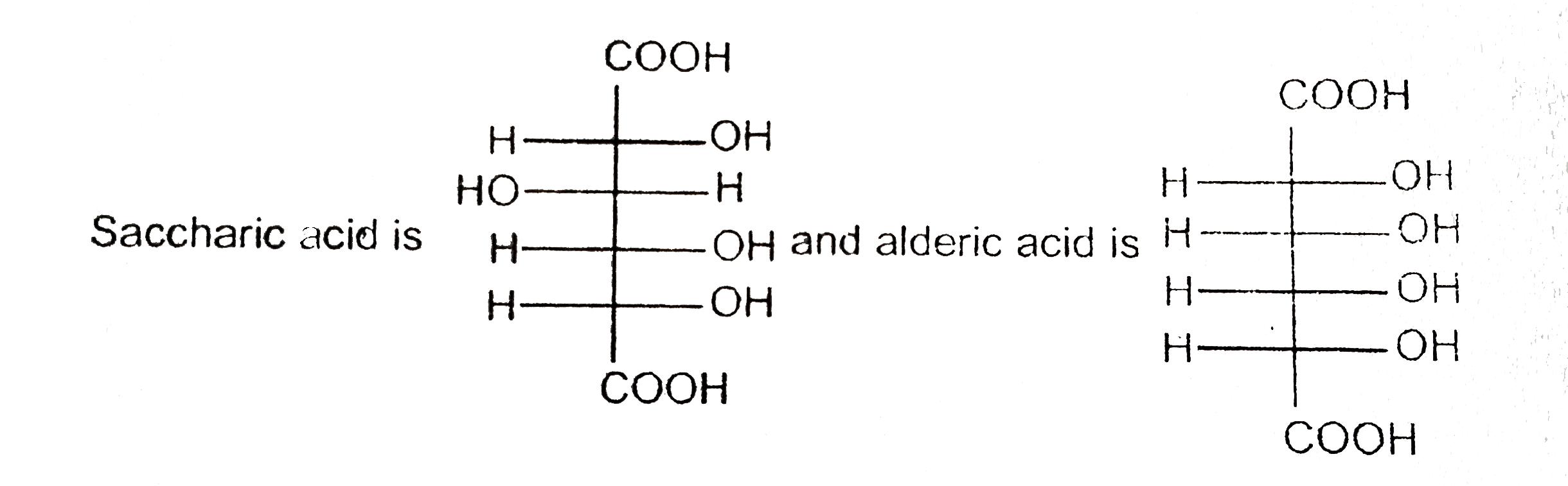 .
.